An abdominal contusion is caused by a direct blow to the abdomen, which results in bruising of the superficial abdominal skin or deeper to the musculature. The signs and symptoms of an abdominal contusion are pain and tightness in the area of the injury.
What causes pain in the abdominal wall?
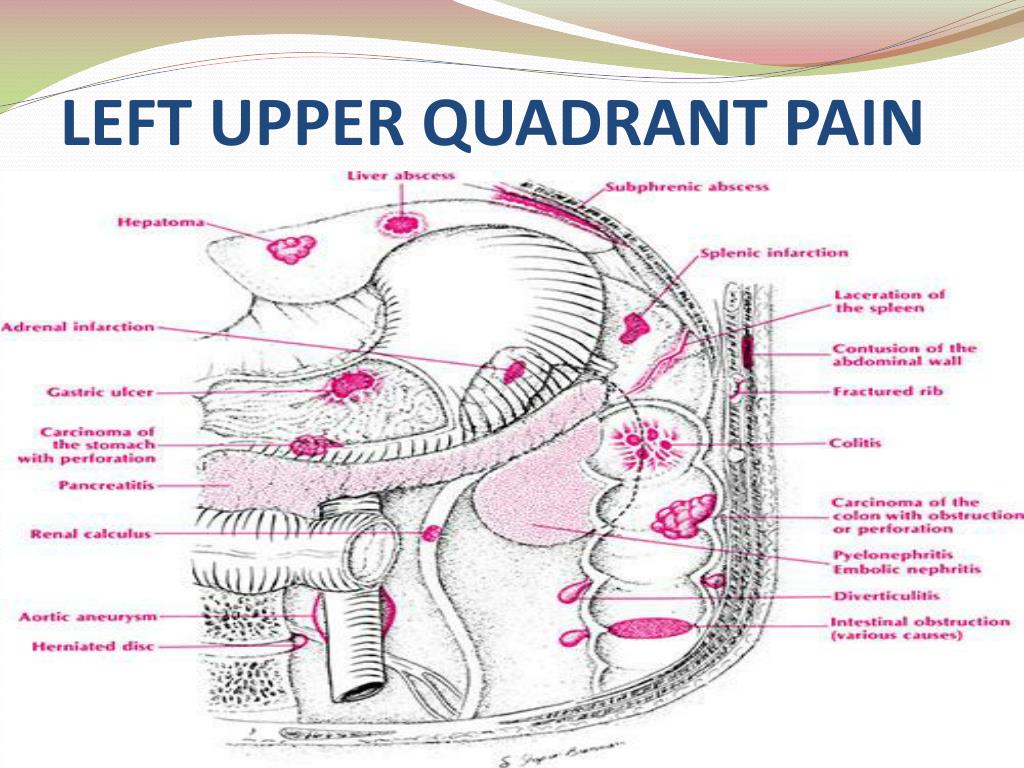
The Abdominal Wall: An Overlooked Source of Pain
- Evaluation. In patients with acute or chronic abdominal pain, a number of clinical findings point to disease inside the abdomen ( Table 1).
- Identifiable Causes. In addition to the familiar inguinal, femoral and umbilical hernias, a number of unusual hernias can occur ( Figure 2).
- Illustrative Case. ...
- Idiopathic Abdominal Wall Pain. ...
How to repair torn muscles in the abdomen?
- wrap an ice pack in a towel or cloth
- apply the pack to the abdomen for 20 minutes
- repeat 2–3 times each day
What does abdominal wall mean?
The abdominal wall surrounds the abdominal cavity, providing it with flexible coverage and protecting the internal organs from damage. It is bounded superiorly by the xiphoid process and costal margins, posteriorly by the vertebral column and inferiorly by the pelvic bones and inguinal ligament.. The abdominal wall can be divided into two sections: anterolateral and posterior abdominal walls.
What causes lower abdominal pain and how to treat it?
Some of the common causes of acute pain in the lower left region of the abdomen are:
- Constipation – the pain may be felt as cramps in the lower left part of the abdomen.
- Diverticulitis – this condition is characterized by the bulging or inflammation of the diverticulum at the end of the colon. ...
- Pseudomembranous colitis – this condition is caused by long-term use of antibiotics that kills the normal flora of the intestine. ...

How long does it take for a abdominal wall contusion to heal?
The majority of patients recover well with no complications as the hematoma is reabsorbed in 2 to 3 months.
