What are catalysts in biological reactions called?
Catalysts in biological reactions are called enzymes. Catalysts do not appear in the overall chemical equation for a reaction.
What is the difference between a catalyst and an enzyme?
Different substances catalyse different reactions. Catalysts in biological reactions are called enzymes. Catalysts do not appear in the overall chemical equation for a reaction. A catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway that has a lower activation energy than the uncatalysed reaction.
How many types of catalysts are there?
The table describes three common catalysts. Notice that these catalysts are transition metals or compounds of transition metals. A catalyst allows an alternative reaction pathway that has a lower activation energy than the uncatalysed reaction.
How many types of reactions can enzymes catalyse?
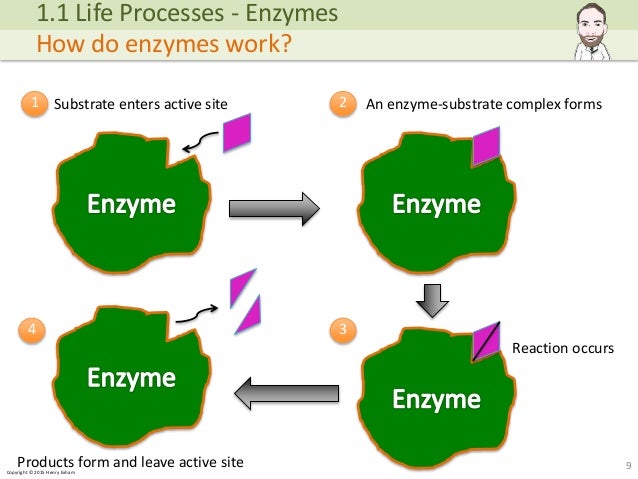
Each type of enzyme can usually catalyse only one type of reaction (some may catalyse a few types of reactions). The diagram shows how this works. In this example, the enzyme splits one molecule into two smaller ones. The breakdown of a substrate molecule by an enzyme.

What is a biological catalyst?
Biological catalysts are called enzymes. There is, for instance, an enzyme in our saliva which converts starch to a simple sugar, which is used by the cell to produce energy, and another enzyme which degrades the excess lactic acid produced when we overexert ourselves.
What is a biological catalyst GCSE?
An enzyme is a protein that functions as a biological catalyst – a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction.
What is a biological catalyst simple?
An enzyme is a biological catalyst and is almost always a protein. It speeds up the rate of a specific chemical reaction in the cell. The enzyme is not destroyed during the reaction and is used over and over.
Why are enzymes called biological catalysts BBC Bitesize?
Enzymes are proteins that function as biological catalysts . So, they are molecules that speed up a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction.
Why enzymes are called biological catalysts?
The enzymes are called biocatalyst because it increases the speed of biochemical reaction in an organism. As, the enzymes accelerate the chemical reaction, without changing the state of equilibrium, it is known as the biocatalyst.
What is a biological catalyst a level biology?
Enzymes are biological catalysts - they speed up the rate of chemical reactions happening inside our body. They work by reducing the activation energy of a reaction.
What is the difference between biological and chemical catalysts?
Answer: Chemical catalysts are catalysts that can speed up chemical reactions. They may be artificial also. Biological catalysts are enzymes that speed up cellular processes.
What is the difference between biocatalyst and chemical catalyst?
The difference between catalysts and enzymes is that enzymes are largely organic in nature and are bio-catalysts, while non-enzymatic catalysts can be inorganic compounds. Neither catalysts nor enzymes are consumed in the reactions they catalyze.
What is an enzyme GCSE AQA?
Enzymes are biological catalysts – they speed up chemical reactions. Enzymes are required for most of the chemical reactions that occur in organisms . These reactions occur in the breakdown of chemical molecules, which we see in the digestive system .
What is an example of an enzyme catalyzed reaction?
Examples of enzyme-catalyzed reactions Conversion of glucose into ethyl alcohol: The zymase enzyme breaks down glucose to produce ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. Conversion of starch into maltose: Diastase is an enzyme that converts starch to maltose.
What are enzymes BBC Bitesize ks3?
Enzymes are protein molecules which act as catalysts to speed up reactions. They are not used-up in these reactions. Enzymes can be grouped into two types: Those that break larger molecules apart (like digestive enzymes).
How does a catalyst work?
How catalysts work. A catalyst allows an alternative reaction pathway that has a lower activation energy than the uncatalysed reaction. This does not change the frequency of collisions. However, it does increase the frequency of successful collisions because a greater proportion of collisions has the activation energy or more.
What is the purpose of a catalyst?
Catalysts. A catalyst is a substance that: increases the rate of a reaction , but. does not alter the products of the reaction, and. is unchanged chemically and in mass at the end of the reaction. Only a very small mass of catalyst is needed to increase the rate of a reaction.
Why are enzymes important?
An enzyme is a biological catalyst. Enzymes are important for controlling reactions in cells. They are also important in industry. The use of enzymes allows some industrial reactions to happen at lower temperatures and pressures than traditionally needed.
How many types of reactions can an enzyme catalyze?
Each type of enzyme can usually catalyse only one type of reaction (some may catalyse a few types of reactions). The diagram shows how this works. In this example, the enzyme splits one molecule into two smaller ones. The breakdown of a substrate molecule by an enzyme.
What is enzyme in biology?
Enzymes are biological catalysts which speed up reactions. They are specific for their substrate. The lock and key hypothesis models this. Enzymes are denatured at extremes of temperature and pH.
What are the molecules that speed up a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction?
Enzymes. Enzymes are proteins that function as biological catalysts. So, they are molecules that speed up a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction.