
What is a compression wave for kids? A longitudinal wave travels in the same direction as the disturbance that caused it. Longitudinal waves move through a medium from the point of the disturbance in the form of compressions (where particles of the medium are bunched together) followed by rarefactions (where particles of the medium are farther apart).
Full Answer
What is a compression wave?
: a longitudinal wave (such as a sound wave) propagated by the elastic compression of the medium — called also compression wave.
What is the meaning of compression?
Compression. KidzSearch Safe Wikipedia for Kids. Jump to: navigation. , search. Compression could mean: Gas compression, raising the pressure and reducing the volume of gases. Physical compression, the result of the subjection of a material to compressive stress.
What is the difference between longitudinal and compression waves?
Compression waves are waves where the vibration is parallel to the direction of motion. The term 'compression wave' is usually reserved for use as a mechanical term, while longitudinal wave is much more common for what we're talking about.
What is a wave?
What is a wave? When we think of the word "wave" we usually picture someone moving their hand back and forth to say hello or maybe we think of a curling wall of water moving in from the ocean to crash on the beach. In physics, a wave is a disturbance that travels through space and matter transferring energy from one place to another.
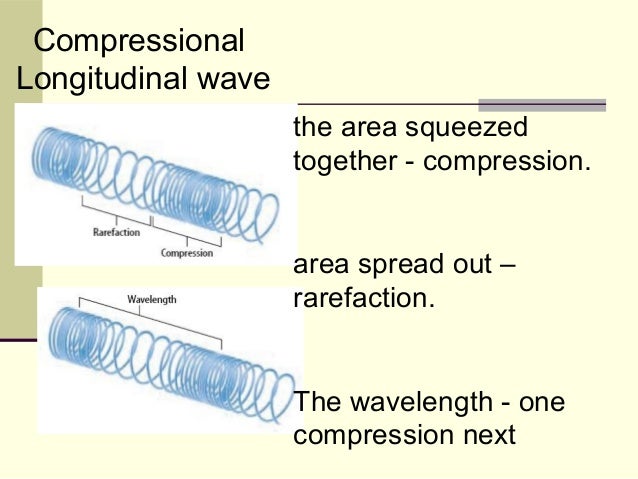
What is a compression wave easy definition?
Definition of compressional wave : a longitudinal wave (such as a sound wave) propagated by the elastic compression of the medium. — called also compression wave.
What is compression in sound waves?
Compression is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are closest together. A rarefaction is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are furthest apart. The region where the medium is compressed is known as compression and the region where the medium is spread out is known as a rarefaction.
Why is it called compression wave?
Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called compressional or compression waves, because they produce compression and rarefaction when traveling through a medium, and pressure waves, because they produce increases and decreases in pressure.
How do you explain waves to a child?
Waves are a pattern of motion that transfer energy from place to place without transferring matter. There are different types of waves. Sound waves travel through air and allow us to hear sound. Water waves move on top of water.
What is a compressional wave example?
A compressional wave is made up of compressions and rarefactions that flow through the medium of the wave. A wavelength is the distance from one compression to another compression, or rarefaction to another rarefaction. Some examples of compressional waves include sound and P-waves, which are from earthquakes.
How do compressional waves move examples?
Sound waves are a great example of compressional/longitudinal waves. Sound waves moving air particles back and forth. Your voice does the same thing to the air!
Which wave is also known as compressional wave?
Longitudinal waves are also called compressional waves or rarefactional waves because they produce compression and rarefaction of the pressure when traveling through a medium.
What are the parts of a compression wave?
The compression is the part of the compressional wave where the particles are crowded together. The rarefaction is the part of the compressional wave where the particles are spread apart. The wavelength is the distance from compression to compression or rarefaction to rarefaction in a compressional wave.
What are waves 6th grade?
A wave is either mechanical, like an ocean wave, or electromagnetic, like the radiation that heats your food in the microwave. The shorter the wavelength, the greater the energy. The higher the frequency, the greater the energy. The higher the amplitude, the greater the energy.
What are the two types of waves?
Waves come in two kinds, longitudinal and transverse. Transverse waves are like those on water, with the surface going up and down, and longitudinal waves are like of those of sound, consisting of alternating compressions and rarefactions in a medium.
What are the 7 types of waves?
