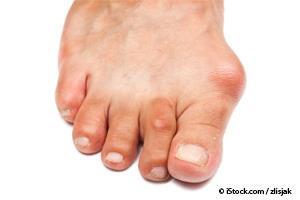
Symptoms
Bunions occur when muscles, tendons, and joints become misaligned within the foot. This misalignment creates pressure on the foot and causes a bunion to form. Bunions can take a long time to develop. Many bunions start out small and painless.
Causes
- Ongoing big toe or foot pain
- A visible bump on your big toe joint
- Decreased movement of your big toe or foot
- Difficulty finding shoes that fit properly because of a bunion
Prevention
What you need to know about bunions
- Causes. Bunions are bony bumps that often form at the base of the big toe. ...
- Symptoms. The classic symptom of a bunion is a bump that forms at the base of the big toe. ...
- Pictures. Here are some pictures of bunions and some of the complications they can lead to.
- Diagnosis. ...
- Home remedies. ...
- Treatment. ...
- Prevention. ...
- Outlook. ...
Complications
While on one side, corn refers to the skin of the feet of a person that gets inflamed. But Bunion, on the other side, is the bending first toe of a person towards the second toe. Corn is also known as callus, while bunion is also known as hallux valgus.
What is a bunion and how does it start?
How do you know if you have a bunion?
What are bunions and what causes them?
What is the difference between a bunion and a corn?

What is the main cause of bunions?
0:001:02But it's actually an abnormal alignment of the bones in the toe. The exact cause isn't clear it mayMoreBut it's actually an abnormal alignment of the bones in the toe. The exact cause isn't clear it may run in the family footwear that squashes the toes or have high heels. Probably out the sole cause.
What is a bunion filled with?
A fluid-filled sac, called a bursa, cushions the bone near the joint on your big toe. When that joint gets bigger because of a bunion, the bursa can get swollen and painful -- that's called bursitis.
How serious is a bunion?
A bunion at this critical junction of bones, tendons, and ligaments can seriously impair the foot's functioning. For one thing, a bunion on the big toe can damage the other toes. Under the pressure of the big toe, they may develop corns or become bent, forming hammertoes.
What is a bunion look like?
A bunion looks like a bump on the side of the big toe. This bump is actually the result of an abnormality of the foot bones that causes your big toe to lean toward your second toe instead of being straight. This angle produces the bump you see on your toe. In some cases, the bump is painless.
Does a bunion have a root?
"The root cause of a bunion is an unstable joint at the base of the foundation of the metatarsal bone." With an unbalanced foundation, the bone leans out of alignment and creates a bump on the side of the foot at the base of the big toe.
Can you pop a bunion back into place?
The short answer is no. Bunions can't be reversed, and unfortunately, they don't go away on their own. Once you have a bunion, it will likely continue to grow over time. Luckily, many people don't need to have surgery to treat their bunions.
Is removing a bunion worth it?
The only permanent cure for a bunion is surgically removing it. Bunion surgery is worth it for those who want to ease pain and resume their ability to do things like walk barefoot, play sports, and wear their favorite shoes again.
What happens if bunion is left untreated?
If left untreated, a bunion can cause arthritis, especially if the joint in the big toe has sustained extensive, long-term damage. Bunions may cause the cartilage in the joint to deteriorate. While bunions can be remedied through surgery, arthritis and the possibility of chronic pain are not curable.
Does walking make bunions worse?
A sure-fire way to exacerbate your bunion is to stand on your feet all day. Walking or running a marathon is the worst thing you can do for your bunion, and if you have a job that keeps you on your toes, you may need to take some time off to heal.
What is the fastest way to get rid of a bunion?
The Only Way to Get Rid of Bunions In reality, surgery is the only way to get rid of a bunion for good. In the past, many patients were hesitant to undergo traditional bunion surgery. Bunion surgeries were –– at one time –– considered painful and inconvenient.
Is going barefoot good for bunions?
