
Raised level of direct bilirubin is seen in:
| Type of Jaundice | Causes | Pathophysiology |
| Drugs like Rifampicin and Gilbert syndr ... | There is a defect in the uptake of uncon ... | |
| Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia | Mechanical obstruction by tumors, stones ... | There is a defect in the flow of conjuga ... |
| Drugs like estrogen and cyclosporineDubi ... | There is a defect in the transmembrane s ... | |
| Sepsis | Like above |
What is meant by conjugation of bilirubin?
Once in the liver, bilirubin becomes “conjugated.” This means it is water-soluble and can be excreted. This means it is water-soluble and can be excreted. Unconjugated bilirubin is toxic, but conjugated bilirubin is usually not, because it can be removed from the body, as long as nothing is interfering with its removal.
How does conjugated bilirubin appear in the bloodstream?
So, there must be a mechanism for secretion of conjugated bilirubin into the bloodstream on the basolateral (sinusoidal) membrane of hepatocytes. ESP: Probably it makes homeostatic sense to have conjugated bilirubin and xenobiotics also transported via the hepatocyte basolateral membrane into the circulation so that they may be excreted in the urine.
What is the difference between direct and indirect bilirubin?
What is the difference between direct and indirect bilirubin?
- conjogated ...direct. Bilirubin is a breakdown product of heme (which, in turn is part of the hemoglobin molecule that is in red blood cells).
- Unconjugated ("Indirect. Erythrocytes generated in the bone marrow are disposed of in the spleen when they get old or damaged.
- Conjugated ("Direct")
What could be causing elevated direct bilirubin levels?
The most common causes of increased conjugated bilirubin levels are related to liver problems. Hepatitis: Damage to liver cells caused by inflammation can increase direct bilirubin levels. cirrhosis of the liver: Diseases such as alcoholism or certain viruses can cause liver cells to replace scar tissue; severe cirrhosis causes jaundice.
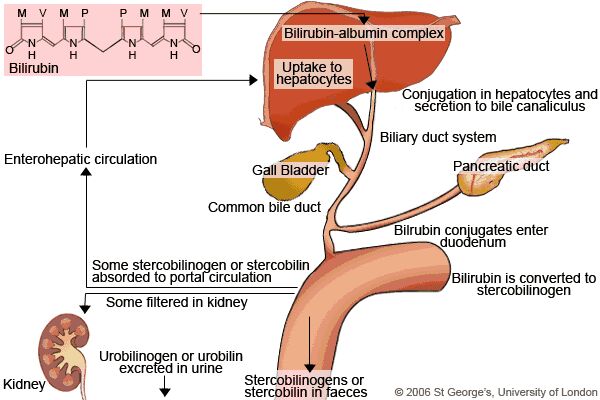
What causes high conjugated bilirubin?
The conjugated (direct) bilirubin level is often elevated by alcohol, infectious hepatitis, drug reactions, and autoimmune disorders. Posthepatic disorders also can cause conjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
What does high conjugated bilirubin mean?
Elevation in unconjugated bilirubin indicates prehepatic or hepatic jaundice and may be managed medically;[12] whereas an increase in conjugated bilirubin suggests hepatocellular injury or cholestasis, which may necessitate bile duct surgery or therapeutic endoscopy.
Why is it called conjugated bilirubin?
Unconjugated bilirubin does not react well in this system unless alcohol is added to promote its solubility in water. Conjugated bilirubin also is called direct bilirubin because it reacts directly with the reagent, and unconjugated bilirubin is called indirect because it has to be solubilized first.
What is the difference between total bilirubin and conjugated bilirubin?
In the liver, bilirubin undergoes a process called conjugation with a substance called glucuronide, through which bilirubin becomes “conjugated.” Conjugated bilirubin is water-soluble and ready to be excreted into bile. A total bilirubin blood test includes unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin.
Should I worry about high bilirubin?
