
What is a Cross Collateralization
Cross-collateralization
Cross-collateralization is a term used when the collateral for one loan is also used as collateral for another loan. If a person has borrowed from the same bank a home loan secured by the house, a car loan secured by the car, and so on, these assets can be used as cross-collaterals for all the loans.
Cross-collateralization
Cross-collateralization is a term used when the collateral for one loan is also used as collateral for another loan. If a person has borrowed from the same bank a home loan secured by the house, a car loan secured by the car, and so on, these assets can be used as cross-collaterals for all the loans.
What is a collateralization agreement?
A collateralized loan agreement allows a lender to take ownership of the property that was used as collateral and sell it to recover at least a portion of what the borrower was loaned.
Why would cross-collateralization occur?
Cross-collateralization in real estate can occur in two ways: When a borrower uses a non-real estate asset to secure a real estate loan, or when a borrower uses real estate to secure a loan.
How do I get out of cross-collateralization?
If you already have a cross collateralized loan, it's still not too difficult to get out of it. By taking both securities to a new lender at the same time, the original bank cannot refuse your request so long as both loan accounts are paid out.
How do I know if my loan is cross-collateralized?
Cross collateralization also occurs if different types of financing are secured with the same asset. If you're paying off a car loan, the car becomes collateral for this loan. If you use the car as collateral for another type of financing, like a credit card, this is cross-collateralization.
Is cross-collateralization good?
Cross-collateralisation may be a good option in order to score a sharper owner-occupied rate and avoid having to put up your own funds to buy an investment property. At this LVR, it should also be possible to unlock or decouple your properties if you needed to sell your properties.
What happens if you don't pay back a loan that is collateralized?
In the case of a collateral loan, if you don't make your minimum monthly payments on time, the lender may end up repossessing the asset that you used to secure the loan as part of the loan terms, whether that's your house, your car or your cash.
How does a cross collateral mortgage loan work?
Cross collateralization involves using an asset that's already collateral for one loan as collateral for a second loan. The loans can be of the same type, as in a second mortgage, but cross collateralization also includes using an asset, such as a vehicle, to secure another sort of financing, such as a credit card.
Which type of risk does collateralization reduce?
Key Takeaways. Collateralization provides a lender with security against default on a loan. Because it greatly reduces the lender's risk, the interest rates on collateralized loans are substantially lower.
What is the point of a collateralized loan?
A collateralized or securities-based loan allows you to utilize securities, cash, and other assets in brokerage accounts as collateral to obtain variable or fixed-rate loans for almost any purpose.
What are the two most common types of collateralized loans?
Mortgages and car loans are two types of collateralized loans. Other personal assets, such as a savings or investment account, can be used to secure a collateralized personal loan.
What does it mean to be 100% collateralized?
100% Collateralization Level means the pledge and delivery to the Board of Collateral equal to One Hundred Percent (100%) of a Depository's Public Funds on Deposit.
What interest rate can you get on a collateralized loan?
If you have good credit, you can expect rates between 3% and 6%. However, if you have poor credit, you may have rates as high as 36%. Repayment terms depend on the collateral backing your loan.
What are the reasons for taking collateral and what are the types of collateral?
Collateral is an item of value pledged to secure a loan. Collateral reduces the risk for lenders. If a borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can seize the collateral and sell it to recoup its losses. Mortgages and car loans are two types of collateralized loans.
What are some reasons why anyone will use securities as collateral?
Borrowers benefit from easy access to capital, lower interest rates, and greater repayment flexibility and also avoid having to sell their securities.
What is the point of a collateralized loan?
A collateralized or securities-based loan allows you to utilize securities, cash, and other assets in brokerage accounts as collateral to obtain variable or fixed-rate loans for almost any purpose.
Why are crypto loans Overcollateralized?
In fact, many platforms ask that you overcollateralize, which means put up more value than you want to borrow. This is because crypto loans are permissionless, which means you usually don't need to pass know-your-customer (KYC) verifications to take out a loan.
