What is the function of biogenic amines?
The biogenic amines regulate brain functions such as movement, behavior, emotions, temperature, blood pressure and endocrine secretion.
Where are biogenic amines found?
Biogenic amine (BA)s are nitrogenous, and organic compounds and can be found in some fermented foods such as cheese, sausage, fermented vegetable, wine, and fish [1, 2]. Main interest in BAs is due to their potential toxicity to human health and indicators of food quality.
Is Acetylcholine is a biogenic amine?
Biogenic amines are one of two broad classes of classical neurotransmitters (the other being amino acids) and include: acetylcholine, serotonin, histamine, and the catecholamines epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
What are the effects of biogenic amines?
The most common health effects are nausea, vomiting, severe headaches, hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, various allergic reactions, abdominal pain and death in more severe cases. For these reasons, legislations on biogenic amines in foods have been established with some restrictions.
What are two examples of biogenic amines?
There are five established biogenic amine neurotransmitters: the three catecholamines—dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline)—and histamine and serotonin (see Figure 6.3).
Are biogenic amines harmful?
Biogenic amines (BAs) in food constitute a potential public health concern due to their physiological and toxicological effects. The consumption of foods containing high concentrations of biogenic amines has been associated with health hazards.
Is dopamine a catecholamine?
Examples of catecholamines include dopamine, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine (noradrenaline).
What are the 5 catecholamines?
The main types of catecholamines are dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. Epinephrine is also known as adrenaline. Catecholamine tests measure the amount of these hormones in your urine or blood. Higher than normal levels of dopamine, norepinephrine, and/or epinephrine can be a sign of a serious health condition.
What are the 2 types of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters, at the highest level, can be sorted into two types: small-molecule transmitters and neuropeptides. Small-molecule transmitters, like dopamine and glutamate, typically act directly on neighboring cells.
What is the benefit of biogenic?
Biogenic substrates are beneficial to activated sludge's acclimation and degradation of a xenobiotic by enriching the energy contents of the sludge cells.
How are amines used in the body?
Biogenic amines play an essential role in cell membrane stabilization, immune functions, and prevention of chronic diseases, as they participate in the nucleic acid and protein synthesis [14].
Is wine high in amines?
You'll find biogenic amines in many foods including processed fish, meat, cheese, and fermented things (such as beer, wine, and kimchi). Higher levels of biogenic amines (especially histamine and tyramine) cause flushing, headaches, nausea, and fatigue.
Where are amines found in the body?
Hormonal Amines Within the nervous system they are important neurotransmitters; outside the nervous system the cells that produce them are modified post-synaptic neurons (e.g., adrenal medulla), blood-derived cells (e.g., basophils, mast cells), or APUD2 cells (e.g., enterochromaffin cells).
Where can amines be found?
Amine functional groups are found in a wide variety of compounds, including natural and synthetic dyes, polymers, vitamins, and medications such as penicillin and codeine. They are also found in many molecules essential to life, such as amino acids, hormones, neurotransmitters, and DNA.
Where are amines found in nature?
Aliphatic amines occur in nature, principally as products of the putrefaction of protein material, but they are also present in living tissue (e.g., histamine, a cyclic aliphatic amine). The methylamines occur in small amounts in some plants.
How are biogenic amines produced?
Biogenic amines are produced by the decarboxylation of their respective free precursor amino acids, through the catalytic action of substrate-specific microbial decarboxylases that remove the α-carboxyl group of amino acids to give the corresponding amines.
How are monoamines synthesized?
All monoamine (MA) neurotransmitters are synthesized from amino acids through a series of enzyme catalyzed reactions in which hydroxylation, decarboxylation and/or methylation convert the precursor amino acid into the active monoamine neurotransmitter.
What are monoamines?
Monoamines (also known as "biogenic amines") include three classes of neurotransmitters: Dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE, also called noradrenaline) and epinephrine (E, also called adrenaline) make up a class of neurotransmitters named on the basis of the hydroxylated phenol ring termed a catechol nucleus.
What is the red pathway in Parkinson's disease?