Lower than normal bilirubin levels are usually not a concern. Elevated levels may indicate liver damage or disease. Higher than normal levels of direct bilirubin in your blood may indicate your liver isn't clearing bilirubin properly. Elevated levels of indirect bilirubin may indicate other problems.
How do I lower my conjugated bilirubin?
However, following these four tips can help you boost overall liver health in addition to medical guidance.Stay hydrated. Staying hydrated helps lower bilirubin levels by facilitating the removal of waste from the body. ... Consume fresh fruits and vegetables. ... Increase your intake of fiber. ... Avoid alcohol.
What is conjugated in liver function test?
Conjugated (“direct”) bilirubin. This is the bilirubin once it reaches the liver and undergoes a chemical change. It moves to the intestines before being removed through your stool. For adults over 18, normal total bilirubin can be up to 1.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) of blood.
Is jaundice conjugated or unconjugated bilirubin?
Jaundice is a yellowish discoloration of the skin and sclerae that is an important symptom of elevated serum bilirubin, which is caused by an abnormality of bilirubin metabolism or excretion. The bilirubin can be either unconjugated or conjugated.
How do you know if bilirubin is conjugated or unconjugated?
A urine test positive for bilirubin indicates conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Conjugated bilirubin is soluble in water; therefore, it can be excreted via urine but not unconjugated bilirubin due to water insolubility.
What is the difference between conjugated and unconjugated?
The conjugated bilirubin is present in bile, while the unconjugated bilirubin is not present in bile. The conjugated bilirubin is normally not present in urine, but appears in high plasma concentrations. The unconjugated bilirubin is not present in urine. The conjugated bilirubin is not toxic to the tissues.
Is conjugated bilirubin toxic?
Unlike unconjugated bilirubin, conjugated bilirubin does not bind significantly to neural tissue and does not lead to kernicterus or other forms of toxicity.
Where does bilirubin get conjugated?
Bilirubin: Bilirubin that has been conjugated in the liver to be excreted into the intestine may accumulate in the blood of patients who have bile duct obstruction. Alkaline phosphatase: This enzyme is found along the liver cell membrane lining the intercellular canaliculi.
What is the name of the fraction of serum bilirubin that has been conjugated with glucuronic
Synonym (s): conjugated bilirubin.
Where is bilirubin stored?
Direct bilirubin Bilirubin chemically bound to a glucuronide in the liver, which is excreted in bile by the liver and stored in the gallbladder or transferred to the duodenum Ref range Direct BR: 0–0.3 mg/dL ↑ in Bile duct obstruction, cirrhosis, Crigler-Najjar syndrome, Dubin-Johnson syndrome, hepatitis. See Bilirubin.
Does conjugated bilirubin cross the placenta?
Because conjugated bilirubin does not cross the placenta from the fetal into the maternal circulation, it is excreted into the fetal bile or amniotic fluid, where it is then transferred to the maternal circulation. Management of drug-induced hyperbilirubinaemia in early pregnancy.
Continuing Education Activity
Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia is usually secondary to hepatocellular disease or cholestasis (intrahepatic and extra-hepatic ). Early workup and diagnosis is necessary for the appropriate management and to prevent future complications.
Introduction
Pathologic elevation of conjugated or direct bilirubin (concentration higher than 2 mg/dL or more than 20% of total bilirubin) is termed conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. [1] It is a biochemical marker of cholestasis and hepatocellular dysfunction. [1] Approximately 80% of the bilirubin is derived from hemoglobin metabolism.
Epidemiology
Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia is a common abnormality, usually due to hepatocellular or cholestatic diseases; moreover, it may be observed in systemic illnesses with hepatic involvement. As conjugated hyperbilirubinemia may result from secondary causes, the epidemiology will correlate with the specific disease state.
Pathophysiology
Various congenital and acquired etiologies of conjugated hyperbilirubinemia have been listed above.
History and Physical
The initial workup must be aimed towards identifying the underlying etiology, manifestations of hyperbilirubinemia, and complications of hyperbilirubinemia. The presenting symptoms and signs are likely to be vague and vary according to the primary condition.