Is Cross-Collateralization Legal?
Cross collateralization is legal and fairly common, but a lender is required to inform you that cross-collateralization is occurring.
What happens if you default on a mortgage?
If you have a mortgage, your house is the collateral—so if you default on your mortgage, the lender then can collect the collateral and repossess your house.
What are the two types of loans?
There are 2 main types of loans: secured loans and unsecured loans. These loans differ in regard to collateral requirements. Collateral is an asset that a borrower offers up as a way to guarantee the amount of a loan. Common forms of collateral include cash deposits, real estate, or vehicles.
How to untangle yourself from a bad cross collateralization situation?
The best way to untangle yourself from a bad cross-collateralization situation is to contact the lender and attempt to renegotiate your loan. You might, for example, be able to secure the remaining debt with other collateral, although the repayment terms might be worse.
What is cross collateralization?
Cross collateralization refers to a situation where multiple loans are secured with the same asset.
Do secured loans require collateral?
Secured loans require collateral, while unsecured loans do not . If you default on secured loans, the lender can seize the collateral as repayment for the loan amount. Lenders of unsecured loans, like credit cards, have no such recourse, but this usually causes the repayment terms of unsecured loans to be less favorable for the borrower.
Do small business owners need to offer assets?
As a small business owner, you’re probably familiar with at least a few of the many loan products available. Many lenders require you to offer an asset to secure a debt. As time goes by, you might find yourself securing multiple loans with the same asset—a process called cross-collateralization.
What happens if you default on a cross collateralized asset?
If you default on an asset that is cross-collateralized, the first position lender receives payment first, followed by the lenders in subsequent positions. Get Home Mortgage Loan Offers Customized for You Today. Get Started.
What happens if a borrower defaults on a loan secured by an asset that is cross-collateral?
If a borrower defaults on a loan secured by an asset that is cross-collateralized, they could lose the asset even if they’re current on the payments for that asset. Borrowers involved in commercial real estatetransactions and credit union customers are most likely to be impacted by cross-collateralization.
What is cross default clause?
Cross-defaultclauses also appear in some loan agreements. They stipulate that borrowers are automatically in default on all loans with a lender if they default on just one. This permits the lender to use assets from one loan to cover the default of another. Credit unions and cross-collateralization.
What is dragnet clause?
The properties and land collectively secure a single loan. Dragnet clausesapply to borrowers with multiple loans at the same institution. A separate asset may secure each loan, but a dragnet clause stipulates that any asset used to secure a debt can be used as collateral for any other debt with the same creditor.
What is blanket loan?
Blanket loans. Taking out a single loan to cover multiple transactions is a form of cross-securitization. Real estate transactions. Borrowers can put up a paid-for property or one with equity as collateral to increase their buying power.
What is a second mortgage?
Second mortgagesare a form of cross-collateralization, as one asset serves as security for two loans. Credit union transactions. Some credit unions stipulate that any asset that secures a loan also guarantees all loans with the same institution. Blanket loans.
What is mortgage cross collateralization?
Mortgage cross-collateralization is when a property is used to secure the debt for more than one loan. Learn how it works, the risks and when to use it. Mortgage cross-collateralization is when a property is used to secure the debt for more than one loan. Learn how it works, the risks and when to use it. You are using an outdatedbrowser.
Cross Collateralization - Explained
If you still have questions or prefer to get help directly from an agent, please submit a request.
What is Cross Collateralization?
Cross-collateralization refers to the act of utilizing an asset as collateral in a loan, and that asset is currently used as collateral for another loan.
