
In nature, convection currents formed from air raising above sunlight-warmed land or water are a major feature of all weather systems. Convection
Convection
Convection is the concerted, collective movement of groups or aggregates of molecules within fluids (e.g., liquids, gases) and rheids, through advection or through diffusion or as a combination of both of them. Convection of mass cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor signifi…
What are 5 facts about convection currents?
What are 5 facts about convection currents? Vertical circulation within a fluid that results from density differences caused by temperature variations. In meteorology, the process in which air, having been warmed close to the ground, rises. Within the Earth, the radiogenic heat release results in convective motions causing tectonic plate ...
What are some examples of convection currents?
Everyday Examples of Convection
- boiling water - When water boils, the heat passes from the burner into the pot, heating the water at the bottom. ...
- radiator - A radiator puts warm air out at the top and draws in cooler air at the bottom.
- steaming cup of hot tea - The steam you see when drinking a cup of hot tea indicates that heat is being transferred into the air.
What are convection currents associated with electricity?
Convection currents form because a heated fluid expands, becoming less dense. The less-dense heated fluid rises away from the heat source. As it rises, it pulls cooler fluid down to replace it. This fluid in turn is heated, rises and pulls down more cool fluid.
What are convection currents on Earth?
In the case of the Earth, convection currents refer to the motion of molten rock in the mantle as radioactive decay heats up magma, causing it to rise and driving the global-scale flow of magma. The Earth is made out of a number of different layers, and though we live on the crust of the Earth there are miles of Earth beneath our feet.

What is a convection current climate?
Updated April 23, 2018. By Herb Kirchhoff. Convection currents transfer heat from one place to another by mass motion of a fluid such as water, air or molten rock. The heat transfer function of convection currents drives the earth's ocean currents, atmospheric weather and geology.
What is a convection current short definition?
Definition of convection current 1a : a stream of fluid propelled by thermal convection. b : thermally produced vertical air flow. 2 : a surface charge of electricity on a moving body — compare convection sense 3c.
How does convection happen in weather?
Convection – When warm, moist air near the surface rises to be above the heavier cool, dry air this is a form of heat transfer or convection. The rising motion typically cools the air. As the air cools, it reaches the dewpoint and all of the moisture in the air condenses– forming clouds.
Why is convection important in weather?
Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world.
Why do convection currents lead to rain?
Convectional rainfall occurs when surface of the earth is heated up by the sun. The warm surface also heats up the air. As air rises it cools down and begins to condensate. Further rising and cooling causes a large amount of condensation to occur and rain is formed.
What is a convection current example?
A simple example of convection currents is warm air rising toward the ceiling or attic of a house. Warm air is less dense than cool air, so it rises. Wind is an example of a convection current. Sunlight or reflected light radiates heat, setting up a temperature difference that causes the air to move.
How does convection affect climate?
In meteorology, convection is often associated with rising air and clouds, and at times, thunderstorms. Air that is rising cools as it reaches lower pressures, and may reach the point where water vapor in the air condenses and forms clouds. These rising columns of air are called "thermals".
Do convection currents cause thunderstorms?
The up and down motions associated with convection help fuel monstrous thunderstorms. A thunderstorm feeds off of warm air underneath it. Warm air near the ground rises because it's less dense. When the air reaches the base of the cloud, water vapor in the air condenses and builds onto the cloud.
Is wind an example of convection?
Convection currents are present in the air– A good example of convection current is the warm air that rises towards the ceiling in your house. The process happens as the warm air is said to be less dense than that of the colder air. Another good example of convection current is wind.
What is convection definition and example?
Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of heated parts of liquids and gases. Convection happens in liquids and gases because, unlike in a solid, molecules are able to freely move. For example, the air molecules in your living room continually move around, all moving at about the same speed.
Are clouds an example of convection?
Convective Clouds Cumulus, towering cumulus, Cumulonimbus, and Altocumulus Castellanus clouds are all visible forms of convection. They are also all examples of "moist" convection (convection where the excess water vapor in the rising air condenses to form a cloud).
What happens to cold air in convection?
In this section you will investigate the effects of convection in a house. Hot air rises, because it's less dense than cold air. Warm air in a room quickly rises upward, and cold air sinks downward, even if the tempera- ture differences are quite small.
What is convection class 7th?