What is the treatment for a contusion?
Initial treatment for contusion should include rest, icing the affected area for 20 minutes, and applying a compression wrap to help minimize swelling. If there is an accompanying open wound, keep the area clean and bandaged.
How long does it take for a contusion to resolve?
Bruises usually fade away in about 2 weeks. Over that time, the bruise changes color as the body breaks down and reabsorbs the blood. The color of the bruise can give you an idea how old it is: When a bruise first happens, it's kind of red as the blood appears under the skin.
How do you know if a contusion is serious?
Call your doctor or nurse call line now or seek immediate medical care if:Your pain gets worse.You have new or worse swelling.You have tingling, weakness, or numbness in the area near the contusion.The area near the contusion is cold or pale.
What are 5 symptoms of a contusion?
Contusions on your bonesstiffness or swelling.tenderness.trouble bending or using the affected area.pain that lasts longer than the symptoms of a typical bruise would.
What is the difference between bruise and contusion?
There is no difference between a bruise and a contusion. Contusion is the medical term for bruise.
How do you get a contusion?
Contusions occur when a direct blow or repeated blows by a blunt object strike part of the body, crushing underlying muscle fibers and connective tissue without breaking the skin. A contusion can result from falling or jamming the body against a hard surface.
Can you get a blood clot from a bruise?
Can't bad bruises cause blood clots? The bruise itself won't cause a blood clot. In very rare circumstances, the hit that caused the bruise can. If a deep-seated vein is damaged during the collision, it could lead to a deep-vein clot.
Can a contusion get worse?
Follow-up care. Sometimes a bruise gets worse instead of better. It may become larger and more swollen. This can occur when your body walls off a small pool of blood under the skin (hematoma).
What is a severe contusion?
a deep bruise after an injury. a lump under the skin that is firm to the touch. deep aching after a significant injury, such as a bicycle or car accident, sports injury, or fall.
What is the fastest way to heal a muscle contusion?
Treating a bruised muscleRest. Protect your injury from further damage by stopping unnecessary physical activity.Ice. Apply ice to your injury to reduce pain, swelling, and bleeding. ... Compression. Wrap your injury with a bandage to provide additional support. ... Elevation.
Can a contusion cause a blood clot?
The bruise itself won't cause a blood clot. In very rare circumstances, the hit that caused the bruise can. If a deep-seated vein is damaged during the collision, it could lead to a deep-vein clot. This is called deep-vein thrombosis (DVT).
How long does it take for a bone contusion to heal?
Most bone bruises slowly heal over 4-8 weeks, although this can vary considerably based on the age and health of the athlete, as well as the size and location of the bone contusion. In general, a larger bone bruise may take longer to heal.
What is a deep contusion?
a deep bruise after an injury. a lump under the skin that is firm to the touch. deep aching after a significant injury, such as a bicycle or car accident, sports injury, or fall.
What is abdominal wall injury?
Abdominal wall injuries comprise a set of injuries of the abdominal wall and include different forms of muscle injuries, traumatic hernias and injuries to the subcutaneous tissue. They are often overshadowed by the attention to associated “more severe” abdominal visceral injuries.
What are the complications of abdominal wall injuries?
Complications of abdominal wall injuries differ with the type of injury and include 1: hematoma formation. skin or muscle necrosis. infection. myositis ossificans. incarceration or strangulation (in case of traumatic hernias)
What is a spindle shaped hematoma?
Muscular hematoma (e.g. rectus sheath hematoma) will appear as spindle-shaped or spherical muscular swelling in the affected abdominal muscle. Muscle contusions or muscle strains will typically show fluid-signal along and around the muscle fibers.
What are non-penetrating abdominal injuries?
The most common mechanisms of non-penetrating abdominal wall injuries are direct impact with an elevation in intraabdominal pressure or a shearing injury caused by a collision e.g. in a road traffic accident or during a fall 1. Penetrating injuries involve a piercing or slashing mechanism.
What sports increase the likelihood of sustaining an abdominal wall injury?
Sports or behavioral patterns that increase the likelihood of sustaining an abdominal wall injury include: football (soccer) rugby / American football. martial arts/wrestling.
What is the preferred imaging technique for groin injury?
MRI is considered the modality of choice in the workup and classification of Morel-Lavallée lesions 1 and the preferred imaging technique in the workup of an acute groin injury.