Going barefoot is ideal in the beginning stages of bunions. When barefoot, the joints of the toes will get stronger, an important part of good foot health.
How can I shrink my bunions naturally?
What Can I Do to Shrink a Bunion?Wear wide shoes with a low heel and soft sole. In most cases, bunion pain is relieved by wearing wider shoes with adequate toe room and using other simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe.Try bunion pads. ... Hold an ice pack. ... Take paracetamol or ibuprofen. ... Try to lose weight.
Is there fluid in a bunion?
The skin over the bunion can also rub on the inside of your shoes. This can cause the skin and tissues over the big toe joint to thicken and become inflamed, swollen and painful. Sometimes a fluid filled sac (bursa) develops over the joint.
What is bunions made out of?
A bunion is a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of your big toe. It occurs when some of the bones in the front part of your foot move out of place. This causes the tip of your big toe to get pulled toward the smaller toes and forces the joint at the base of your big toe to stick out.
What are bunions composed of?
0:003:49Bunions are one of the most misunderstood conditions that are probably on the internet there's allMoreBunions are one of the most misunderstood conditions that are probably on the internet there's all these gadgets. What a bunion is is it's a deviation of a long bone in the foot when that bone
What happens if a bunion goes untreated?
If left untreated, a bunion can cause arthritis, especially if the joint in the big toe has sustained extensive, long-term damage. Bunions may cause the cartilage in the joint to deteriorate. While bunions can be remedied through surgery, arthritis and the possibility of chronic pain are not curable.
What is a bunion?
A bunion, or a hallux valgus, refers to a bulge at the metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP joint) of the big toe, also referred to as the base of the bi...
What causes bunions?
Bunions may develop due to a variety of biological or environmental factors, including arthritis, biomechanical factors, neuromuscular disorders, g...
Are bunions genetic?
Bunions are not necessarily genetic; however, some of the causes of bunions can be inherited, or passed down from a person’s parents. For example,...
What does a bunion look like?
A bunion typically presents as a red or swollen bulge at the base of the big toe. Over time, the phalanges of the big toe may gradually protrude fu...
What are the signs and symptoms of a bunion?
Signs and symptoms of a bunion vary depending on severity. Regardless, all bunions appear as a bulge at the base of the big toe. A dull, achy pain...
How is a bunion diagnosed?
A bunion is usually diagnosed through physical examination. During the physical exam, a clinician will typically ask about the severity of the symp...
How is a bunion treated?
Initial treatment for a bunion typically consists of conservative measures, like wearing supportive, well-fitting shoes with a wider toe box (i.e.,...
What are the most important facts to know about bunions?
Bunions, characterized by a bulge of the joint at the base of the big toe, where the metatarsal and phalangeal bones meet, are among the most commo...
What is a bunion?
A bunion, or a hallux valgus, refers to a bulge at the metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP joint) of the big toe, also referred to as the base of the big toe. The MTP joint is the link between the metatarsal bone (i.e., the long bone of the toe) and the proximal, or first, phalange (i.e., the short bone of the toe). Bunions are one of the most common foot problems, especially among older adults and individuals who frequently wear tight shoes or high heels.
How is a bunion diagnosed?
A bunion is usually diagnosed through physical examination. During the physical exam, a clinician will typically ask about the severity of the symptoms, inspect the foot, and observe the person’s gait, or the way they walk. Depending on the physical exam, an X-ray may be ordered to confirm diagnosis of a bunion and classify the severity (i.e., mild, moderate, or severe). A weight-bearing X-ray, which requires the individual to stand on the foot of interest while the image is taken, can highlight specificities of the bunion deformity, including lateral deviation of the phalange of the big toe and narrowing of the MTP joint. Occasionally, a biopsy may be performed to rule out other potential diagnoses, such as infection, gout, or inflammatory arthritis.
How is a bunion treated?