Evaluation
Evaluation is usually directed to the underlying etiology of the conjugated hyperbilirubinemia based on history and physical findings, which includes biliary obstruction, intrahepatic cholestasis, hepatocellular injury, or an inherited condition. Following studies are performed as a part of a workup for conjugated hyperbilirubinemia: [21]
Differential Diagnosis
As conjugated hyperbilirubinemia is a manifestation of the disease, rather than a disease itself, the potential etiologies listed below serve as possible differential diagnoses as well.
What is unconjugated bilirubin?
Unconjugated Bilirubin. Bilirubin is a product of the degradation of hemoglobin and some other blood components. It is a yellow-red pigment. The fraction of the bilirubin, conjugated with glucuronic acid in the liver to form bilirubindiglucuronide is called conjugated bilirubin.
What is the fraction of bilirubin that is not conjugated in the liver called?
The fraction of the bilirubin, not conjugated in the liver is called unconjugated bilirubin. The conjugated bilirubin is soluble in water, insoluble in fat and alcohol.
How much bilirubin is produced daily?
What is Conjugated Bilirubin? Approximately 250-300 mg of bilirubin is produced daily in the human body. About 20% of the bilirubin is formed as a result of the breakdown of cytochromes, catalases, peroxidases, and myoglobin. The majority of these breakdown processes occur in the liver.
What happens if you increase bilirubin?
The increase of the total bilirubin over 30-35 mmol/l results in bilirubin deposition in the tissues and yellow pigmentation of the skin, sclera and mucous membranes. This condition is called jaundice (icterus). Upon increase of serum bilirubin between 22-35 mmol/l, some people may notice slightly yellowish sclera pigmentation, ...
What is the color of the gallbladder?
It is a yellow-red pigment and is included in the gallbladder bile. Red blood cells (erythrocytes) live on average about 120 days in the circulation, then break down and the hemoglobin degrades to bilirubin. The increase of the total bilirubin over 30-35 mmol/l results in bilirubin deposition in the tissues and yellow pigmentation of the skin, ...
Where does bilirubin come from?
Approximately 80% of the bilirubin originates from the breakdown of hemoglobin released by the degradation of obsolete erythrocytes in the monocyte-macrophage system. This happens predominantly in the spleen and to a lesser extent in the bone marrow and the liver (Kupffer cells).
Where does bilirubin breakdown occur?
The majority of these breakdown processes occur in the liver. 95% of the unconjugated bilirubin is transported to the liver, associated with blood serum albumin. In the liver, the albumin-bilirubin complex passes into the sinusoidal space, releases the albumin, and the bilirubin molecule is transferred to the hepatocyte.
Where does bilirubin come from?
Approximately 80% of the bilirubin is derived from hemoglobin metabolism . The breakdown of heme molecules in hemoglobin, myoglobin, cytochromes, catalase, tryptophan pyrrolase, and peroxidase results in the production of the catabolic product, bilirubin.
How does bilirubin get converted to hydrophilic form?
Hepatic and renal elimination of bilirubin, at the physiologic level, requires its conversion into the hydrophilic form through the breakdown of hydrogen bonds via glucuronic acid conjugation of the propionic acid side chains of bilirubin.
What is hydrophilic direct bilirubin?
Hydro philic direct bilirubin reacts readily when reagents are added to the blood specimen; likewise, lipophilic indirect bilirubin reacts to the reagents solely following the addition of accelerants like caffeine or methanol. Total bilirubin tallies direct and indirect bilirubin levels. Indirect bilirubin comprises over 90% ...
Where does bilirubin enter the intestine?
With this conversion, the hydrophilic bilirubin glucuronide, or conjugated bilirubin, travels into the bile canaliculus via ATP binding cassette transporter, the multi-drug resistance protein 2 (MRP2), and subsequently, enters the intestine.
Which cells are responsible for sequential degradation?
The primary site of this sequential degradation, reticuloendothelial cells, as well as phagocytic cells such as the Kupffer cells in the liver, contain high concentrations of heme oxygenase. Notably, heme oxygenase is suggested to be the rate-limiting entity in the unconjugated bilirubin production process.