Where do hernias occur in the abdominal wall?
Traumatic abdominal wall hernias usually occur at various weak spots of the abdominal wall most frequent are lumbar hernias affecting the inferior lumbar triangle. Spigelian hernias can also occur in a traumatic event and rarely there are trans-diaphragmatic intercostal hernias. Morel-Lavallée lesions affect mostly the subcutaneous tissue.
What is abdominal wall injury?
Abdominal wall injuries comprise a set of injuries of the abdominal wall and include different forms of muscle injuries, traumatic hernias and injuries to the subcutaneous tissue. They are often overshadowed by the attention to associated “more severe” abdominal visceral injuries.
What are the complications of abdominal wall injuries?
Complications of abdominal wall injuries differ with the type of injury and include 1: hematoma formation. skin or muscle necrosis. infection. myositis ossificans. incarceration or strangulation (in case of traumatic hernias)
What is a spindle shaped hematoma?
Muscular hematoma (e.g. rectus sheath hematoma) will appear as spindle-shaped or spherical muscular swelling in the affected abdominal muscle. Muscle contusions or muscle strains will typically show fluid-signal along and around the muscle fibers.
What are non-penetrating abdominal injuries?
The most common mechanisms of non-penetrating abdominal wall injuries are direct impact with an elevation in intraabdominal pressure or a shearing injury caused by a collision e.g. in a road traffic accident or during a fall 1. Penetrating injuries involve a piercing or slashing mechanism.
What sports increase the likelihood of sustaining an abdominal wall injury?
Sports or behavioral patterns that increase the likelihood of sustaining an abdominal wall injury include: football (soccer) rugby / American football. martial arts/wrestling.
What is the preferred imaging technique for groin injury?
MRI is considered the modality of choice in the workup and classification of Morel-Lavallée lesions 1 and the preferred imaging technique in the workup of an acute groin injury.
Where do hernias occur in the abdominal wall?
Traumatic abdominal wall hernias usually occur at various weak spots of the abdominal wall most frequent are lumbar hernias affecting the inferior lumbar triangle. Spigelian hernias can also occur in a traumatic event and rarely there are trans-diaphragmatic intercostal hernias. Morel-Lavallée lesions affect mostly the subcutaneous tissue.
What is the abdominal wall?
The abdominal wall is divided into anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments ( 14, 15 ). From superficial to deep, the anterior abdominal compartment is composed of skin, superficial subcutaneous fat (also called Camper fascia), deep subcutaneous membranous tissue (also called Scarpa fascia), layers of muscles separated by their investing fascia, a thin layer of extraperitoneal fat, and, finally, the parietal peritoneum ( 15 ). The rectus abdominis muscles are two parallel and longitudinally oriented muscles that make up the anterior compartment, which are located just to the right and left of midline, extending from the anteroinferior costal cartilages to the pubis ( 15 ). The superior and inferior epigastric vessels run along the posterior border of the rectus abdominis muscles; the superior epigastric artery arises as the terminal branch of the internal thoracic artery, and the inferior epigastric artery arises from the external iliac artery ( 16 ).
Why are abdominal walls overlooked?
These injuries are often overlooked either because of the lack of associated findings at physical examination or because of the association of these injuries with other more-distracting intra-abdominal injuries. This fact underscores the need for radiologists to maintain a high index of suspicion for abdominal wall injuries and to actively search for these injuries in patients undergoing cross-sectional imaging after blunt trauma. If an abdominal wall injury is observed, careful review of the vasculature and intra-abdominal organs should be performed to look for associated injuries.
What are the three lateral abdominal muscles?
The lateral compartment is made up of three flat muscles: the external oblique, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis muscles (from superficial to deep). The rectus abdominis muscles are separated from the lateral abdominal musculature by the semilunar line, best known as the site of the spigelian hernia ( 17 – 19 ). The rectus muscles are enclosed by a fascial “sheath,” which arises from the aponeuroses of the three lateral abdominal muscles (made up of the external and internal oblique and transversus abdominis muscles ). Rectus sheath anatomy undergoes a change at the arcuate line of Douglas, a horizontal or transverse line that lies just below the umbilicus. Above the arcuate line, the rectus abdominis muscle is fully enclosed both anteriorly and posteriorly by the fascial “sheath”; but below the arcuate line, the aponeuroses join to form the sheath only anteriorly, with just a thin posterior lining made up of the transversalis fascia and peritoneum ( Fig 1) ( 20 ).