Initial treatment for a bunion typically consists of conservative measures, like wearing supportive, well-fitting shoes with a wider toe box (i .e., the section of the shoe that surrounds the toe) or using orthotic inserts, which are removable shoe insoles that provide increased foot support . Occasionally, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs ), such as ibuprofen, may be prescribed to reduce swelling. While these approaches may relieve pain and discomfort from a bunion, surgery is the only curative option. There are a variety of options for bunion surgery, including reshaping the toe or fusing a joint together. The surgical approach selected generally depends on the severity of symptoms, cause of the bunion, and anatomy of the individual’s foot.
Are bunions genetic?
Bunions are not necessarily genetic; however, some of the causes of bunions can be inherited, or passed down from a person’s parents. For example, the shape of an individual's foot is typically passed down through families. Additionally, some inherited genetic disorders can increase the likelihood of bunion formation in an individual. Other disorders, like rheumatoid arthritis, can run in families and may also make an individual more prone to bunion development.
What are the most important facts to know about bunions?
Bunions, characterized by a bulge of the joint at the base of the big toe, where the metatarsal and phalangeal bones meet, are among the most common foot problems. Bunions may develop due to a variety of causes, including medical conditions (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) or lifestyle factors, like frequently wearing tight shoes. Although bunions are not genetic, some conditions that increase the risk of bunion formation can be passed down from parents to their children. Bunions typically appear as a red and swollen bulge, with associated dull and achy pain, at the base of the big toe. Bunions are often diagnosed through a physical exam, which may include an X-ray. Conservative treatments, such as wearing well-fitting shoes and taking anti-inflammatory medications, are aimed at minimizing symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, surgery may be required to resolve the bunion.
What is a bunion on the big toe?
A bunion typically presents as a red or swollen bulge at the base of the big toe . Over time, the phalanges of the big toe may gradually protrude further outward as the bunion becomes more severe.
What causes a bunion in the MTP joint?
Arthritic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, typically cause inflammation of many joints in the body and may affect the MTP joint. Long-term inflammation can lead to deterioration of the bones that make up the MTP joint, allowing the bones to shift and form a bunion over time.
What are bunions associated with?
Bunions might be associated with certain types of arthritis, particularly inflammatory types, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Why is my big toe sticking out?
It occurs when some of the bones in the front part of your foot move out of place. This causes the tip of your big toe to get pulled toward the smaller toes and forces the joint at the base of your big toe to stick out. The skin over the bunion might be red and sore. Wearing tight, narrow shoes might cause bunions or make them worse.
How to prevent bunions in shoes?
Prevention. To help prevent bunions, choose shoes carefully. They should have a wide toe box — no pointy toes — and there should be space between the tip of your long est toe and the end of the shoe . Your shoes should conform to the shape of your feet without squeezing or pressing any part of your foot.
What are the complications of bunions?
Possible complications of bunions include: Bursitis. This painful condition occurs when the small fluid-filled pads that cushion the bones near your joints become inflamed. Hammertoe. An abnormal bend that occurs in the middle joint of a toe, usually the toe next to your big toe, can cause pain and pressure.
How to tell if you have a bunion?
The signs and symptoms of a bunion include: A bulging bump on the outside of the base of your big toe. Swelling, redness or soreness around your big toe joint. Corns or calluses — these often develop where the first and second toes rub against each other. Ongoing pain or pain that comes and goes. Limited movement of your big toe.
What happens when you have a bunion?
When you have a bunion, the tip of your big toe shifts towards the smaller toes, crowding them. This also forces the joint at the base of your big toe to stick out.
What happens if you wear shoes that are too tight?
Ill-fitting shoes. People who wear shoes that are too tight, too narrow or too pointed are more likely to develop bunions.
How to get rid of bunions on toes?
If you need to get rid of bunions, wear bunion pads or shoe inserts to realign your toes. You could also wrap tape around your foot and toes to hold your toes in a normal alignment. If you are having trouble with pain due to your bunions, soak your feet in warm water for about 20 minutes.
How to get your toes back into alignment?
Wear bunion splints at night. Try bunion splints to push your toes back into the proper alignment for greater comfort. You can buy these at your local shoe or orthotics store.