Convection: The process of heat transfer from one part of a fluid to another part by the actual movement of the particles of the fluid is called convection. Liquid and gases are heated by the process of convection.
What are conduction currents?
Definition of conduction current : a movement of electricity in an electric conductor — compare displacement current.
What is a sentence for convection?
1. These fires create convection funnels, and throw a lot of particles into the upper atmosphere. 2. In convection, hot currents flow upwards.
Which of these best describes convection currents?
The best description of a convection current is that e. it is the process in which warm material expands and rises while cool material contracts and falls.. Convection current in the atmosphere causes warm air to rise up from the surface.
What is convective precipitation?
In contrast to non-convective precipitation (which results when air is lifted by force), convective precipitation requires instability, or the ability for air to continue rising on its own.
What happens to the air when convection continues?
As convection continues, the air cools as it reaches lower air pressures and may reach the point where the water vapor within it condenses and forms (you guessed it) a cumulus cloud at its top! If the air contains a lot of moisture and is quite hot, it will continue to grow vertically and will become a towering cumulus or a cumulonimbus.
When Does Convection Stop?
Only when the pocket of warm, rising air has cooled to the same temperature of the surrounding air will it stop rising.
Why is convection active in summer?
The stronger the surface heating, the stronger and higher up into the atmosphere the convection extends. (This is why convection is especially active on hot summer afternoons.) After this main process of convection is complete, there are a number of scenarios that could happen, each which forms a different weather type.
What are some examples of convective winds?
As the heated air rises, air from elsewhere flows in to replace it. We feel this balancing movement of air as wind. Examples of convective winds include foehns and sea breezes .
What are the steps of convection?
Steps to the Process of Convection. The process of convection begins at sunrise and continues as follows: The sun's radiation strikes the ground, heating it. As the ground's temperature warms, it heats the layer of air directly above it through conduction (the transfer of heat from one substance to another). Because barren surfaces like sand, ...
What is the average temperature of the Earth without convection?
Without it, it has been calculated that the average surface air temperature on earth would be somewhere around 125° F rather than the current liveable 59° F.
How does convection produce electricity?
Convection is often associated with lightning production! As these air particles rise they create winds moving upward. Those winds lift the tiny frozen droplets of water as gravity tries to bring them crashing down to the earth’s surface. The particles moving past each other generate electricity and when the charge gets strong enough– a bolt of lightning!
What type of convection is not associated with storms?
Dry Convection – The type of convection not associated with storms is called dry convection. This occurs when warm air at the surface rises to be above the cooler air overhead. Because there is no moisture, this typically doesn’t have cloud cover associated with it.
What is the process of heat transfer?
Convection – Heat transfer through the movement of a liquid or gas. That is, the liquid or gas of a certain temperature moves to a new area, thus changing the temperature of the new area. This is the heat transfer we are most interested in.
Why does a storm happen horizontally?
This happens horizontally due to heating differentials at the surface as well. But lets just focus on those storms.
Why does the sun heat us from so far away?
Radiation – (Not like the nuclear stuff we are all afraid of) But instead, the sun heating us from so far away because it’s that hot! Or like the radiator in a room that heats up and therefore heats up the whole room.
Does convection depend on heat transfer?
Before we get into the meat and potatoes of this, let me just reiterate that convection greatly depends on the other two types of heat transfer in order to occur .
Is convection a thunderstorm?
In a meteorologist’s vocabulary, convection and thunderstorm are practically interchangeable. The upward vertical motion of the warm, moist air is what fuels thunderstorms and on a much larger scale– even hurricanes!
Why are convection currents occurring in the ocean?
These are caused due to the difference in the water density and the temperature occurring in different parts of the ocean. Convection currents are present in the air – A good example of convection current is the warm air that rises towards ...
What are some examples of convection currents?
Convection currents are present in the air – A good example of convection current is the warm air that rises towards the ceiling in your house. The process happens as the warm air is said to be less dense than that of the colder air. Another good example of convection current is wind. The wind is mainly caused when the reflected radiation ...
What is the process of heating up liquids called?
Hence, Convection Current is defined as “a process of continuous heating up of liquids or gases by the process called as Convection. “
What is the process that involves the movement of energy from one place to another?
Convection Currents . A convection current is a process that involves the movement of energy from one place to another. It is also called convection heat transfer. What is the reason that makes you feel hotter when placing hands above a campfire or when sitting next to it?
