What are the three types of muscular contractions?
What are different types of muscle contractions
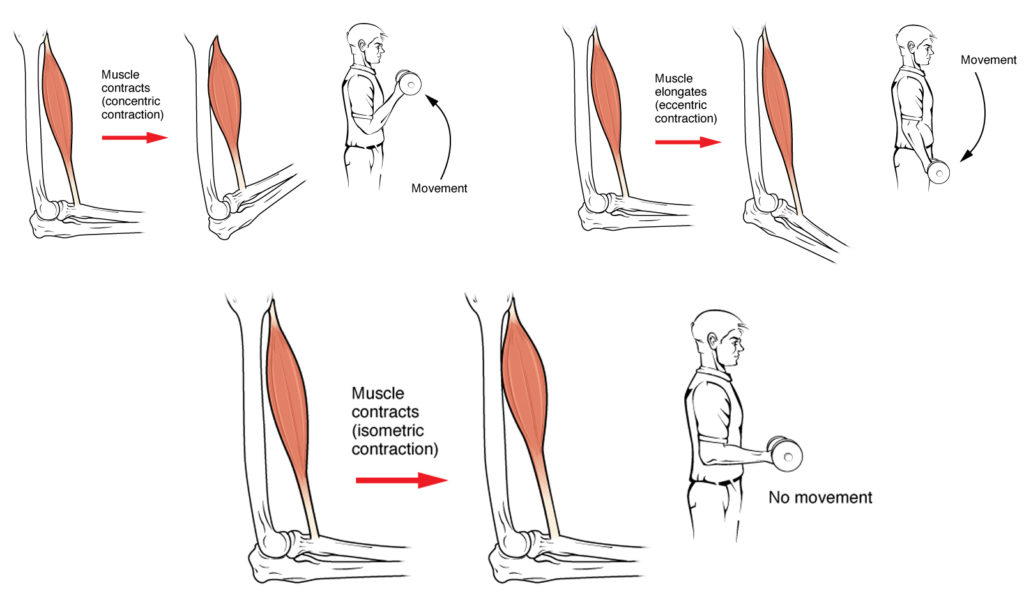
- Isotonic muscle contractions. Isotonic contractions are those where the muscle changes length as it contracts whilst the load or resistance remains the same.
- Isometric muscle contraction. Isometric contractions occur when there is no change in the length of the contracting muscle.
- Isokinetic contractions.
Which can shorten during a muscle contraction?
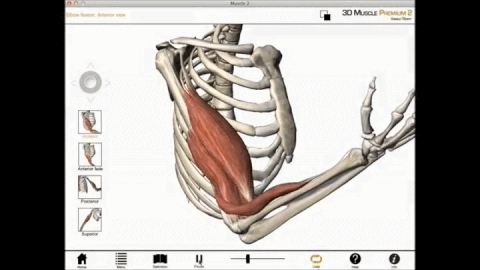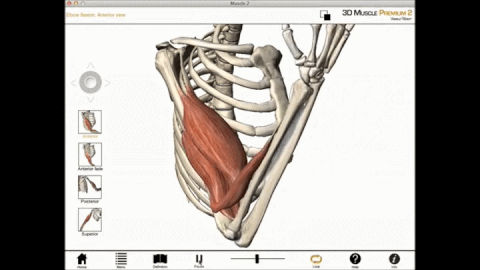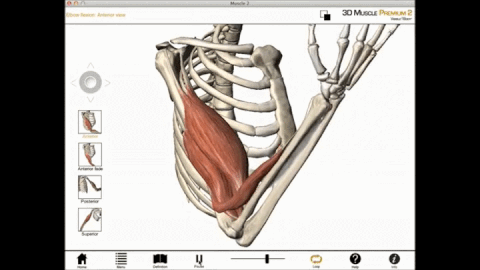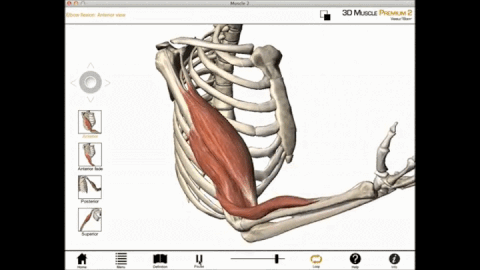
During a muscle contraction, every sarcomere will shorten (1) bringing the Z-lines closer together (2). The myofibrils shorten (3) too, as does the whole muscle cell. Yet the myofilaments – the thin and thick filaments – do not get shorter (4). They slide by each other, overlapping as the Z-lines pull closer together, the I-Bands shorten (5),
What does a muscle contraction feel like?