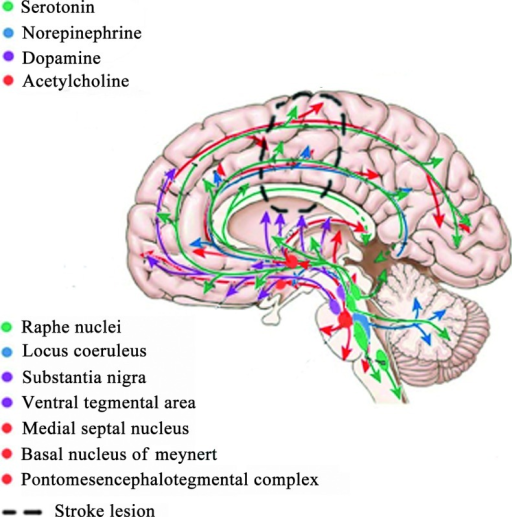
The destruction of the nigrostriatal cells in Parkinson's disease produces marked motor deficits. The ventral mesostriatal pathway (red) also originates in the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area, and innervates the nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercles and medial caudate-putamen.
How is catecholamines regulated?
TH is phosphorylated and activated by both calcium and cAMP dependent protein kinases. A longer-term regulation of CA synthesis also occurs. This regulation is mediated through altered transcription of TH mRNA and altered TH mRNA stability. Both mechanisms lead to increased levels of TH protein.
How does serotonin affect the brain?
First, because tryptophan is not synthesized in mammals, the level of tryptophan available for serotonin biosynthesis is dependent on diet. Thus, diets high in tryptophan can markedly elevate serotonin levels. Second, because tryptophan is transported across the blood brain barrier by a transport system which also transports certain other amino acids, diets high in these amino acids can reduce the level of serotonin in the brain by competing with tryptophan for transport into the CNS. As will be discussed later, altered serotonin level in the CNS can have marked consequences on behavior.
Which pathway is associated with the corpus striatum?
These two pathways are important for movement control and reward mechanisms. The dorsal mesostriatal pathway (blue) originates in the substantia nigra par compacta and ascends to innervate the corpus striatum (caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus), where it modulates the output of the corpus striatum.
What is the DA system?
Mesolimbocortical DA System - The Mesolimbocortical DA system (purple) originates in the midbrain and projects to limbic structures (septum, amygdala, hippocampus, olfactory nucleus, and limbic cortex). This DA system is believed to participate in schizophrenia.
How do biogenic amines affect T cells?
By interacting with TAAR1 and TAAR2, biogenic amines also seem to affect the secretion of cytokines by human T cells ( Table 7.3 ). 28 As a part of the adaptive immune system, T cells are activated by specific antigens presented on the surface of professional antigen-presenting cells. Once activated, T helper cells (CD3 + CD4 +) can differentiate mainly into two types of effector cell: Th1 cells and Th2 cells. Whilst differentiation into Th1 cells leads to the secretion of, for example, interleukin-2 (IL-2) and interferon γ, differentiation into Th2 cells results in the secretion of, for example, interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-5 (IL-5). 48 Stimulation of non-siRNA-transfected T cells with 2-PEA, TYR, and T1AM in a range from 0.01 to 1 nM concentration-dependently increased the secretion of IL-4 up to 300% of the control. 28 In this regard, 2-PEA revealed the highest efficacy of the three biogenic amines tested, whilst the respective EC 50 values were comparable (2-PEA: 0.23 ±0.008 nM, TYR: 0.24 ±0.04 nM, T1AM: 0.1 ±0.05 nM). In contrast, IL-4 secretion of T cells transfected with siRNA specific for TAAR1 and TAAR2 was barely affected by incubation of the cells with the biogenic amines.
What are the biogenic amines in cheese?
Tyramine (aromatic, primary, and monoamine) and histamine (heterocyclic, primary, and monoamine) are the main biogenic amines produced by enterococci in cheeses. They can be formed through the microbial decarboxylation of free amino acids during fermentation such as during cheese ripening.
How are biogenic amines formed?
Biogenic Amines. Biogenic amines (Table 7) are formed from amino acids by decarboxylation, or by amination and transamination of aldehydes and ketones. Because of the structure of their precursor amino acids, they can have either aliphatic, aromatic, or heterocyclic chemical structures. Although some play a role in the physiology ...
How do enterococci cause food intoxication?
Enterococci can cause food intoxication through the production of biogenic amines, which after ingestion can result in a number of symptoms, including headache, abdominal pain, vomiting, flushing, increased blood pressure, and even allergic reactions. The symptoms may occur in conjunction with monoamine oxidase (MAO) and diamine oxidase, which metabolize normal dietary intakes of biogenic amines in the intestinal tracts of mammals. Oxidative deamination catalyzed by MAO is the detoxification mechanism for tyramine and histamine. Under normal circumstances (a low concentration of biogenic amines ingested by a healthy person), the biogenic amines adsorbed from food are detoxified by oxidative deamination, and the end metabolites are readily excreted in the urine. However, the detoxifying mechanisms in humans are not sufficient when the intake in a diet is too high, if individuals are allergic, and if patients are taking drugs that act on MAO inhibitors.