How to realign toes?
Wear a bunion pad or shoe inserts to realign toes. If you catch your bunion in the early stages, a bunion pad purchased at any pharmacy or drugstore may help to alleviate pain and direct your toe back to the proper direction. Shoe inserts may also help to realign your toes when you are wearing shoes.
What is a bunion in the foot?
A bunion is a bony lump that forms at the base joint in the big toe. Bunions form when tight or high-heeled shoes, an injury, or a person's inherited bone structure result in the big toe being pushed toward the other toes on the foot. Eventually, the big toe joint becomes enlarged and painful, and can lead to difficulties with exercising and walking. This article discusses lifestyle changes, home remedies, and medical interventions to get rid of bunions.
Why do people wear night splints?
Night splints, which are worn over the toes and feet at night, may prevent children from developing bad bunions by correcting bone growth. Since adults' feet are already fully formed, night splints are not effective for treating bunions in adults.
How to get your big toes to align?
Use your fingers to pull your big toe into proper alignment with the rest of your toes. Stretch the rest of your toes. Simply point them straight ahead for 10 seconds, then curl them under for 10 seconds. Repeat several times. Flex your toes. Press your toes against the floor or a wall until they are bent back.
How to stop bunion surgery?
Try foot exercises . Exercises can help slow or even halt the progression of your bunion, preventing the need to eventually get surgery. Try the following exercises every day, especially after removing your shoes: Stretch your big toe. Use your fingers to pull your big toe into proper alignment with the rest of your toes.
Why is my little toe red?
It is usually characterized by inflammation, pain and redness of the little toe. Often a tailor's bunion is caused by a faulty mechanical structure of the foot. The fifth metatarsal bone starts to protrude outward, while the little toe moves inward.
Why is tailor's bunion easily diagnosed?
Tailor's bunion is easily diagnosed because the protrusion is visually apparent. X-rays may be ordered to help the surgeon find out the severity of the deformity.
What are non surgical treatments for toe pain?
Non-surgical therapies include: Shoe modifications: wearing shoes that have a wide toe box, and avoiding those with pointed toes or high heels. Oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may help in relieving the pain and inflammation. Injections of corticosteroid are commonly used to treat the inflammation.
What is a type 4 bunion?
Type 4: a combination of at least two types of bunionettes (TB).
Why is it called a tailor's bunion?
It is called Tailor's Bunion because in past centuries, tailors sat cross-legged, and this was thought to cause this protrusion on the outside aspect of the foot.
How to treat inflammation in the shin?
Injections of corticosteroid are commonly used to treat the inflammation. Bunionette pads placed over the affected area may help reduce pain. An ice pack may be applied to reduce pain and inflammation. Surgery is often considered when pain continues for a long period with no improvement in these non-surgical therapies.
Which type of TB has the greatest lateral angular disposition of the 5th metatarsal compared?
Type 3: has the greatest lateral angular disposition of the 5th metatarsal compared to the 4th metatarsal, this phenomenon increases the 4th and 5th inter-metatarsal angles. This is generally, the most symptomatic TB is type 3.
What is the MTP joint?
The MTP joint helps us bear and distribute weight during a range of activities. A bunion at this critical junction of bones, tendons, and ligaments can seriously impair the foot's functioning. For one thing, a bunion on the big toe can damage the other toes. Under the pressure of the big toe, they may develop corns or become bent, forming hammertoes. The nails may become ingrown, and calluses may form on the bottom of the foot. If you constantly shift your weight off the painful big toe joint to other metatarsals, you may develop discomfort in the ball of the foot. As the misshapen joint becomes more uncomfortable and harder to fit into shoes, you may have to curtail exercise and other activities. Even walking may become difficult.
How do you know if you have a bunion?