Though the sciences generally classify EM waves into seven basic types, all are manifestations of the same phenomenon.Radio Waves: Instant Communication. ... Microwaves: Data and Heat. ... Infrared Waves: Invisible Heat. ... Visible Light Rays. ... Ultraviolet Waves: Energetic Light. ... X-rays: Penetrating Radiation. ... Gamma Rays: Nuclear Energy.
How do compressional waves move?
Compressional waves move longitudinally. The motion is in the same, or parallel direction as that of the flow of energy of the wave.
What are compression and transverse waves?
A compression wave is a where the movement of the medium, or the vibration/disturbance within the medium, is in the same, or parallel, direction as...
What causes compression waves?
Compression waves are caused by a disturbance or a vibration in a medium. Disturbances could include a stick hitting the head of a drum or a vibrat...
What are 3 examples of longitudinal waves?
Three examples of longitudinal waves include sound waves, ultrasound and seismic P-waves. Ultrasound waves are used in many medical imaging techniq...
Wave
Waves are one of the ways that the natural world transfers energy from one location to another. A wave is a disturbance, or transfer, of energy through a medium from one location to another location, without the matter in the medium changing location. A wave transfers energy in a unique and efficient way.
Compressional Wave
The compressional wave definition is a wave where the movement of the medium, or the vibration or disturbance within the medium, is in the same or parallel direction as that of the motion of the wave.
Parts of a Compressional Wave
There are multiple important parts of a compressional wave. The first part of the compressional wave is the medium, through which the energy is flowing. The medium is the matter or material that is transferring the energy. For a sound wave going through the air, the air is the medium. It is the air that is moving and transferring the energy.
What is sound wave?
A sound wave is a special kind of wave that can be detected by the human ear. Sound waves have special characteristics that make them unique. Mechanical Waves. One important characteristic of sound waves is that they are mechanical waves. This means that they travel through a medium.
What is the peak of the compression or rarefaction on the graph?
The amplitude is the peak of the compression or rarefaction on the graph. Intensity of a Sound Wave. Sound waves are sometimes measured using a quantity called intensity. The intensity of a sound wave (I) is equal to the sound power (P) over the area (A):
Why are sound waves called pressure waves?
Sound waves can also be thought of as pressure waves. This is because the compressions and rarefactions that move through sound waves have different pressures. The compressions are areas of high pressure while the rarefactions are areas of low pressure.
How do molecules move in a wave?
Here you can see how the molecules move in a left to right motion causing the wave and the disturbance to move in the same direction. In some areas of the wave the molecules get bunched together. This is called compression. In other areas the molecules become spread out. This is called rarefaction.
Can sound waves travel through space?
Normally, we hear sound waves that have traveled through air, but sound can also travel through water, wood, the Earth, and many other substances. Sound cannot travel through a vacuum like outer space, however. The source of sound waves is something vibrating.
What is transverse wave?
Transverse waves are waves where the disturbance moves perpendicular to the direction of the wave. You can think of the wave moving left to right, while the disturbance moves up and down. One example of a transverse wave is a water wave where the water moves up and down as the wave passes through the ocean. Other examples include an oscillating ...
What are the different types of waves?
Below we describe some of the different terms that scientists use to describe waves. Mechanical Waves and Electromagnetic Waves. All waves can be categorized as either mechanical or electromagnetic .
What is longitudinal wave?
Longitudinal waves are waves where the disturbance moves in the same direction as the wave. One example of this is a wave moving through a stretched out slinky or spring. If you compress one portion of the slinky and let go, the wave will move left to right.
How do mechanical waves travel?
This means that they have to have some sort of matter to travel through. These waves travel when molecules in the medium collide with each other passing on energy. One example of a mechanical wave is sound. Sound can travel through air, water, or solids, but it can't travel through a vacuum.
How do sound waves propagate?
As sound waves propagate through a medium, the molecules collide with each other in the same direction as the sound is moving. and the bottom wave is longitudinal. Waves in the ocean are mostly generated by the wind moving across the ocean surface. The "medium" is the substance or material that carries a mechanical wave.
Why is it important to study waves?
When studying waves it's important to remember that they transfer energy, not matter. Waves in Everyday Life. There are lots of waves all around us in everyday life. Sound is a type of wave that moves through matter and then vibrates our eardrums so we can hear. Light is a special kind of wave that is made up of photons.
How are waves generated?
Waves in the ocean are mostly generated by the wind moving across the ocean surface. The "medium" is the substance or material that carries a mechanical wave. One of the most important things to remember about waves is that they transport energy, not matter. This makes them different from other phenomenon in physics.
