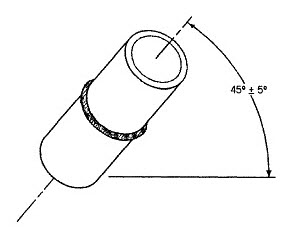
What is 6 GR welding? In welding, a 6G position requires one pipe to be positioned at a 45-degree angle to the other. Both are horizontal. This presents a very challenging position for a welder, who uses all his skills and a variety of body positions to accomplish the most difficult weld in the 6G join: the overhead weld.
What is the difference between 5g and 6G welding?
What is 5G and 6G welding? There are mainly four types of pipe welding positions- 1G – Horizontal Rolled Position. 2G – Vertical Position. 5G – Horizontal Fixed Position. 6G – Inclined Position. What is a 3F weld? Vertical Position (3F or 3G) In vertical position welding, the axis of the weld is approximately vertical.
What is 6g, and how does it work?
6G (sixth-generation wireless) is the successor to 5G cellular technology. 6G networks will be able to use higher frequencies than 5G networks and provide substantially higher capacity and much lower latency.One of the goals of 6G internet will be to support one microsecond-latency communication. This is 1,000 times faster -- or 1/1000th the latency -- than one millisecond throughput.
What is the difference between 6g and 6GR welders?
This is called restriction welding, which the “R” in the term 6GR is with restriction ring, while 6G in the term 6GR is the same as in 6G position. The difference with the 6G and 6GR position is the restriction ring and the the bevel preparation.
What is meant by 6G welding?
What is the highest welding certification? The highest level for them is usually 6G, which means they can weld 360 degrees around a pipe that doesn’t move. Producing this weld to the satisfaction of a certified welding inspector is tough sledding for a beginner.

What is 1F 2F 3F 4F welding?
To help operators understand the type of weld joint (fillet or groove) and the weld position, each weld is given a number and a letter — 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G or 1F, 2F, 3F, 4F — to indicate the position and the type of weld required. Welds with a 1 are flat position, 2 is horizontal, 3 is vertical and 4 is overhead.
What are the 5 welding positions?
What Are the Different Welding Positions?Flat position.Horizontal position.Vertical position.Overhead position.
What are the 4 basic welding positions?
The common type of weld performed in the fabrication world is Fillet and groove weld. These two welds can be obtained with the four basic welding positions which include: flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead. Take your time to understand the explanation!
What is 5G & 6G weld?
5G and 6G Welding Positions In the 5G welding position, the pipe is in the horizontal position, whereas in 6G position, the pipe slopes at approximately 45° from the horizontal (X) axis or 45° from the vertical (Y) axis. Unlike the 1G and 2G position, the pipe is in a fixed position and not rotating.
What is 1G 2G 3G 4G 5G in welding?
1G – (flat welding position) 2G – (horizontal welding position) 3G – (vertical welding position) 4G – (welding position overhead or overhead) 5G – (uphill/downhill vertical welding position)
What is F number in welding?
Filler MetalsFiller Metals: The F Number This number is used to group filler metals used in welding procedures and welder performance qualifications.
What is 3G means in welding?
Welding in a 3G position means moving the torch vertically, up and down across a surface. This is in contrast with 1G (flat surface welding), 2G (horizontal welding), and 4G (overhead ceiling welding).
What is a 2G weld test?
A 2G weld test checks your proficiency at producing welds that meet specific criteria for the finished weld and includes: Welding two horizontal beveled plates. Proper setup. Making the weld with or without a backer plate. Passing a final review or other tests.
What does 5G welding mean?
In the 5G position, the pipe is fixed at one or both ends and the welding operator must travel in one of two directions, either vertical-up or vertical-down. Depending on the location of the pipe, the application may also require welding either overhead or in a flat position.
What is 1G 2G 3G 4G 5G 6G?
1G, 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G are the five generations of mobile networks where G stands for Generation, and the number denotes the generation number. 5G is the latest generation, whereas 1G networks are now obsolete. The cellular technologies GSM, UMTS, LTE and NR enable 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G, respectively. Term.