A bunion is most likely to develop when susceptible feet are repeatedly squeezed into narrow, pointed-toe footwear. The big toe pushes against the other toes, sometimes diving over or under them. As a result, the base of the big toe — the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint — juts or angles out from the foot. To judge how severe a bunion is, clinicians take an x-ray and measure angles between certain bones in the foot, in particular, the hallux valgus angle (HVA) — the angle between the first metatarsal and the big toe — and the angle formed by the first and second metatarsals, called the intermetatarsal angle (IMA). The upper limit of normal for the HVA is 15 degrees; for the IMA, 9 degrees.
What is a bunion in shoes?
Many women have a bunion — a deformity of the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint at the base of the big toe. A bunion develops when the first metatarsal bone of the foot turns outward and the big toe points inward (toward the other toes), causing the joint to jut out (see "Anatomy of a bunion"). The Latin name for the deformity is hallux valgus ( hallux means big toe, and valgus means turned away from the midline of the body). Most shoes don't accommodate the resulting protrusion and so put pressure on the misaligned joint. Eventually, the bursa (a fluid-filled sac that surrounds and cushions the joint) becomes inflamed, and the entire joint becomes stiff and painful.
What is the Latin name for a big toe?
The Latin name for the deformity is hallux valgus ( hallux means big toe, and valgus means turned away from the midline of the body). Most shoes don't accommodate the resulting protrusion and so put pressure on the misaligned joint. Eventually, the bursa (a fluid-filled sac that surrounds and cushions the joint) becomes inflamed, ...
How long does it take to recover from bunion surgery?
You won't necessarily get rid of all your symptoms, and you'll have to stay off your foot for many weeks. Complete recovery can take a year or more, depending on the procedure. As with any surgery, you'll want to make sure the surgeon is experienced in performing the particular operation you've decided to undergo. You may also want to talk to other patients who've had the operation.
How to protect a bunion from a sprain?
You can also protect the bunion with a moleskin or gel-filled pad, available at drugstores. (Make sure your shoes have enough space to accommodate it.) A clinician may recommend semisoft orthoses (shoe inserts) to help position the foot correctly as it strikes the ground. You can also wear a splint at night to hold the toe straight and ease discomfort.
Why do women have bunions?
Women can develop bunions and other foot problems during pregnancy because hormonal changes loosen the ligaments and flatten the feet. Bunions are also associated with arthritis, which damages the cartilage within the joint.
How to stop bunion pain?
Your provider can recommend other treatment options, such as shoe gear modifications, physical therapy, medications and orthotics. Treatments can reduce pain and stop bunion symptoms from getting worse. If the pain becomes severe, surgery to remove the bunion and realign the big toe can help you get moving again.
What is the most common bunion on the big toe?
Juvenile or adolescent hallux valgus: Tweens and teens between the ages of 10 and 15 may develop bunions. Tailor’s bunion: Also called a bunionette, this bunion forms on the outside base of the little (pinky) toe.
What is a bunion on the outside of the big toe?
What is a bunion? A bunion is a bump that forms on the outside of the big toe. This foot deformity occurs from years of pressure on the big toe joint (the metatarsophalangeal, or MTP, joint). Eventually, the toe joint gets out of alignment, and a bony bump forms. The medical term for bunions is hallux abducto valgus.
How to prevent bunions from getting worse?
Proper-fitting footwear is key to preventing bunions or keeping an existing bunion from getting worse. Your healthcare provider can offer tips on how to select appropriate shoes. In general, you should buy shoes with a wide toe box and soft soles.
Why does my big toe bend in towards the second toe?
Pressure from the way you walk (foot mechanics) or the shape of your foot (foot structure) causes your big toe to bend in toward the second toe. Bunions happen gradually over time. Standing for long periods and wearing ill-fitting, narrow shoes can make bunion pain worse, but they don’t cause the problem.
How to prevent bunions in feet?
Avoid shoes that are narrow and pointed at the tip, and high heels that put pressure on the front of the foot. If you have flatfeet or another inherited structural foot problem, custom-fitted orthotics can help prevent, or slow the progression of, bunions.
What is the procedure to get your big toe back?
