
Why are DC motors usually gear motors?
Why are DC Motors Usually Gear Motors. Many battery-operated devices rely on DC motors for power. Because of their high shaft speeds—typically 1500-6000 RPM under load—DC motors are commonly paired with a gearbox. Without the gearbox, the shaft speed of DC motors often exceeds the requirements of most applications.
What is the function of a DC gear motor?
What is a DC Gear Motor? A gear motor is an all-in-one combination of a motor and gearbox. The addition of a gear head to a motor reduces the speed while increasing the torque output. The most important parameters in regards to gear motors are speed (rpm), torque (lb-in) and efficiency (%).
How do I control the speed of a DC motor?
- Just make your motor spin
- Control motor speed
- Control the direction of the spin of DC motor
How to control speed of DC series motor?
Speed control of series motor
- Flux control method Field diverter: A variable resistance is connected parallel to the series field as shown in fig (a). ...
- Variable resistance in series with armature By introducing resistance in series with the armature, voltage across the armature can be reduced. And, hence, speed reduces in proportion with it.
- Series-parallel control

What is the difference between a DC motor and a DC gear motor?
A DC gear motor features the same basic motor design as a DC motor but also includes a gearbox to create a single motion control component. This design allows speed reduction while increasing torque output in electromechanical applications.
What is a DC gear motor used for?
Electric Gear motors are used in applications that require high output torque and lower output shaft rotational speed, especially where space and available power are limited. This describes a wide range of common equipment applications across multiple industries.
What is a gear motor?
A gearmotor (or geared motor) is a small electric motor (AC induction, permanent magnet DC, or brushless DC) designed with an integral (non-separable) gear reducer (gearhead) attached. The end shield on the drive end of the motor (light blue, below) is designed to provide a dual function.
What is the difference between motor and gearmotor?
It is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Therefore, the difference between the geared motor and the ordinary motor is that the ordinary motor is only a power drive, while the geared motor is a power drive + transmission.
What are the main advantages of gear motors?
10 Advantages of Geared MotorsHigh Torque Output.Speed Reduction.High Resolution.Drive Large Inertial Loads.Shorter Positioning Time.Downsize.Improved Damping Characteristics.Increased Axial and Radial Load.More items...•
What are the two main advantages of gear motors?
Top Benefits of Using Geared MotorsSavings On Expenses. Using a gear motor to increase torque and lower speed eliminates the expense of running the system. ... Reduced Speed. ... Environmental Advantage. ... Torque. ... Increased Rigidity.
How do I choose a DC gear motor?
The three main specifications you will need to know for any DC motor application are voltage, speed and torque. Once these aspects are determined, you are now ready to get started on your journey to select the ideal motor solution. The key is to use a motor that is operating at or near its maximum efficiency.
How do gear motors operate?
Essentially, a gearmotor is a pairing of gear reducer and ac or dc electrical motor. The gear and the motors are combined into one unit. A gearmotor delivers high torque at low horsepower or low speed. The speed specifications for these motors are normal speed and stall-speed torque.
What is the main purpose of a gear?
Gears serve two main purposes: increasing speed or increasing force.
What are the 4 types of motors?
There are 4 main types of DC motors:Permanent Magnet DC Motors. The permanent magnet motor uses a permanent magnet to create field flux. ... Series DC Motors. In a series DC motor, the field is wound with a few turns of a large wire carrying the full armature current. ... Shunt DC Motors.Compound DC Motors.
Which is better gear motor or brushless motor?
Compared with conventional motors, brushless DC gear motors are more compact, lighter in weight, and more energy efficient. In this paper, we describe the technology used to achieve the brushless DC gear motor's high efficiency and the features of the new BMU driver.
What are the 4 main types of gears?
Types of GearsSpur Gear: The spur gear has a helix angle of 0°.Worm Gear: Worm gears are found in right angle gearboxes. They “turn a corner.”Helical Gear: This is an angle toothed gear. ... Bevel Gear: Bevel gears tend to have a lower ratio and run at a higher efficiency than worm gears.