What injuries should be considered in patients with abdominal pain after nonpenetrating trauma?
Groin injuries, such as athletic pubalgia, and inferior costochondral injuries should also be considered in patients with abdominal pain after nonpenetrating trauma, because these conditions may manifest with referred abdominal pain and are often included within the field of view at cross-sectional abdominal imaging.
Where do abdominal hematomas occur?
Abdominal wall hematomas most commonly occur within the rectus muscle (also known as RSH s) and less commonly involve the lateral and posterior abdominal wall ( 25, 26 ). This discussion will focus primarily on RSH, with brief comments on the rest of the abdominal wall.
Where is Brigham and Women's Hospital?
From the Departments of Radiology (S.A.M., A.D.S., B.K.) and Trauma, Burns, and Critical Care (R.A., J.D.G.), Brigham and Women’s Hospital, 75 Francis St, Mellins Library, Boston, MA 02115; and Shields Radiology, Brockton, Mass (K.P.).
Can a twisting injury occur during exercise?
Twisting injury can occur in athletes or even during regular exercise, especially in patients with predisposing factors such as anticoagulant therapy or coagulopathy ( 24) ( Figs 3 – 5 ). Figures 3. Rectus abdominis strain and tear in a 17-year-old girl after yoga.
What is the term for a bruise that hits the skull?
As the brain is jolted from the injury, it can hit the skull and cause another bruise, called the contrecoup.
What is bruising in the back?
Bruising typically occurs when an area of the back is compressed due to the accident or injury.
What causes a bruise in the leg?
Bruising in the legs is very common in people who play sports. Direct blows or falls typically cause the injury. When the injury occurs, the muscles of your leg become compressed and are crushed in an unnatural way.
What is a bruise on the skin called?
A bruise, also called a contusion, occurs when an injury breaks blood vessels under your skin. This causes blood to leak into the tissue beneath your skin, resulting in a visible blue-black spot.
What does it mean when you have a hematoma?
hematoma, a pool of blood that collects around the injured site. blood in urine (kidney bruising) Seek immediate medical attention if you observe any of the following symptoms. They may indicate more severe internal bleeding or shock: symptoms that don’t get better or get worse. fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher.
Where does bruising occur in the legs?
Bruising in the legs often occurs in the quadriceps muscle at the front of your thigh, an area that can be prone to direct blows.
Where does internal bruising occur?
Internal bruising can occur in the muscles of the legs and back. It can also occur in internal organs, such as the liver and spleen. Read on to find out more about the symptoms, causes, and treatments.
Epidemiology
Clinical Presentation
- The main symptom will be abdominal pain and history will often reveal the mechanism of injury frequently a blunt and less often a penetrating abdominal trauma. The physical examination might reveal skin discolouration or ecchymosis in case of blunt trauma or a laceration, stab or gunshot wound in case of penetrating trauma. Other findings include a soft tissue mass or bulge. Typical …
Pathology
- The most common mechanisms of non-penetrating abdominal wall injuries are direct impact with an elevation in intraabdominal pressure or a shearing injury caused by a collision e.g. in a road traffic accident or during a fall 1. Penetrating injuries involve a piercing or slashing mechanism. Abdominal wall injuries can be classified based on type and location into the following 1: 1. non-…
Radiographic Features
- Abdominal wall injuries can be depicted and assessed with ultrasound, CT and MRI and their appearance will vary with the type of injury. Acute injuries will be probably most frequently evaluated in CT in an emergency after blunt abdominal injury. Muscular hematoma (e.g. rectus sheath hematoma) will appear as spindle-shaped or spherical muscular swelling in the affected …
Radiology Report
- The radiological report should include a description of the following: 1. type of the abdominal wall injury 2. location and extent of the lesion 3. signs of active bleeding 4. associated injuries (especially vascular, visceral injuries and associated fractures)
Treatment and Prognosis
- Treatment will depend on the type and extent of the injury. Most muscle contusions, hematoma or muscle strains can be managed conservatively with rest and pain control. In some larger hematomas, patients might need a blood transfusion because of blood loss. A smaller percentage of rectus sheath hematomas with active bleeding might require surgery or endovascular treatme…
Differential Diagnosis
- The differential diagnosis of abdominal wall injuries includes the following: 1. costochondral injuries 2. chest wall injury 3. osteitis pubis
See Also