What are the amines that are found in food?
Biogenic amines. Biogenic amines such as histamine, tyramine, phenylethylamine, putrescine, cadaverine, and spermidine are found in certain foods and play a role as regulatory agents in human metabolism.
What causes a biogenic amine to form?
Formation of Biogenic Amines by Enterococci. Biogenic amines in foods could be a result of the decarboxylase activity of the fermentative microflora. Favorable conditions for their production may be achieved by the increase in precursor amino acids or the level of biogenic amines may be reduced by the elimination of decarboxylating bacteria.
What is the cause of histamine poisoning?
Histamine fish poisoning (or scombroid poisoning) is a type of food poisoning caused by elevated levels of histamine being present in the fish such as tuna, sardines, mackerel, swordfish, and marlin. Naturally occurring bacteria in fish produce an enzyme, which converts histidine in the fish to histamine.
What are the TAs linked to?
In this article, we focus on the relevance of TAs and their receptors to nervous system-related disorders, namely schizophrenia and depression; however, TAs have also been linked to other diseases such as migraine, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, substance abuse and eating disorders [7,8,36 ].
What is the difference between dopamine and epinephrine?
Epinephrine (adrenaline) – an adrenal stress hormone, as well as a neurotransmitter present at lower levels in the brain. Dopamine – a neuro transmitter involved in motivation, reward, addiction, behavioral reinforcement, and coordination of bodily movement.
What are lactic acid bacteria?
Some lactic acid bacteria isolated from commercial bottled yoghurt have been shown to produce biogenic amines. They play an important role as source of nitrogen and precursor for the synthesis of hormones, alkaloids, nucleic acids, proteins, amines and food aroma components.
How to determine biogenic amines in wine?
The determination of amines in wines is commonly achieved by liquid chromatography, using derivatization reagents in order to promote its separation and detection.
What are some examples of biogenic monoamines?
Monoamines. Some prominent examples of biogenic monoamines include: Histamine – a substance derived from the amino acid histidine that acts as a neurotransmitter mediating arousal and attention, as well as a pro- inflammatory signal released from mast cells in response to allergic reactions or tissue damage.
How are endogenous and exogenous amines produced?
Endogenous amines are produced in many different tissues (for example: adrenaline in adrenal medulla or histamine in mast cells and liver ). The amines are transmitted locally or via the blood system. The exogenous amines are directly absorbed from food in the intestine. Alcohol can increase the absorption rate. Monoamine oxidase ( MAO) breaks down biogenic amines and prevents excessive resorption. MAO inhibitors (MAOIs) are also used as medications for the treatment of depression to prevent MAO from breaking down amines important for positive mood.
What is a biogenic amine?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Jump to navigation Jump to search. A biogenic amine is a biogenic substance with one or more amine groups. They are basic nitrogenous compounds formed mainly by decarboxylation of amino acids or by amination and transamination of aldehydes and ketones. Biogenic amines are organic bases with low molecular ...

Overview
A biogenic amine is a biogenic substance with one or more amine groups. They are basic nitrogenous compounds formed mainly by decarboxylation of amino acids or by amination and transamination of aldehydes and ketones. Biogenic amines are organic bases with low molecular weight and are synthesized by microbial, vegetable and animal metabolisms. In food and beverages they are formed by the enzymes of raw material or are generated by microbial decarb…
List of notable biogenic amines
Some prominent examples of biogenic monoamines include:
Monoamine neurotransmitters
• Imidazoleamines
• Indolamines
• The three catecholamine neurotransmitters:
Physiological importance
There is a distinction between endogenous and exogenous biogenic amines. Endogenous amines are produced in many different tissues (for example: adrenaline in adrenal medulla or histamine in mast cells and liver). The amines are transmitted locally or via the blood system. The exogenous amines are directly absorbed from food in the intestine. Alcohol can increase the absorption rate. Monoamine oxidase (MAO) breaks down biogenic amines and prevents excessive resorption. M…
Importance in food
Biogenic amines can be found in all foods containing proteins or free amino acids and are found in a wide range of food products including fish products, meat products, dairy products, wine, beer, vegetables, fruits, nuts and chocolate. In non-fermented foods the presence of biogenic amines is mostly undesired and can be used as indication for microbial spoilage. In fermented foods, one can expect the presence of many kinds of microorganisms, some of them being capa…
See also
• Monoamine neurotransmitter
• Trace amine
External links
• The Biogenic Amines – Neuroscience 2nd edition, Dale Purves et al.