
What is a covered entity? A covered entity is a healthcare provider, health plan, payer, clearing house or any other entity that processes health data electronically. Because of the kind of health information it processes, and the way it is processed, a covered entity must comply with HIPAA
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 was enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed by President Bill Clinton in 1996. It was created primarily to modernize the flow of healthcare information, stipulate how Personally Identifiable Information maintained by the healthcare and healthcare insurance industries should be protected from fraud and theft, and address lim…
What determines a covered entity under HIPAA?
HIPAA regulation defines a covered entity as healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses involved in the transmission of protected health information (PHI). This transmission can take place for the purpose of payment, treatment, operations, billing, or insurance coverage. Covered entities can include organizations ...
What does a covered entity include?
Covered entities under HIPAA include health plans, healthcare providers, and healthcare clearinghouses. Health plans include health insurance companies, health maintenance organizations, government programs that pay for healthcare (Medicare for example), and military and veterans’ health programs.
Who should complaints be directed to within the Covered Entity?
Who should HIPAA complaints be directed to within the covered entity? Any healthcare employee who believes they have witnessed a HIPAA violation should report the incident internally. Typically, the person to report the violation to is your Privacy Officer, if your organization has appointed one. Reporting Potential HIPAA Violations Internally
What is a covered entity in the complaint process?
A covered entity should assess potential HIPAA violations and make a decision whether HIPAA Rules were violated, and determine whether the incident needs to be reported to the Department of Health and Human Services’ Office for Civil Rights (OCR) as per the HIPAA Breach Notification Rule requirements. Not every breach is reportable.
What are examples of a covered entity?
A Covered Entity is one of the following:Doctors.Clinics.Psychologists.Dentists.Chiropractors.Nursing Homes.Pharmacies.
What is a covered entity required to do?
A business associate can be an individual or company that provides services to a HIPAA-covered entity which requires them to have access to, store, use, or transmit protected health information.
Who would not be considered a covered entity under HIPAA?
Are there exceptions to the definition of a HIPAA covered entity? Yes. HIPAA does not apply to employer-administered health plans with fewer than 50 participants, to some government-funded programs (i.e., the food stamp program), and to educational institutions that provide healthcare services solely for students.
What is covered under HIPAA?
Health information such as diagnoses, treatment information, medical test results, and prescription information are considered protected health information under HIPAA, as are national identification numbers and demographic information such as birth dates, gender, ethnicity, and contact and emergency contact ...
What three 3 entities are covered under HIPAA?
HIPAA-covered entities include health plans, clearinghouses, and certain health care providers as follows:Health Plans.Clearinghouses.Providers.About Business Associates.
Is an employer a covered entity under HIPAA?
Employers may not be aware they may be considered covered entities under HIPAA. Most employers that provide self-funded or self-administered health insurance benefits to their employees are covered entities and must comply with HIPAA privacy rules.
What is not covered entity?
Non-covered entities are not subject to HIPAA regulations. Examples include: Health social media apps. Wearables such as FitBit.
What is the difference between a business associate and a covered entity?
What Is a “Business Associate?” A “business associate” is a person or entity that performs certain functions or activities that involve the use or disclosure of protected health informationprotected health informationPHI stands for Protected Health Information. The HIPAA Privacy Rule provides federal protections for personal health information held by covered entities and gives patients an array of rights with respect to that information.https://www.hhs.gov › answers › hipaa › what-is-phiWhat is PHI? | HHS.gov on behalf of, or provides services to, a covered entity. A member of the covered entity's workforce is not a business associate.
Who are exempt from the HIPAA security Rule?
The HIPAA Exemption applies to use of identifiable health information when such use is regulated for any of three purposes under HIPAA: “research”; “health care operations”; or “public health activities and purposes.” Given that the Common Rule applies only to “research,” and that the HIPAA definition of “research” is ...
What is the most common HIPAA violation?
Failing to Secure and Encrypt Data Perhaps the most common of all HIPAA violations is the failure to properly secure and encrypt data. In part, this is because there are so many different ways for this to happen.
What is the difference between Hippa and HIPAA?
HIPAA is the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. HIPPA is simply a typo. Probably in part because English would typically put two Ps together in the middle of a word (think oppose or appear), HIPAA is often wrongly spelled as HIPPA.
Does HIPAA apply to everyone?
In this respect, HIPAA applies to the majority of workers, most health insurance providers, and employers who sponsor or co-sponsor employee health insurance plans. However, HIPAA consists of four further titles covering topics from medical liability reform to taxes on expatriates who give up U.S. citizenship.
Which of the following must a covered entity or business associate do before sharing PHI?
Before the covered entity discloses the PHI to the business associate, the covered entity must obtain satisfactory assurances, generally in the form of a contract, that the business associate will appropriately safeguard the information.
What should you do as a covered entity to protect PHI?
A covered entity must implement hardware, software, and/or procedural mechanisms to record and examine access and other activity in information systems that contain or use e-PHI. Integrity Controls. A covered entity must implement policies and procedures to ensure that e-PHI is not improperly altered or destroyed.
What is covered entity quizlet?
The covered entities (CEs) - health care organization that are required by law to obey HIPAA regulations. - organization that electronically transmit any information that is protected under HIPAA. these include- health plans, clearing house, and health care provider.
Does a covered entity must have an established complaint process?
A covered entity (CE) must have an established complaint process. The e-Government Act promotes the use of electronic government services by the public and improves the use of information technology in the government.
What are Healthcare Providers?
Healthcare providers are exactly who you think they are: they are the doctors, clinics, medical practices, dentists, hospitals, nursing homes, and pharmacies that provide healthcare services to their communities.
What are healthcare plans as defined by HIPAA?