What Does a Contraction Feel Like? Warm-up contractions are mostly noticed as a “tight belly.”. When we suddenly notice that are baby feels like a firm basketball, we are having a contraction. These are usually only felt in the front of our bellies (not our backs). Contractions may feel crampy at times, and then only “tight” at other times.
What are the three ions of muscle contractions?
Understanding Muscle Contractions
- Concentric Contractions. This type of contraction happens when your muscle is actively shortened. ...
- Eccentric Contractions. This type of contraction happens when your muscle is actively lengthened during normal activity. ...
- Isometric Contraction. This type of muscle contraction happens when your muscle is actively held at a set length. ...
- Passive Stretch. ...
What is an example of a concentric contraction?
Concentric contraction occurs when the total length of the muscle shortens as tension is produced. For example, the upward phase of a biceps curl is a concentric contraction.
What is concentric contraction quizlet?
concentric contraction- wherein a muscle contracts and shortens (force required to move the muscle is greater than or equal to the resistance force)
What are concentric and eccentric examples of?
The best example of both concentric and eccentric movements is the biceps curl. When you curl your arm up toward your shoulder, your arm muscles contract (a concentric movement). When you lower the weight back toward your waistline, your arm muscles lengthen (an eccentric movement).
Which is an example of a concentric contraction quizlet?
When a person lifts a weight with his arm, the biceps shortens and moves forearm to an upper arm which is an example of a concentric contraction.
What is the difference between concentric and eccentric muscle contraction quizlet?
In an eccentric contraction, the muscle will shorten if the load is greater than the peak tension the muscle can develop. In a concentric contraction, the tension in the skeletal muscle increases as the muscle shortens.
How do you tell if a muscle is concentric or eccentric?
In a concentric contraction, the muscle tension rises to meet the resistance then remains stable as the muscle shortens. During eccentric contraction, the muscle lengthens as the resistance becomes greater than the force the muscle is producing.
Is a push up concentric or eccentric?
concentricThe concentric phase is the phase of the movement that is overcoming gravity or load, while the eccentric phase is the phase resisting gravity or load. So for push ups the concentric phase is the up phase where gravity is overcome, and the eccentric phase is the downward phase where gravity is resisted.
How do you remember eccentric and concentric?
A simple method to learn the difference between Eccentric and Concentric contractionsConcentric = Collapsing (shorter)Eccentric = Elongating (longer)Concentric phase: ... Eccentric phase: ... [NOTE: The answers are below the 3rd questions]During the concentric phase of the squat what happens to the quadriceps?More items...•
What is an eccentric contraction quizlet?
An eccentric muscle contraction is a type of muscle activation that increases tension on a muscle as it lengthens. Eccentric contractions typically occur when a muscle opposes a stronger force, which causes the muscle to lengthen as it contracts.
What happens to a muscle during a concentric contraction quizlet?
In a concentric contraction, the muscles shorten to produce movement. In an eccentric contraction (often known as a yielding contraction), the muscle lengthens (stretches) as it contracts. In an isometric contraction, the muscle exhibits strength but the limbs do not move.
What is an example of an isometric contraction?
Isometric contraction occurs when muscle length remains relatively constant as tension is produced. For example, during a biceps curl, holding the dumbbell in a constant/static position rather than actively raising or lowering it is an example of isometric contraction.
What happens to a muscle during an eccentric contraction quizlet?
During an eccentric contraction, a muscle lengthens while the contractile element is active. What happens to the magnitude of the muscle tension (force) as the speed of the eccentric contraction increases? There is an increase of tension (force) as the speed of the eccentric contraction increases.
What is eccentric contraction?
On the other hand, as you slowly lower the dumbbell, the muscle will lengthen but still remain tense. This is the phase known as the eccentric muscle contraction. It is the yang to concentric muscle contraction's yin. Examples include:
How to visualize a concentric contraction?
A simple way to visualize a concentric muscle contraction is to do a biceps curl with a dumbbell. As you raise the dumbbell from the full-extended (downward) position toward the shoulder, you will see the biceps muscle being activated.
What is the process of incorporating isometric contractions?
