
What is an example of a cross sectional survey?
Cross-Sectional Surveys. Cross-sectional surveys assess the prevalence of disease and the prevalence of risk factors at the same point in time and provide a "snapshot" of diseases and risk factors simultaneously in a defined population. For example, US government agencies periodically send out large surveys to random samples of the US population, asking about health status and risk factors and ...
What is the definition of cross - sectional study?
Cross-sectional study is a research tool used to capture information based on data gathered for a specific point in time. The data gathered is from a pool of participants with varied characteristics and demographics known as variables. Age, gender, income, education, geographical locations, and ethnicity are all examples of variables.
What is a cross-sectional study?
In medical research and social science, a cross-sectional study (also known as a cross-sectional analysis, transverse study, prevalence study) is a type of observational study that analyzes data from a population, or a representative subset, at a specific point in time—that is, cross-sectional data.
What is cross sectional survey?
The cross-sectional survey measures smoking, smokeless tobacco use, cessation, secondhand smoke exposure, economics, media, as well as knowledge, attitudes and perceptions towards tobacco use. It is designed to produce national and regional estimates based ...

What is cross-sectional study design in epidemiology?
Introduction to Epidemiology A cross-sectional study observes a sample population at a nominal single point in time. Although the cross-sectional design is often used for descriptive prevalence studies, this design is also used to investigate associations between risk factors and diseases.
What is a cross-sectional study study?
A cross-sectional study is a type of research design in which you collect data from many different individuals at a single point in time. In cross-sectional research, you observe variables without influencing them.
What is a cross-sectional study example?
Another example of a cross-sectional study would be a medical study examining the prevalence of cancer amongst a defined population. The researcher can evaluate people of different ages, ethnicities, geographical locations, and social backgrounds.
What are the 3 major types of epidemiological studies?
Three major types of epidemiologic studies are cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional studies (study designs are discussed in more detail in IOM, 2000). A cohort, or longitudinal, study follows a defined group over time.
How do you identify a cross-sectional study?
Defining Characteristics of Cross-Sectional StudiesThe study takes place at a single point in time.It does not involve manipulating variables.It allows researchers to look at numerous characteristics at once (age, income, gender, etc.)It's often used to look at the prevailing characteristics in a given population.More items...•
What is the difference between cohort and cross-sectional study?
Cohort studies are used to study incidence, causes, and prognosis. Because they measure events in chronological order they can be used to distinguish between cause and effect. Cross sectional studies are used to determine prevalence.
What are some examples of cross-sectional data?
Cross-sectional data refer to observations of many different individuals (subjects, objects) at a given time, each observation belonging to a different individual. A simple example of cross-sectional data is the gross annual income for each of 1000 randomly chosen households in New York City for the year 2000.
What are the benefits of a cross-sectional study?
The benefit of a cross-sectional study design is that it allows researchers to compare many different variables at the same time. We could, for example, look at age, gender, income and educational level in relation to walking and cholesterol levels, with little or no additional cost.
What are cross-sectional studies useful for?
Cross-sectional studies serve many purposes, and the cross-sectional design is the most relevant design when assessing the prevalence of disease, attitudes and knowledge among patients and health personnel, in validation studies comparing, for example, different measurement instruments, and in reliability studies.
What are the 4 methods of epidemiology?
Epidemiology utilizes an organized approach to problem solving by: (1) confirming the existence of an epidemic and verifying the diagnosis; (2) developing a case definition and collating data on cases; (3) analyzing data by time, place, and person; (4) developing a hypothesis; (5) conducting further studies if ...
What are the 4 measures of epidemiology?
Incidence proportion (attack rate) Incidence rate. Prevalence. Mortality rate.
What is the best type of epidemiological study design?
Randomized, controlled clinical trials are the most powerful designs possible in medical research, but they are often expensive and time-consuming. Well-designed observational studies can provide useful insights on disease causation, even though they do not constitute proof of causes.
What is the difference between a cross-sectional and longitudinal study?
Longitudinal studies differ from one-off, or cross-sectional, studies. The main difference is that cross-sectional studies interview a fresh sample of people each time they are carried out, whereas longitudinal studies follow the same sample of people over time.
What are cross-sectional studies useful for?
Cross-sectional studies serve many purposes, and the cross-sectional design is the most relevant design when assessing the prevalence of disease, attitudes and knowledge among patients and health personnel, in validation studies comparing, for example, different measurement instruments, and in reliability studies.
What is cross sectional research?
A cross-sectional study is a type of research design in which you collect data from many different individuals at a single point in time. In cross-sectional research, you observe variables without influencing them. Researchers in economics, psychology, medicine, epidemiology, and the other social sciences all make use of cross-sectional studies in ...
What is the difference between longitudinal and cross sectional studies?
What is the difference between a longitudinal study and a cross-sectional study? Longitudinal studies and cross-sectional studies are two different types of research design. In a cross-sectional study you collect data from a population at a specific point in time; in a longitudinal study you repeatedly collect data from ...
What are some examples of cross-sectional data?