Surgery: If nonsurgical treatments don’t help, and walking becomes extremely painful, your provider may recommend surgery. This procedure is called a bunionectomy. Your provider removes the bunion and realigns bones to bring the big toe back into the correct position.
What is Hallux Valgus?
Definition. Hallux valgus is the most common foot deformity. It is a progressive foot deformity in which the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint is affected and is often accompanied by significant functional disability and foot pain and reduced quality of life.
What age should I wear shoes with hallux valgus?
Footwear (tight pointed shoes) Wearing tight shoes and/or heeled shoes between 20 and 39 years of age can be crucial in the development of hallux valgus in later years. Hallux valgus is also associated with hip and knee OA and is inversely associated with a higher BMI.
How many people have hallux valgus?
There is a high prevalence of hallux valgus in the overall population (23% of adults aged 18-65 years and 35.7% of adults over 65 years of age)
How many sesamoid bones articulate with the first metatarsal bone?
Two sesamoid bones articulate with the first metatarsal bone. These sesamoid bones:
What is the first toe?
The Hallux or first toe is the medio-distal part of the foot. Formed by the first metatarsal (articulates with two sesamoid bones), the first proximal phalanx and the first distal phalanx. Formed by three bones instead of four, unlike the other toes who have an extra bone called the intermediate phalanx.
What angle is considered severe?
An angle of 45-50° is considered severe. Footwear (tight pointed shoes) Wearing tight shoes and/or heeled shoes between 20 and 39 years of age can be crucial in the development of hallux valgus in later years. Hallux valgus is also associated with hip and knee OA and is inversely associated with a higher BMI.
How many synovial joints does the Hallux have?
The Hallux (first toe) has three synovial joints.
How to treat a bunion?
Nonsurgical treatments that may relieve the pain and pressure of a bunion include: 1 Changing shoes. Wear roomy, comfortable shoes that provide plenty of space for your toes. 2 Padding. Over-the-counter, nonmedicated bunion pads or cushions may be helpful. They can act as a buffer between your foot and your shoe and ease your pain. 3 Medications. Acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve) can help you control the pain of a bunion. Cortisone injections also might help. 4 Shoe inserts. Padded shoe inserts can help distribute pressure evenly when you move your feet, reducing your symptoms and preventing your bunion from getting worse. Over-the-counter supports can provide relief for some people; others require prescription orthotic devices. 5 Applying ice. Icing your bunion after you've been on your feet too long or if it becomes inflamed can help relieve soreness and swelling. If you have reduced feeling or circulation problems with your feet, check with your doctor first before applying ice.
How to stop bunion from getting worse?
Shoe inserts. Padded shoe inserts can help distribute pressure evenly when you move your feet, reducing your symptoms and preventing your bunion from getting worse. Over-the-counter supports can provide relief for some people; others require prescription orthotic devices.
What to do if your toes hurt?
Padding. Over-the-counter, nonmedicated bunion pads or cushions may be helpful. They can act as a buffer between your foot and your shoe and ease your pain. Medications.
How long does it take to recover from a bunion?
It's possible that you'll be able to walk on your foot right after a bunion procedure. However, full recovery can take weeks to months. To prevent a recurrence, you'll need to wear proper shoes after recovery.
Can bunion surgery be done?
Surgery is not recommended for cosmetic reasons; only when a bunion causes you frequent pain or interferes with your daily activities. There are many surgical procedures for bunions, and no one technique is best for every problem. Surgical procedures for bunions can be done as single procedures or in combination.
Can you walk on your foot after a bunion surgery?
They might involve: Realigning one or more bones in the forefoot to a more normal position to correct the abnormal angle in your big toe joint. It's possible that you'll be able to walk on your foot right after a bunion procedure.

Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
Prevention
- The signs and symptoms of a bunion include: 1. A bulging bump on the outside of the base of your big toe 2. Swelling, redness or soreness around your big toe joint 3. Corns or calluses — these often develop where the first and second toes rub against each other 4. Ongoing pain or pain that comes and goes 5. Limited movement of your big toe