Incorporating Isometric Contractions. Increasing muscle mass and strength is a complex physiologic process that requires both muscle activation and rest. A concentric muscle contraction is one of the three types of activation. 3 The other two are eccentric muscle contractions and isometric muscle contractions.
What is the process of pushing a muscle?
The actual process of "pushing" or "lifting" in these exercises involves an action known as a concentric muscle contraction. By definition, a concentric contraction is one in which the tension on a muscle increase as it shortens. 1
What is the process of muscle contraction?
Concentric contractions are a central aspect of the growth and development of muscles. As muscle contracts, they begin the process of hypertrophy ("hyper" meaning increased and "trophy" meaning growth). With muscle hypertrophy, each muscle cell will grow under the influence of consistent stress. The muscle fibers themselves, known as myofibrils, will also split and increase muscle mass.
What is strength training?
When we think about strength training, we tend to refer to the process of building muscle mass. It may involve lifting a barbell to build biceps or using a Smith machine or a pec-deck to increase the size and strength of your chest muscles.
Which activation is used to build muscle mass?
Although concentric contractions are central to building muscle mass, eccentric and isometric activations should also be utilized to build muscle in a more cohesive way.
What is concentric contraction?
First, let’s briefly focus on what a concentric contraction actually is.A concentric contraction uses energy and will result in acceleration of an object. When a muscle is activated and required to lift a load that is less than the maximum tension it can generate, the muscle begins to shorten.
Why do we reduce the velocity and force of the concentric portion of the rep?
During the concentric portion of a movement, the body as a protected device, must reduce the velocity and force of the concentric portion of the rep to guard against jerking the tendons or creating undue stress on the joint when coming to an abrupt stop at the end range of motion.
What are Concentric Contractions?from differencebetween.com
Concentric contraction is a type of isotonic contraction which causes muscles to shorten while generating a force. Concentric contraction occurs throughout the muscle in the direction of contraction of a muscle. These contractions are required when lifting a load. For instance, when lifting a heavy load, a concentric contraction of the biceps causes the arm to bend at the elbow. During the concentric contraction, cross-bridge cycling occurs in order to produce the force.
Which muscle fibers shorten during concentric contraction?from differencebetween.com
Sarcomere, muscle fiber and muscle shorten during concentric contraction. In contrast, sarcomere, muscle fiber and the muscle lengthen in the eccentric contraction.
WHY YOU SHOULD FOCUS ON CONCENTRIC, ECCENTRIC & ISOMETRIC CONTRACTION IN YOUR TRAINING?from setforset.com
But we didn't really emphasize the importance of isometric contraction, which is to gain strength at specific ranges in a movement.
WHAT IS AN ISOTONIC EXERCISE?from setforset.com
While isotonic exercises can further fall into two different categories of concentric and eccentric movement, let's not get ahead of ourselves.
What is the functional unit of a muscle fiber?from differencebetween.com
During the concentric contraction, cross-bridge cycling occurs in order to produce the force. A sarcomere is the functional unit of a muscle fiber.
What is the process of muscle contraction?from differencebetween.com
Muscle contraction is a complex process which changes the length of the muscle fibers. Muscle fibers generate tension. It involves the interaction between contractile proteins actin and myosin in the presence of calcium. There are different types of muscle contractions based on the changes in the length of the muscle during contraction. Isometric and isotonic are the two main types. Isotonic contractions generate a force by changing the length of the muscle while isometric contractions generate a force without changing the length of the muscle. Isotonic contractions are categorized into two types as concentric and eccentric contractions.
What is the opposite of a concentric lift?from setforset.com
Eccentric lifts or exercises are the exact opposite of concentric lifts. They will allow you to put in the most force with the least effort. These are usually exercises that focus on specific muscle groups and help increase muscle mass and strength.
What are some examples of concentric contractions?
An example of a concentric muscle contraction is picking up a heavy box. If you squat down to lift a box, your arm muscles may contract to hold the weight, but your leg muscles tighten as you stand up with the additional weight.. Eccentric Contractions.
What is passive muscle contraction?
Passive Stretch. This type of muscle contraction happens when your muscle is passively lengthened. For example, you lean down to touch your toes. There’s no additional weight that your hamstring muscle needs to hold or lift by applying force, but it still stretches from the movement. How You Use Muscle Contractions.
What type of contraction happens when you lower something heavy?