Prominent examples include the censuses of several countries like the US or France, which survey a cross-sectional snapshot of the country’s residents on important measures. International organisations like the World Health Organization or the World Bank also provide access to cross-sectional datasets on their websites.
Why are cross sectional studies so cheap?
Because you only collect data at a single point in time, cross-sectional studies are relatively cheap and less time-consuming than other types of research.
Why do we need a cross sectional study?
Because all you need to know is the current number of low-income families, a cross-sectional study should provide you with all the data you require. Sometimes a cross-sectional study is the best choice for practical reasons – for instance, if you only have the time or money to collect cross-sectional data, or if the only data you can find ...
Why do you design longitudinal studies?
You then decide to design a longitudinal study to further examine this link in younger patients. Without first conducting the cross-sectional study, you would not have known to focus on younger patients in particular.
How to study the impact of low carb diet on diabetes?
You first conduct a cross-sectional study with a sample of diabetes patients to see if there are differences in health outcomes like weight or blood sugar in those who follow a low-carb diet. You discover that the diet correlates with weight loss in younger patients, but not older ones.
What is cross sectional study?
Cross-sectional studies are observational studies that analyze data from a population at a single point in time. They are often used to measure the prevalence of health outcomes, understand determinants of health, and describe features of a population.
Why are cross sectional studies important?
They are usually inexpensive and easy to conduct. They are useful for establishing preliminary evidence in planning a future advanced study.
Descriptive
A cross-sectional survey may be purely descriptive and used to assess the burden of a particular disease in a defined population.
Analytical
Analytical cross-sectional surveys may also be used to investigate the association between a putative risk factor and a health outcome.
Applications of Cross-sectional studies
Cross-sectional studies are relatively easy and inexpensive to conduct and are useful for investigating exposures that are fixed characteristics of individuals, such as ethnicity or blood group.
Limitations of Cross-sectional studies
Difficult to determine whether the outcome followed exposure in time or exposure resulted from the outcome.
Why is cross sectional research important?
Cross-sectional studies can be a useful research tool in many areas of health research. By learning more about what is going on in a specific population, researchers are better able to understand relationships that might exist between certain variables and develop further studies that explore these conditions in greater depth.
How does cross sectional research differ from longitudinal research?
This type of research differs from longitudinal studies in that cross-sectional studies are designed to look at a variable at a particular point in time. Longitudinal studies involve taking multiple measures over an extended period.
What is cross sectional research?
Cross-sectional studies are observational in nature and are known as descriptive research, not causal or relational, meaning that you can't use them to determine the cause of something, such as a disease. Researchers record the information that is present in a population, but they do not manipulate variables .
Why are longitudinal studies more expensive than cross sectional studies?
As you might imagine, longitudinal studies tend to require more resources and are often more expensive than cross-sectional resources. They are also more likely to be influenced by what is known as selective attrition, which means that some individuals are simply more likely to drop out of a study than others. This can influence the validity of the study.
Why do we use cross sectional studies?
Cross-sectional studies are usually allow researchers to collect a great deal of information quite quickly. Data is often obtained inexpensively using self-report surveys. Researchers are then able to amass large amounts of information from a large pool of participants.
Why is cross sectional study better?
One of the advantages of cross-sectional studies is that since data is collected all at once, it's less likely that participants will quit the study before data is fully collected.
How can groups be affected by cohort differences?
Individuals born during the same period may share important historical experiences, but people in that group who are born in a given geographic region may share experiences limited solely to their physical location .
Why are cross sectional surveys important?
For example, sometimes the National AIDS Programme conducted cross-sectional sentinel surveys among high-risk groups and ante-natal mothers every year to monitor the prevalence of HIV in these groups.
What is cross sectional study design?
