What is the complementary strand of DNA? Complementary DNA (cDNA) is a copy of a region of a strand of DNA. For example, if the original DNA stand had a sequence of ATT, the complementary sequence will be TAA.
Are the two strands of DNA identical or complementary?
The two strands are internally connected by hydrogen bonding between complementary bases. The two strands of DNA are not identical because their sequence of bases has to be complementary to each other.. Why DNA is a double helix? The double comes from the fact that the helix is made of two long strands of DNA that are intertwined—sort of like ...
What are the complimentary bases of a strand of DNA?
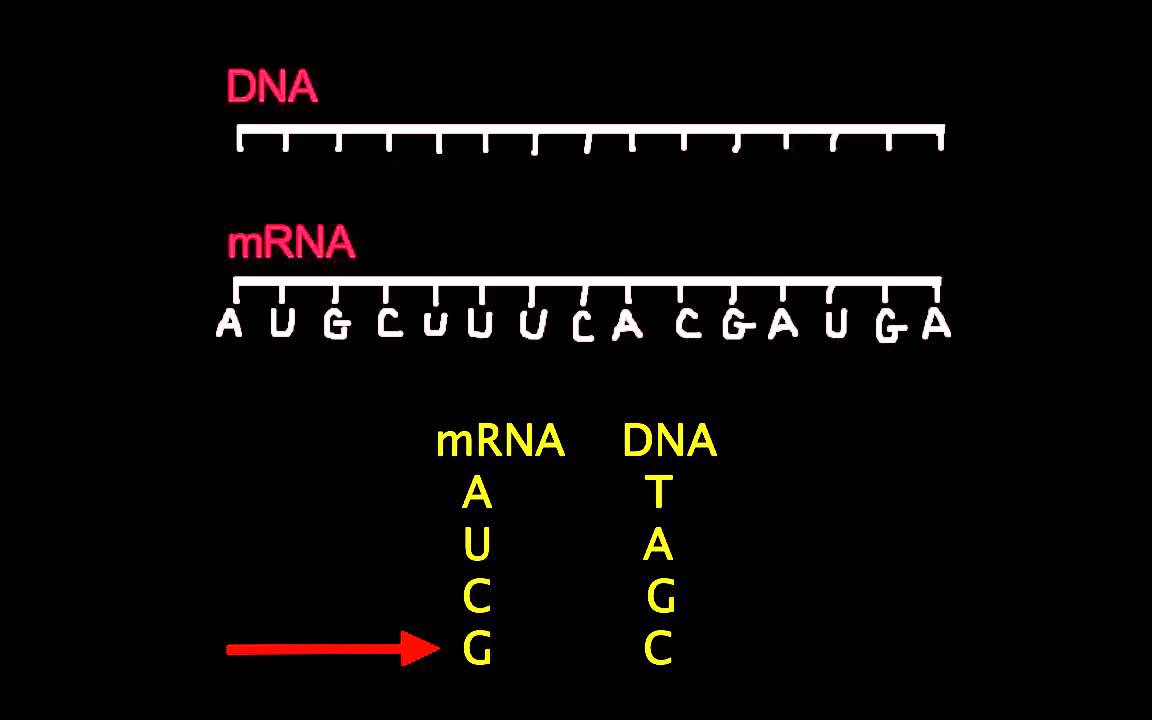
Complementary bases are: adenine (A) and thymine (T), and cytosine (C) and guanine (G). So if one strand of DNA reads A-C-G-C-T-A, then the complementary strand is T-G-C-G-A-T. You can find the sequence of the mRNA transcript in the same way, by using the complements of the bases shown in the DNA sequence.
What are the two strands wound together in DNA called?
double helixNucleotides are arranged in two long strands that form a spiral called a double helix. The structure of the double helix is somewhat like a ladder, with the base pairs forming the ladder's rungs and the sugar and phosphate molecules forming the vertical sidepieces of the ladder. What are the 4 strands of DNA?
Can you determine DNA with one strand?