Eccentric muscle contractions also happen when you lower something heavy. Your muscle has to remain tight to manage the weight, but it lengthens to shift the weight into a different position.. Isometric Contraction. This type of muscle contraction happens when your muscle is actively held at a set length. Instead of lengthening and shortening as ...
How do you use isometric muscle contractions?
Isometric muscle contractions. This type of contraction is used when your muscle stays in a single position and the attached joint doesn’t move. It doesn’t provide overall strengthening to the muscle group. Instead, it strengthens your muscle for that single, specific movement.
What is the fiber that makes muscles contract?
How Your Muscles Contract. Your muscles contain fibers called myosin. Depending on how you need to use your muscles, the myosin fibers either tighten up and shorten or loosen up and stretch out. Myosin is also responsible for muscle contractions like your heartbeat that happens at regular intervals.
Why do muscles contract?
Your muscles contract for any number of reasons, but they primarily do the following:. Offer stability to your joints and connective tissues – Your muscles lengthen and shorten, sometimes involuntarily, as your body needs them. Produce heat to maintain your body temperature – Around 40% of your body’s temperature converts into muscle work.
What is an example of a contraction?
An example of this type of contraction is carrying something in your arms in front of you. You aren’t trying to raise or lower the object but keep it at a steady position..
What are the 3 types of muscle action?
Muscle contractions are classified into three types: isometric, concentric, and eccentric. Isometric muscles contract but do not move. Concentric muscles shorten but do not stretch. Eccentric muscles lengthen but do not contract. These three types of muscle actions are useful in many sports and activities.
What are the 3 types of muscle contraction?
Muscle contractions are classified into three types: isometric, concentric, and eccentric.
Which type of contraction causes the most muscle damage?
Damage is more likely to occur and the degree of the injury is greatest during lengthening contractions among the three types of contractions—shortening (concentric), isometric, and lengthening (eccentric). Lengthening contracts drain energy from the muscle fiber by extending its sarcomeres past their resting length.
What type of contraction is hip flexion?
Muscle Eccentric Contraction: Also called eccentric exercise, this form of training stresses the muscles by requiring them to work against resistance. As the muscle contracts while pulling something away from its normal position, it becomes stronger, builds muscle mass, and increases blood flow during exertion.
What are isotonic muscle contractions?
An isotonic muscle contraction occurs when the force or tension in the muscle remains constant while the length of the muscle changes. There are two types of isotonic contractions in muscle movement: concentric and eccentric.
When tension remains unchanged but the muscle length varies, it is what type of contraction?
Hill distinguished two types of muscular contractions in 1925: isometric (muscle length does not alter during contraction) and isotonic. The tension remains constant throughout this contraction while the muscle length varies. Isotonic contractions are classified into two types: concentric and eccentric.
Do Bones Contract As You Move?
There is no definitive answer to this question as it is still a matter of scientific debate. Some scientists believe that bones do contract as we move, while others believe that they simply become more compact due to the force of gravity.
Which Muscle Type Contracts And Moves Bones?
Skeletal muscles are responsible for the movement of bones by contracting and relaxing in response to voluntary signals from the nervous system. Skeletal muscle tissue, which includes striated muscle fibers, is made up of long cells.
How Does Muscle Move Bone?
Muscles move bones by contracting and pulling on the tendons that are attached to the bone. The tendons act like a rope that the muscle pulls on to move the bone.
How Do Muscles Help The Bones To Move
The muscles that connect your bones to your bones are made up of tough cords of tissue known as tendons (TEN-duhns). When the muscle contracts, it pulls on the tendons, which move the bone. ligaments (LIG-uh-muhnts) are similar to tendons and help hold your skeleton together, allowing your bones to stay attached.
What Happens When Muscles Contract
Muscle contraction occurs when the thin filaments of actin and myosin collide. As ATP hydrolyses from the myosin filaments, it is widely assumed that this process occurs in cycles.
How Do Bones Move
There are a few ways that bones can move. The first way is by using muscles. Muscles are attached to bones and when they contract, they pull on the bones and cause them to move. The second way that bones can move is by using joints. Joints are where two bones meet and they allow the bones to move in specific ways.
Muscle Contractions
Muscle contractions are the body’s way of generating force. The contraction of a muscle is accomplished by the shortening of the muscle fibers. This is done by the activation of the muscle’s motor units. Motor units are composed of a motor neuron and the muscle fibers that it innervates.