Healthcare plans are the health insurance companies, HMOs, company healthcare plans, Medicare, and Medicaid. Additionally, employers and schools that handle PHI to enroll their employees and students fall under the definition of a health plan.
What is a healthcare clearinghouse?
Healthcare Clearinghouses are a little tricky. They’re defined as organizations that process nonstandard health information in order to ensure that it conforms to data standards on behalf of other organizations.
What about Business Associates?
A Business Associate is a person or organization that performs certain functions for a covered entity that involves the usage or exposure to Protected Health information. In order to protect both parties in the event of a breach, Business Associates are required to adhere to HIPAA and sign a Business Associate Agreement.
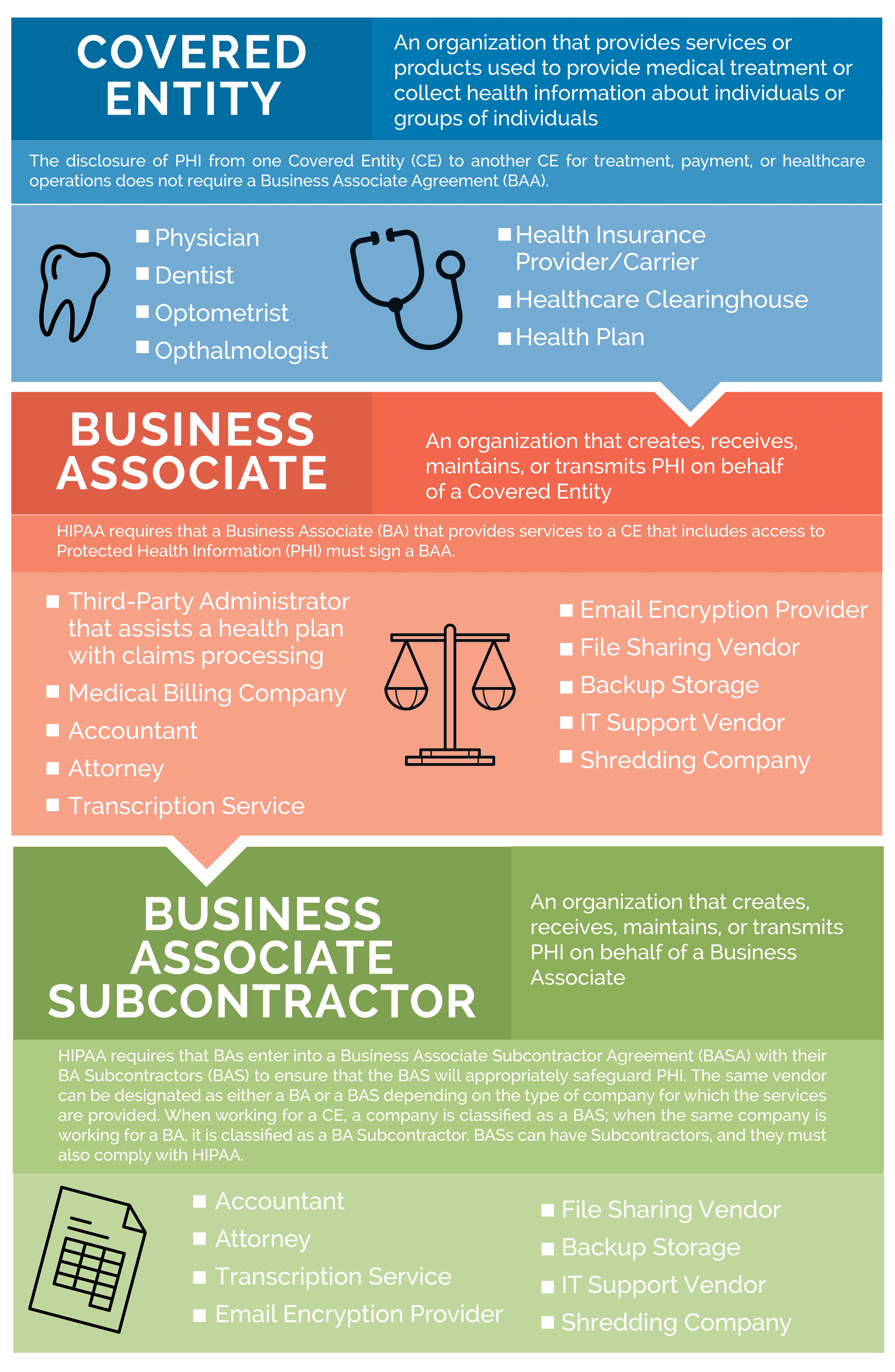
What is a Covered Entity?
A covered entity is any provider of medical or other health services or people that have or handle PHI (protected health information). Covered entities include the following:
What are Some Examples of Covered Entities?
The list of covered entities is quite substantial and includes the following:
What is Required of a Covered Entity?
A covered entity is required to comply with all of HIPAA's regulations. These would include the following:
Covered Entities Under HIPAA
Covered entities under HIPAA are individuals or entities that transmit protected health information for transactions for which the Department of Health and Human Services has adopted standards (see 45 CFR 160.103).
What is a Business Associate?
A business associate can be an individual or company that provides services to a HIPAA-covered entity which requires them to have access to, store, use, or transmit protected health information. The list of business associates is long, and the range of companies included under the definition of business associate is diverse.
Penalties for Noncompliance with HIPAA Rules
Covered entities under HIPAA, and business associate that have signed a BAA with a covered entity, must comply with HIPAA Rules. The failure to comply with any aspect of HIPAA can result in financial penalties. The maximum penalty for a HIPAA violation is $50,000 per incident, up to a maximum of $1.5 million, per violation category, per year.