How does heat transfer?
The heat energy can be transferred by the process of convection by the difference occurring in temperature between the two parts of the fluid. Due to this temperature difference, the hot fluids tend to rise, whereas cold fluids tend to sink. This creates a current within the fluid called Convection current. The mantle within the earth’s surface ...
What is the process of convection?
Convection is one among the forms of heat transfers , of which the other two are radiation and conduction. Convection process only happens in the fluids i.e. in liquids and gases. This happens due to the reason that molecules within liquids or gases are free to move.
Where does the heat come from?
The heat comes from various kinds of heat transfers such as radiation. But while placing your hand above a campfire, a lot of convection currents rises towards you. Changes in the weather- The cool air and breeze occurring near to a beach are all the effects of convection currents.
How does convective current work?
Often the areas of heating and cooling are fixed, and allow convective cycles or currents to become established. For example, a saucepan of water over a flame may develop convective currents as the water is heated from below, rises to the surface, and cools. Once cooled enough, the water then sinks back to the bottom of the saucepan where the cycle is repeated, and the convective overturning continues.
How does convection work?
Convection works by areas of a liquid or gas heating or cooling greater than their surroundings, causing differences in temperature. These temperature differences then cause the areas to move as the hotter, less dense areas rise, and the cooler, more dense areas sink.
How is convection different from conduction?
Conduction however, doesn’t necessarily involve particles moving. Instead energy is passed from one particle to another upon contact, transferring heat. As a result, conduction in liquids and gases is a much slower process than convection, as particles are free to move and direct contact is reduced. However, conduction is much more effective in solids than convection, as the particles are densely packed, continuously touching one another to allow an efficient transfer of heat. Additionally, in solids particles fixed and unable to move, stopping the transfer of energy via convection.
How does convection affect ocean currents?
However, these currents are affected by convection due to the influence of ocean temperature and salinity (concentration of salt within the water) on density.
Why is convection important?
Convection is a vital process which helps to redistribute energy away from hotter areas to cooler areas of the Earth, aiding temperature circulation and reducing sharp temperature differences . Without convection simple tasks such as boiling water in a kettle would be much slower as only the water directly in contact with the heat ring at the bottom of the kettle would be able to be heated, with the water at the top staying cool.
What happens to the air above the Earth's surface when the sun heats up?
For example, as the sun heats the Earth’s surface, the air above it heats up and rises. If conditions allow, this air can continue to rise, cooling as it does so, forming Cumulus clouds. Stronger convection can result in much larger clouds developing as the air rises higher before it is cooled, sometimes producing Cumulonimbus clouds ...
Which is more effective, conduction or convection?
However, conduction is much more effective in solids than convection, as the particles are densely packed, continuously touching one another to allow an efficient transfer of heat. Additionally, in solids particles fixed and unable to move, stopping the transfer of energy via convection.
What is dry convection?
Convection which occurs without cloud formation is called dry convection, while the visible convection processes referred to above are forms of moist convection. You can either type in the word you are looking for in the box below or browse by letter.
What is the term for the movement of heat and moisture in the atmosphere?
Convection. Generally, transport of heat and moisture by the movement of a fluid. In meteorology, the term is used specifically to describe vertical transport of heat and moisture in the atmosphere, especially by updrafts and downdrafts in an unstable atmosphere. The terms "convection" and "thunderstorms" often are used interchangeably, ...
Is a thunderstorm a convection?
The terms "convection" and "thunderstorms" often are used interchangeably, although thunderstorms are only one form of convection. Cbs, towering cumulus clouds, and ACCAS clouds all are visible forms of convection. However, convection is not always made visible by clouds.
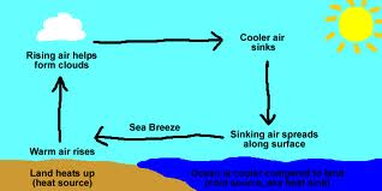
from Your Kitchen to The Air
Steps to The Process of Convection
Convective Clouds
Convective Precipitation
Convective Winds
Convection Keeps Us Surface Dwellers Cool
- Besides creating the above-mentioned weather events, convection serves another purpose -- it removes excess heat from the earth's surface. Without it, it has been calculated that the average surface air temperature on earth would be somewhere around 125° F rather than the current liveable 59° F.
When Does Convection stop?