What is 4G position?
4G Plate or Overhead Position Ideally, you will be below the workpiece to perform an overhead weld. This, of course, presents a number of challenges. The metal deposited to the joint tends to sag resulting in a higher crown bead. To prevent this, it is advisable to keep the molten puddle small.
What is 2G 3G and 4G welding positions?
The positions of groove welds are divided into 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G and 6G, respectively indicating flat welding, horizontal welding, vertical welding, overhead welding, horizontal fixed welding of pipeline and 45 °inclined fixed welding of pipeline.
What is a 5F weld?
A 5F weld joint is a tube welded to a plate where the axis of the tube is horizontal and the plate is vertical. A 5F weld joint is a bit more challenging than a 2F. ... and the thing that makes it difficult is mainly body positioning.
What are 4 clock positions in pipe welding?
When welding in the horizontal fixed position, the pipe is welded in four steps as described below. Starting at the bottom or 6 o'clock position, weld upward to the 3 o'clock position. Starting back at the bottom, weld upward to the 9 o'clock position. Starting back at the 3 o'clock position, weld to the top.
What is 3G and 4G welding positions?
The positions of groove welds are divided into 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G and 6G, respectively indicating flat welding, horizontal welding, vertical welding, overhead welding, horizontal fixed welding of pipeline and 45 °inclined fixed welding of pipeline.
How many types of welding are there?
The four main types of welding are: Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG), Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG), Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), and Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW).
Pipe and Plate Weld Joint Positions
Normally there are six welding positions with certain numbers and letter i.e. 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, and 6G/6GR. All the positions are used in various angles and shapes while performing welding. Generally, the ways and ideas of welding are similar in different countries.
6G Welding Positions-
This is one of the hardest types of welding positions for welders to perform. The position is a pre-condition for getting certified. To some extent, this position is similar to 5G/PH/PJ but the pipe stands at 45° to the other one. Other names are 6G Uphill/H-L045 and 6G Downhill/J-L045 Position.
What is the difference between a 6G and 6GR welder?
The welder cuts a slope at a specific angle on the metal, particularly at the edge. Furthermore, in the 6G certification test, the welder has to weld in all positions while the 6GR position is for TKY joints. That’s it on the difference between the 6G and 6GR welder. Both are used to test welders for certification purpose.
What does the R on a 6GR welder mean?
The R means there’s an obstacle to overcome.
Why is 6GR so challenging?
However, the 6GR is considered to be more challenging because of the obstacles a welder needs to overcome to have a smooth weld. If you are pursuing a 6G or 6GR qualification, then we wish you the best of luck. David Huner.
What is 6G weld?
Firstly, the 6G position is the type whereby your tubular weld joint has to be included at an angle of 45 degrees. It’s a difficult test to pass, though not impossible. For a 6G welder to pass this test and obtain certification, the test piece must be welded in its original position.
What do you need to know about 6G welding?
It has a steep learning curve and takes time to master. Therefore, if you want to pass the 6G certification with flying colors, then you need to know the ins and outs of this style of welding.
Which side should I start welding?
By this, I mean the side you know will be more convenient for you to weld the pipe. It will be wrong for you to start welding from the right-hand side when you are right-handed.
Is the 6GR a restriction ring?
Anyway, the 6GR is still more of the 6G position test position, only that it features a restriction ring.
What does the R in 6G welding mean?
This is another 6G weld position that is also challenging. The “R” in the name stands for restricted. In this position, welding is performed in a ring mode. What this means is that a steel plate is placed under the weld site with an inch gap.
What Is Welding Position?
In welding, the welding position is the relative position of the welding gun (hand-held welding torch) and workpiece. The welding gun is held differently for each welding process because different positions affect what type of weld joint can be made. Welding joints are classified according to how the weld pool forms in each particular position. There Are five basic welding positions.
What certification do you need to weld a pipe?