How do I choose a DC gear motor?
The three main specifications you will need to know for any DC motor application are voltage, speed and torque. Once these aspects are determined, you are now ready to get started on your journey to select the ideal motor solution. The key is to use a motor that is operating at or near its maximum efficiency.
Why are DC motors used in trains?
DC motors are used on trains is because of their high torque and good speed control. Compared to AC motors, DC motors can provide industry applications with a fine balance of strong starting torque and controllable speed for seamless yet precise performance.
What is a DC motor?
A DC motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. In a DC motor, the input electrical energy is the direct current which is transformed into the mechanical rotation.
What is a brushed DC motor?
A brushed DC motor features a commutator that reverses the current every half cycle and creates single direction torque. While brushed DC motors remain popular, many have been phased out for more efficient brushless models in recent years.
What causes the motor armature to rotate?
The conductors located on the other pole are subjected to a force of the same intensity but in the opposite direction. These two opposing forces create a torque that causes the motor armature to rotate.
What is a commutator in a motor?
Commutator. The commutator of a DC motor is a cylindrical structure that is made of copper segments stacked together but insulated from each other using mica. The primary function of a commutator is to supply electrical current to the armature winding.
What is a series wound DC motor?
In a series wound DC motor, the field winding is connected in series with the armature winding as shown in the figure.
What is the armature of a DC motor?
The armature of a DC motor is a cylinder of magnetic laminations that are insulated from one another. The armature is perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder. The armature is a rotating part that rotates on its axis and is separated from the field coil by an air gap.
What are DC motor brushes made of?
The brushes of a DC motor are made with graphite and carbon structure. These brushes conduct electric current from the external circuit to the rotating commutator . Hence, we come to understand that the commutator and the brush unit are concerned with transmitting the power from the static electrical circuit to the mechanically rotating region or the rotor.
How does a DC motor work?
In a geared DC motor, the gear connecting the motor and the gear head is quite small, hence it transfers more speed to the larger teeth part of the gear head and makes it rotate. The larger part of the gear further turns the smaller duplex part. The small duplex part receives the torque but not the speed from its predecessor which it transfers to larger part of other gear and so on. The third gear’s duplex part has more teeth than others and hence it transfers more torque to the gear that is connected to the shaft.
What is a geared DC motor?
Geared DC motors can be defined as an extension of DC motor which already had its Insight details demystified here. A geared DC Motor has a gear assembly attached to the motor. The speed of motor is counted in terms of rotations of the shaft per minute and is termed as RPM .The gear assembly helps in increasing the torque and reducing the speed. Using the correct combination of gears in a gear motor, its speed can be reduced to any desirable figure. This concept where gears reduce the speed of the vehicle but increase its torque is known as gear reduction. This Insight will explore all the minor and major details that make the gear head and hence the working of geared DC motor.
How many cylinders are in a gear assembly?
The gear assembly is set up on two metallic cylinders whose working can be called as similar to that of an axle. A total of three gears combine on these two cylinders to form the bottom gear assembly out of which two gears share the same axle while one gear comes in between them and takes a separate axle.
How are duplex gears connected?
The gears are basically in form of a small sprocket but since they are not connected by a chain, they can be termed as duplex gears in terms of a second cog arrangement coaxially over the base. Among the three gears, two are exactly same while the third one is bigger in terms of the number of teeth at the upper layer of the duplex gear. The third gear is connected to the gear at the upper portion of the gear head. The manner in which they are located near the upper part of the gear head can be seen through the image shown below.
What is gear reduction?
This concept where gears reduce the speed of the vehicle but increase its torque is known as gear reduction. This Insight will explore all the minor and major details that make the gear head and hence the working of geared DC motor.
How do gears work?
The working of the gears is very interesting to know. It can be explained by the principle of conservation of angular momentum. The gear having smaller radius will cover more RPM than the one with larger radius. However, the larger gear will give more torque to the smaller gear than vice versa. The comparison of angular velocity between input gear ( the one that transfers energy) to output gear gives the gear ratio. When multiple gears are connected together , conservation of energy is also followed. The direction in which the other gear rotates is always the opposite of the gear adjacent to it .