Is bilirubin hydrophobic or hydrophobic?
Bilirubin contains intramolecular hydrogen bonding that buffers its polar hydrophilic groups; the resulting hydrophobic molecule is essentially water-insoluble at physiologic pH. This lipophilic form of bilirubin, also known as unconjugated bilirubin, is responsible for associated toxicities such as Kernicterus.
Is glucuronate conjugated with bilirubin?
Subsequently, unconjugated bilirubin is conjugated with glucuronate to create conjugated bilirubin in the liver. Mononuclear heme oxygenase catalyzes the degradation of heme into biliverdin, which in turn is reduced into bilirubin by biliverdin reductase.
What causes conjugated bili to increase?
Chronic, long-term TPN and Intralipid use—This causes damage to the liver and biliary tree and affects bilirubin excretion
How do you treat unconjugated bili?
Phototherapy—Uses UV light to breakdown unconjugated bili into a water-soluble form that can be excreted
What does it mean when bilirubin is conjugated?
If you’ve got a lot of bilirubin around and it’s mostly conjugated, that means it’s been through the conjugation process in the liver – so there’s something preventing the secretion of bilirubin into the bile (like hepatitis, or biliary obstruction), and the bilirubin is backing up into the blood. Back to our question.
Where does bilirubin go?
Most of this conjugated bilirubin goes into the bile and out into the small intestine.
What is the yellow pigment that causes bruises?
Bilirubin is a breakdown product of heme (which, in turn is part of the hemoglobin molecule that is in red blood cells). It is a yellow pigment that is responsible for the yellow color of bruises, and the yellowish discoloration of jaundice.
Can pancreatic carcinoma cause biliary obstruction?
B. Carcinoma of the head of pancreas – this could also cause biliary obstruction, similar to A. (An important aside: it’s nice when pancreatic carcinomas announce themselves this way, because it may allow for earlier detection of the tumor. Unfortunately, this is uncommon.
What does it mean when your bilirubin is high?
If your bilirubin levels are higher than normal, it’s a sign that either your red blood cells are breaking down at an unusual rate or that your liver isn’t breaking down waste properly and clearing the bilirubin from your blood.
Why is bilirubin high in newborns?
In newborns, high bilirubin levels that don’t level out in a few days to 2 weeks may be a sign of: Blood type incompatibility between mother and child. Lack of oxygen. An inherited infection. A disease affecting the liver.
How to check bilirubin levels?
Your doctor may order a bilirubin test if you: 1 Show signs of jaundice 2 Have anemia, or low red blood cells 3 Might be having a toxic reaction to drugs 4 Have a history of heavy drinking 5 Have been exposed to hepatitis viruses 6 Have cirrhosis
What is the normal bilirubin level for adults?
For adults over 18, normal total bilirubin can be up to 1.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) of blood. For those under 18, the normal level will be will be 1 mg/dl. Normal results for conjugated (direct) bilirubin should be less than 0.3 mg/dl. Men tend to have slightly higher bilirubin levels than women.
Why do my eyes turn yellow?
That’s a disorder where red blood cells are destroyed faster than they’re made. High levels of bilirubin can cause a yellowing of your skin and eyes, a condition doctors call jaundice. High bilirubin levels are common in newborns. Doctors use the age of the newborn and the bilirubin type and levels to determine if treatment is necessary.
How to tell if you have jaundice?
Might be having a toxic reaction to drugs. Have a history of heavy drinking. Have been exposed to hepatitis viruses. Have cirrhosis. You might also have your bilirubin tested if you have symptoms like: Dark urine. Nausea and vomiting.
Why is bilirubin used in poop?
It’s used to help find the cause of health conditions like jaundice, anemia, and liver disease. Bilirubin is an orange-yellow pigment that occurs normally when part of your red blood cells break down. Your liver takes the bilirubin from your blood and changes its chemical make-up so that most of it is passed through your poop as bile. ...