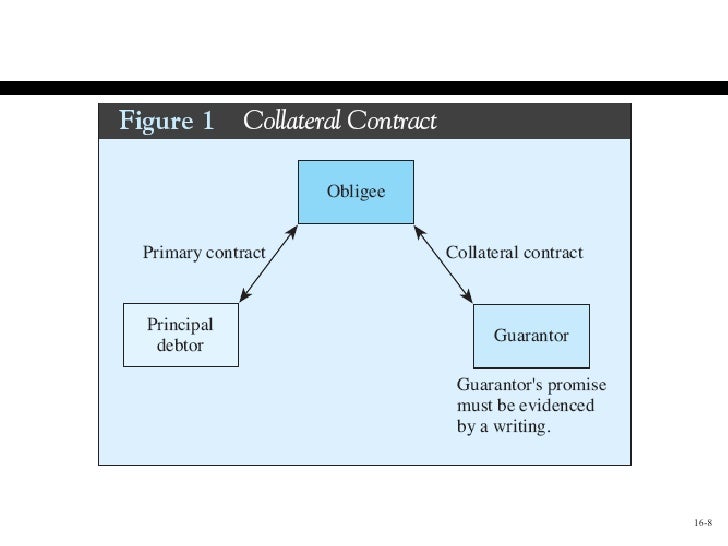
How Cross Collateralization Works
- Cross collateralization is the process of using an asset that is already being pledged as collateral to secure another loan. In their simplest form, cross-collateral loans involve using an asset to secure one loan while simultaneously securing another loan as well. Cross collateralization can be used against different types of loans, including, but...
Benefits and Drawbacks of Cross Collateralization
- Cross collateralization offers several benefits, including: 1. Utilizing equity of existing assets to finance new ventures 2. A source of funding in which new capital does not need to be raised 3. Provides financing for those who with potentially poor credit quality by providing extra assurance to the lender 4. A relatively quick source of funding that may achieve more favorable lending inte…
Practical Example
- A very simple example is if a homeowner who still ha a mortgage loan outstanding on their principal residence decided to make an investment into another property. They could potentially utilize cross collateralization, pledging each property as collateral for the loan. From the lenders’ perspective, it is favorable since they have more security on their loan, given that they now have …
More Resources
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Cross Collateralization. In order to help you become a world-class financial analyst and advance your career to your fullest potential, these additional resources will be very helpful: 1. Credit Score 2. Default Risk 3. Quality of Collateral 4. Secured vs Unsecured Loans
What to Know About Collateral
- There are 2 main types of loans: secured loans and unsecured loans. These loans differ in regard tocollateral requirements. Collateral is an asset that a borrower offers up as a way to guarantee the amount of a loan. Common forms of collateral include cash deposits, real estate, or vehicles. Secured loans require collateral, while unsecured loans d...
What Is Cross-Collateralization?
- Cross collateralization refers to a situation where multiple loans are secured with the same asset. In a second mortgage situation, your home serves as collateral for a mortgage. As you pay down your mortgage, you own more of your home. You can then use your home as collateral for a second loan, i.e., a second mortgage. Cross collateralization also occurs if different types of fina…
Is Cross-Collateralization Legal?
- Cross collateralization is legal and fairly common, but a lender is required to inform you that cross-collateralization is occurring. If you take out multiple secured loans from the same lender, like a bank, it might use the same collateral, making your assets cross-collateralized. You must legally consent to this, but do your due diligence in reading over any loan agreement. Be especia…
Is Cross-Collateralization Bad?
- If you can make your loan repayments on time, you’ll probably have no issues with cross-collateralization. Trouble arises if you default, however. If an asset is cross-collateralized and you default on one of your loans, you will default on allof your loans, because the asset can no longer secure any of them.
Can Banks Cross-Collateralize?
- Banks cross-collateralize often, but cross collateralization is even more common with credit unions. Cross-collateralization is especially conventional when you seek multiple loans from a single lender. With every loan you take out, read over the agreement and make sure you consent to how a loan is secured.
How Do I Get Out of Cross-Collateralization?
- The best way to untangle yourself from a bad cross-collateralization situation is to contact the lender and attempt to renegotiate your loan. You might, for example, be able to secure the remaining debt with other collateral, although the repayment terms might be worse. Bad cross-collateralization situations usually end with the loss of the asset, even if you declare bankruptcy…