Why does the gear cap have an arc cut?
The cap that accommodates the gear has an arc cut from its side to avoid frictional resistance forces with the bottom gear assembly.
Why do you need a DC motor without gears?
Usually such an addition is to reduce speed and increase torque . A DC motor without gears is useful in many applications, for example the simple fan. Contrast that with the motor that operates the turntable in your microwave, a gearbox there reduces the speed so your food isn't thrown against the interior wall.
What is a DC motor?
A DC motor is not the same as a "gear motor" - a "gear motor" may be an AC or DC motor coupled with a gearbox or transmission. A gear motor adds mechanical gears to alter the speed/torque of the motor for an application. Usually such an addition is to reduce speed and increase torque. A DC motor without gears is useful in many applications, for example the simple fan. Contrast that with the motor that operates the turntable in your microwave, a gearbox there reduces the speed so your food isn't thrown against the interior wall.
Is a DC motor the same as a gear motor?
A DC motor is not the same as a "gear motor" - a "gear motor" may be an AC or DC motor coupled with a gearbox or transmission. A gear motor adds mechanical gears to alter the speed/torque of the motor for an application. Usually such an addition is to reduce speed and increase torque.
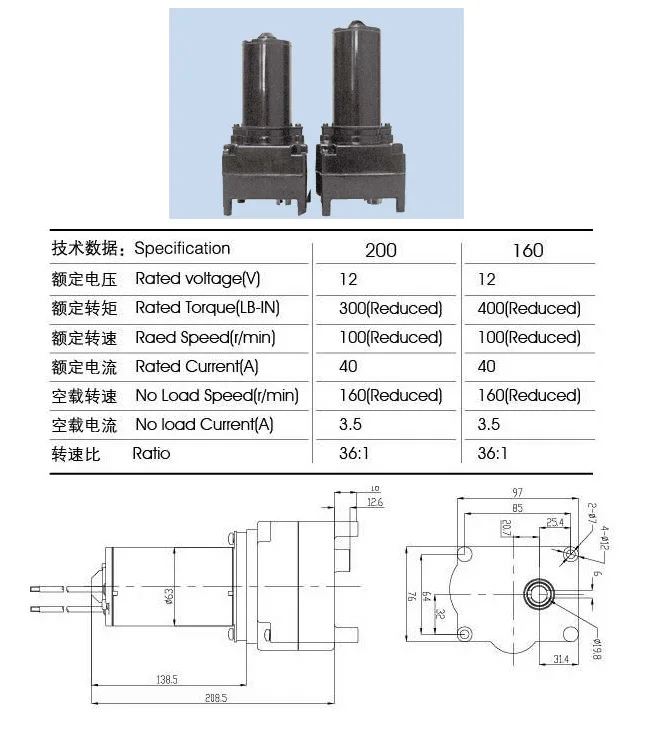
What Is A DC motor?
What Is A DC Gear motor?
- A gear motor is an all-in-one combination of a motor and gearbox. The addition of a gear head to a motor reduces the speed while increasing the torque output. The most important parameters in regards to gear motors are speed (rpm), torque (lb-in) and efficiency (%). In order to select the most suitable gear motor for your application you must first compute the load, speed and torque …
The Motor Selection Process
- Need help determining the right motor for your application? Check out our Motor Selection Guide or Visit the ISL Motor Database. The motor selection process, at the conceptual design phase, can be challenging but our engineers are here to help. We provide a concierge approach to all of our DC motors and gear motors projects. Our team of engineers work with you to provide the op…
Gear Motor Performance Curves
- A motors performance and gearbox performance are combined into one graph by displaying three specific parameters. These three parameters are speed, torque and efficiency. These performance curves are essential when selecting a gear motor for your application. Speed/Revolutions (N) – (unit: rpm)indicated as a straight line that shows the relationship betwe…