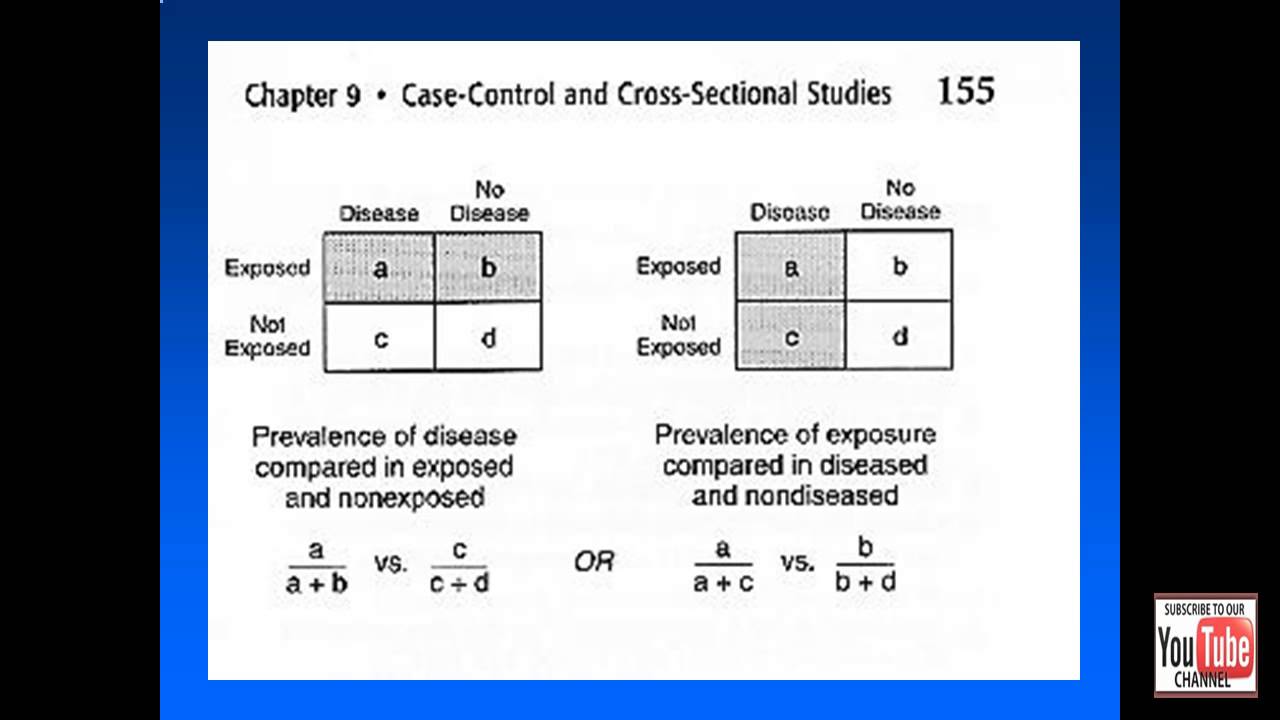
Cross-sectional study design is a type of observational study design. In a cross-sectional study, the investigator measures the outcome and the exposures in the study participants at the same time. Unlike in case–control studies (participants selected based on the outcome status) or cohort studies (participants selected based on the exposure status), the participants in a cross-sectional study are just selected based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria set for the study. Once the participants have been selected for the study, the investigator follows the study to assess the exposure and the outcomes. Cross-sectional designs are used for population-based surveys and to assess the prevalence of diseases in clinic-based samples. These studies can usually be conducted relatively faster and are inexpensive. They may be conducted either before planning a cohort study or a baseline in a cohort study. These types of designs will give us information about the prevalence of outcomes or exposures; this information will be useful for designing the cohort study. However, since this is a 1-time measurement of exposure and outcome, it is difficult to derive causal relationships from cross-sectional analysis. We can estimate the prevalence of disease in cross-sectional studies. Furthermore, we will also be able to estimate the odds ratios to study the association between exposure and the outcomes in this design.
How does prevalence affect the outcome of a disease?
The prevalence of an outcome depends on the incidence of the disease as well as the length of survival following the outcome. For example, even if the incidence of HIV (number of new cases) goes down in one particular community, the prevalence (total number of cases – old as well as new) may increase.
What is the OR of HIV?
Thus, the OR is 3.0. The interpretation of this OR is that males had a higher odds of being HIV infected compared with females. Since the OR is >1, the outcome is more likely in those exposed (males) compared with those who are not exposed (females). However, we will require confidence intervals to comment on further interpretation of the OR.
When was sentinel surveillance instituted?
The exercise has been in place for nearly two decades. The formal annual sentinel surveillance was instituted in 1998. The surveillance provided data on the prevalence of HIV infection in antenatal women, and thus, the trends of HIV infection in this population
Is AIDS a cross sectional study?
The National AIDS Control Organisation's Sentinel Surveillance of HIV is an example of “serial cross-sectional study” or “serial survey.” This may be less expensive compared with a cohort study
Where is the MGM Institute of Health Sciences?
From the Department of Epidemiologist, MGM Institute of Health Sciences, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Advantages
These studies are quick, cheap, and easy to conduct as they do not require any follow-up with subjects and can be done through self-report surveys.
Limitations
Cross-sectional studies can be influenced by antecedent consequent bias which occurs when it cannot be determined whether exposure preceded disease. (Alexander et al.)
Examples
Evaluating the COVID-19 positivity rates among vaccinated and unvaccinated adolescents
Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal Studies
Both cross-sectional and longitudinal studies are observational and do not require any interference or manipulation of the study environment.
Cross-Sectional vs Longitudinal Studies
When to Use A Cross-Sectional Design
- When you want to examine the prevalence of some outcome at a certain moment in time, a cross-sectional study is the best choice. Sometimes a cross-sectional study is the best choice for practical reasons – for instance, if you only have the time or money to collect cross-sectional data, or if the only data you can find to answer your research question was gathered at a single …
How to Perform A Cross-Sectional Study
- To implement a cross-sectional study, you can rely on data assembled by another source or collect your own. Governments often make cross-sectional datasets freely available online. Prominent examples include the censuses of several countries like the US or France, which survey a cross-sectional snapshot of the country’s residents on important measures. International orga…