The answer is, yes, we can. It seems that there are many DNA testing companies that state that it is not possible to extract DNA from strands of hair that do not have the root attached. However, whether or not the root is attached, it is possible to do a DNA test with a strand of hair. In movies or TV shows, oftentimes there are stories where the criminal is identified from hair left behind at the scene of the crime.
What is a complementary DNA strand simple definition?
Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is DNA in which the sequence of the constituent molecules on one strand of the double stranded structure chemically matches the sequence on the other strand.
Which strand is the complementary strand of DNA?
The upper strand of DNA is the "mRNA-like" strand. The lower strand is the strand that is complementary to the mRNA. The -35 region (TTGACA) and -10 region (TATATT) of the promoter sequence and the transcriptional start site (the A) is indicated on the coding strand.
What makes a complementary DNA strand?
Complementary Sequence: Since DNA has two strands, every DNA sequence has a complementary sequence running parallel. In the complementary sequence, Adenine (A) is always paired with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) is always paired with Guanine (G).
How do you find complementary DNA strands?
0:292:07Practice writing the complementary strand of DNA and mRNA during ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTake a moment and write down the complementary strand of this DNA. Okay so here's what theMoreTake a moment and write down the complementary strand of this DNA. Okay so here's what the complementary strand would look like we would have a T a a G G C T a T and then finally one last T.
What bonds do you use to write a complementary base?
Just use the base-pairing rules — C bonds with G, and A bonds with T — and for each base in the original sequence, write the complementary base below it.
What ends of DNA should be labeled?
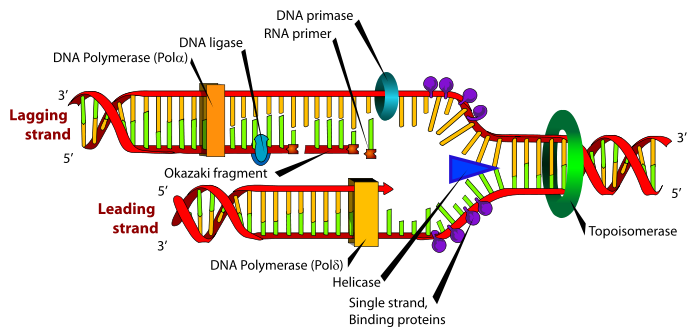
For this reason, you should ALWAYS label the 5′ and 3′ ends of any DNA strand you are working with, as I have done here.
How many nitrogen bases are in DNA?
DNA has 4 nitrogen bases which are Adenine (A) , Guanine (G) , Thymine (T) , Cytosine (C). RNA also has 4 bases but in RNA Uracil (U) is present instead thymine. Adenine always pair with thymine by twi hydrogen bonds in DNA and to Uracil in RNA. Guanine pair with cytosine by three hydrogen bonds. In a double stranded DNA base pairing exists. Thus, adenine is present opposite to thymine and guanine present opposite to cytosine in double strand. This is called as complementary base pairing.
What is the polarity of each strand of RNA?
Each strand is a polynucleotide composed of A (adenosine), T (thymidine), C (cytidine), and G (guanosine) residues polymerized by "dehydration" synthesis in linear chains with specific sequences. Each strand has polarity which runs from 5′ to 3′. While RNA is a single strand molecule.
What is the purpose of a promoter sequence?
In gene expression, a promoter sequence to which RNA polymerase binds is required for the initiation of (significant) transcription. These, along with terminator sequences, are the basis for identifying transcribed regions (or operons) within a longer continuous sequence such as an entire chromosome.
What is anti-parallel transcription?
Anti-parallel transcribed regions are commonly found on a single dsDNA molecule. As transcription only progresses from 5′ to 3′, ‘forward’ and ‘reverse’ transcription necessarily involves different strands, the other strand in each case being described as ‘anti-sense’.
Which enzyme reads the parent strand in the direction of 3 to 5?
The formation of mRNA molecule occurs in the direction of 5` to 3` end of the mRNA molecule. Therefore the polymerase enzyme reads parent strand in the direction of 3` to 5`.
