What are the types of substitution mutations?
Types of Substitution Mutations Transition. There are two basic types which a substitution mutation can be. Within the four nucleotides, there are two types: the purines and pyrimidines. Adenine (A) and guanine (G) are both purines, while cytosine (C) and thymine (T) are pyrimidines.
What is one example of a substitution mutation?
Some mutagens are X-rays, UV rays, extreme heat, or certain chemicals like benzene. A substitution mutation occurs when one base pair is substituted for another. For example, this would occur when one nucleotide containing cytosine is accidentally substituted for one containing guanine. There are three types of substitution mutations:
What is the effect of substitution mutation?
What are the Similarities Between Substitution Insertion and Deletion Mutations?
- Mutations can happen either by substitution, insertion or deletion.
- All these three types of mutations may be harmless or harmful.
- All three types change the original nucleotide sequence.
- They can cause genetic diseases.
When is a substitution mutation called a nonsense mutation?
A nonsense mutation is the substitution of a single base pair that leads to the appearance of a stop codon where previously there was a codon specifying an amino acid. The presence of this premature stop codon results in the production of a shortened, and likely nonfunctional, protein.

What is an example of a substitute mutation?
Substitution mutations are a type of mutation in which a single nucleotide is substituted with a different nucleotide. Examples of (base-pair) substitutions: a purine is substituted with a different purine (A → G) or a pyrimidine, for a different pyrimidine (C → T).
What are the 3 types of base substitution mutations?
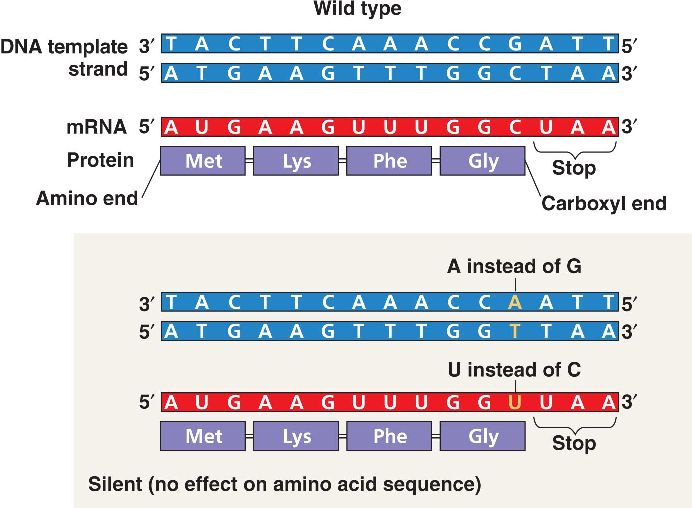
Substitution mutations can be good, bad, or have no effect. They cause three specific types of point mutation: silent, missense, and nonsense mutations.
How is base substitutions caused?
Cytosine methylation, demethylation and deamination, charge transfer reactions in DNA, DNA replication timing, chromatin status and altered DNA proofreading activities are all now known to contribute to the mechanisms leading to base substitution mutagenesis.
What are the 4 main types of mutations?
Mutations can be of many types, such as substitution, deletion, insertion, and translocation.
How do you identify a substitution mutation?
0:232:36Substitution Mutations - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIf you look at this example you'll see that each codon is cat. And cat is the codon that codes forMoreIf you look at this example you'll see that each codon is cat. And cat is the codon that codes for the amino acid histidine. If a substitution mutation occurs to change one of those codons to cac.
How does base substitution mutation affect protein?
A base substitution may have three different effects on an organism's protein. It can cause a missense mutation, which switches one amino acid in the chain for another. It can cause a nonsense mutation, which results in a shorter chain because of an early stop codon.
Why are base substitutions not always harmful?
However, base substitutions do not always cause a change in the sequence of amino acids. This is due to the degeneracy in the genetic code; the fact that there are 64 different possible triplets but only 20 different amino acids, some must code for the same amino acid.
What is a base substitution quizlet?
When a base substitution mutation occurs, one nucleotide in a replicating DNA sequence is substituted for another, which results in the production of a mutant strand of DNA. The result of the mutation depends on how the substituted nucleotide base alters the string of amino acids coded by the mutant DNA.
How many different base substitutions are possible in DNA?
Of the 549 possible single-base substitutions, 134 (one fourth) are substitutions to synonymous codons. These are heritable changes in the genetic material, hence true mutations.
What is a base substitution quizlet?
When a base substitution mutation occurs, one nucleotide in a replicating DNA sequence is substituted for another, which results in the production of a mutant strand of DNA. The result of the mutation depends on how the substituted nucleotide base alters the string of amino acids coded by the mutant DNA.
What is a substitution mutation quizlet?
Substitution Mutation. Occurs when one nucleotide base is replaced by another. Missense Mutation. A type of substitution mutation where a single nucleotide is replaced which results in the coding of an incorrect amino acid which usually causes a malfunctioning protein.
What is the difference between base substitution insertion and deletion?
Substitution mutations are mutations in which a base pair is replaced by a different base pair. Insertion mutations are mutations in which one or more nucleotides are added into the DNA sequence. Deletion mutations are mutations in which one or more nucleotides are removed from the DNA sequence.