In particular, pipe welders can apply for a 5G and 6G certification . These two are used for the most complex welding positions. Therefore they require more experience. The 6G certification is seen as the gold standard of welding certification. Welders with this certification can weld all-around a stationary pipe.
What does the 3 digit mean in welding?
These numbers refer to the characteristics of the electrode. And the third digit in an electrode’s number designation refers to the welding position it can be used in. For instance, the number “1” means an electrode can be used in all ...
What is horizontal 2G welding?
The horizontal or 2G position is a little bit more complicated than the flat position. In this position, the workpiece is placed parallel to your body when welding. Thus the workpiece remains in front of you when welding.
What is it called when two metals are welded together?
When Two metals joints are welded between their surfaces or their edges or both their surface and edges is called groove weld. They create a V, J, or U-shaped cross-section.
Which position is the most difficult to weld?
The first is the horizontal position, which is difficult and is followed by the flat position and finally, the vertical position. A Lot of practice is needed to perfect this weld position.
What is the most challenging position to welding?
The 6G position is the most challenging because it involves the pipe being fixed at a 45º angle. This requires welding in all positions and incorporates the ‘good’ and ‘bad’ sides that were discussed earlier.
What is the most challenging welding job?
Joining curved pieces of metal is more difficult than welding flat sheets, so by far the most challenging process you’re ever likely to come across is pipe welding, where you will be required ...
What side of a pipe is the most difficult to weld?
For right-handed welders the left-hand side of the pipe is the challenge; for left-handed welders, it’s the right-hand side of the pipe which is the most difficult. Anticipating this obstacle and learning how to overcome it is the best way to ensure super strong, neat welds every time. Always remember that gravity will have an effect on the weld pool, so whichever is your strongest hand, the bottom half of the pipe will probably be more challenging than the top.
How to check for internal weld defects?
X-ray testing is the only really practical method of detecting internal weld defects, which is why it’s used on jobs where the quality of the weld is important for safety reasons. It works in a very similar way to X-rays which we have on the human body to look at broken bones, except on a much grander, more industrial scale. As a result, there are some risks associated with this method, so it should only be carried out by trained professionals. It’s an extremely effective way of checking weld quality which is why it’s used for many pipe welding jobs, but it is the most expensive method by a long shot.
Why is 2G welding flat?
This is pretty much just flat welding because the pipe will be lying on its side (on the curved edge) and can be rotated as you weld. The 2G position is fixed, which means that the pipe cannot be turned as you weld. In this case, the pipe is placed on its base, which makes it much sturdier and more stable to weld.
What is NDT welding?
These three methods are called non-destructive testing (NDT), where the welds must remain intact. However, when you’re practicing or being tested as part of your certification, it may be appropriate to actually break apart your pipe weld by separating it into sections and testing the strength and quality of each one.
What does the letter R mean in welding?
If you come across the letter R in pipe welding codes, this indicates a restricted welding position, which can either be physically or visually.

Differences Between The 6G and 6GR Test Positions
Other Differences Between 6G and 6GR Welder
- Well, most individuals claim that the 6GR welders tend to make more money than 6G welders, and that is a reasonable point, given how difficult it is to qualify as a 6GR welder. So, such a claim might not be out of place. But then, other factors can contribute and determine who gets more pay. So, it’s not just a matter of obtaining 6GR certification. However, 6GR welding is somewhat …
What You Need to Consider in 6G Welding
- Pipe welding is not the easiest of welding procedures. It has a steep learning curve and takes time to master. Therefore, if you want to pass the 6G certification with flying colors, then you need to know the ins and outs of this style of welding. Let’s run through some of the things you need to know before facing your 6G welding test.
Conclusion
- So, we have come to the end of the comparison between the 6G vs 6GR Welders. The difference between both is the restriction and the bevel preparations. They are also crucial in tubular structures and pipes. However, the 6GR is considered to be more challenging because of the obstacles a welderneeds to overcome to have a smooth weld. If you are pursuing a 6G or 6GR q…