What is a mutation in DNA?
a mutation affecting the base sequence of a DNA molecule, in which one base is substituted for another one , with no loss or gain of base and therefore no risk of a FRAMESHIFT.
What mutation causes hypogonadism in boys?
A Novel Mutation Ser34Phe in GNRHR causes Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism during Pubertal Development in Boys
Why is substitution impotent?
Such a substitution mutationcan be impotant because of its effect on mRNA stability, its transport or its translation due to codon usage bias.
What is a transition substitution?
A transition substitution mutation is the replacement of a PYRIMIDINEbase by another pyrimidine (e.g. thymine changing to cytosine) or a PURINEby another purine (e.g. adenine replacing guanine). A transversion substitution mutation is the replacement of a pyrimidine by a purine or vice versa.
What is the purpose of capillary and microchip electrophoresis?
Capillary and microchip electrophoresis for rapid detection of known mutations by combining allele-specific DNA amplification with heteroduplex analysis
Is substitution mutation harmful?
For example, a substitution mutation(in which one amino acid is substituted for another) may not have a harmful effect if it does not result in a change in amino acid sequence, if it substitutes an amino acid with similar chemical properties, or if it happens between functional domains (Figure 1).
What is subsitution in RNA?
Subsititution refers to the replacement of one amino acid with another amino acid in a protein or the replacement of one nucleotide with another in DNA or RNA.
What happens when all individuals in a population have the same sequence of a gene?
In either case, all individuals in the population originally had the same sequence of a gene. There were substitution events that resulted in a change in DNA sequence, which resulted in a change in RNA sequence, which then could result in a change in amino acid sequence.
What is substitution in biology?
Substitution. Substitution is a type of mutation where one base pair is replaced by a different base pair. The term also refers to the replacement of one amino acid in a protein with a different amino acid.
What is the result of a substitution?
Substitutions which lead to mutations, which lead to a deleterious outcome, that is the organism having difficulty with living or dying early, those we call mutations, but they're the result of a certain kind of a substitution.
What is it called when you change a codon to one that encodes the same amino acid and causes no change?
change a codon to one that encodes the same amino acid and causes no change in the protein produced. These are called silent mutations .
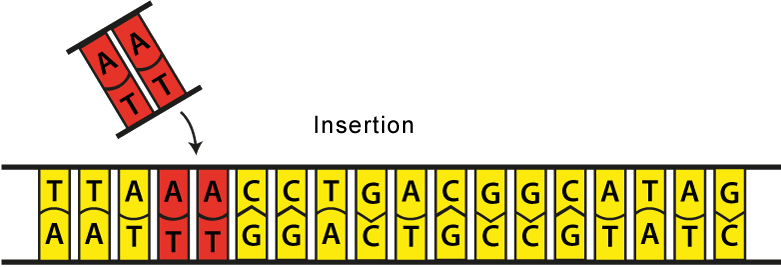
What is the term for mutations in which extra base pairs are inserted into a new place in the DNA?
Insertions are mutations in which extra base pairs are inserted into a new place in the DNA.
What is substitution in biology?
A substitution is a mutation that exchanges one base for another (i.e., a change in a single “chemical letter” such as switching an A to a G). Such a substitution could:
What is the Difference Between Frameshift Mutation and Base Substitution Mutation?
Insertions and deletions cause frameshift mutations , while the exchange of one base from another (substitution) causes base substitution mutations . So, this is the key difference between frameshift mutation and base substitution mutation.
What is frameshift mutation?
A frameshift mutation is a type of mutation that occurs due to insertion or deletion of a base pair or base pairs. It changes the reading frame of the gene and expresses an incomplete or incorrect protein. Generally, nucleotide triplets make codons. Each codon codes for a specific amino acid.
What is the difference between base substitution and frameshift mutation?
The key difference between frameshift mutation and base substitution mutation is that frameshift mutation is an insertion or deletion of a base pair or base pairs from a DNA sequence of a gene that causes changes in the open reading frame while base substitution mutation is the exchange of one nucleotide from another nucleotide in a DNA sequence.
What are the complications of frameshift mutation?
Frameshift mutations lead to several complications including Tay-Sachs disease, Crohn’s disease, Cystic fibrosis, HIV and cancer. Frameshift mutation can occur randomly. It also can occur due to external stimuli such as chemical agents.
What is Dr. Samanthi Udayangani's degree?
Dr.Samanthi Udayangani holds a B.Sc. Degree in Plant Science, M.Sc. in Molecular and Applied Microbiology, and PhD in Applied Microbiology. Her research interests include Bio-fertilizers, Plant-Microbe Interactions, Molecular Microbiology, Soil Fungi, and Fungal Ecology.
What are the effects of mutations?
As a result of mutation, a particular gene sequence can be altered and result in varying effects such as cancers, genetic diseases, birth defects, infertility problems, etc. There are different factors affecting mutations. UV and chemical agents are the major factors among them.
Is a single base mutation silent?
One base exchanges with another, so, it is a type of a point mutation. Some single base mutations are silent mutations. However, some causes diseases. For example, a single substitution in the beta haemoglobin gene causes life-threatening disorder; for example, sickle cell anaemia due to alteration of single amino acid.