What is a time delay fuse?
A time delay fuse is also sometimes known as a slow blow fuse. The purpose of this type of fuse is to allow a surge in electricity for a short time before the fuse actually blows. To many people this sounds like a bad idea.
Can a power surge blow a time delay fuse?
power surge can blow a time delay fuse, these components are still ideal for certain types of appliances. Slow blow fuses come with a built-in delay, which allows for excessive inrush currents – however, they are designed to cut power in the event of an ongoing, sustained overload.
Do you need a time delay fuse for fluorescent bulbs?
So, use a time delay fuse for your fluorescent bulbs, incandescent lights, and electric motors. Otherwise, repeated circuit failures and other electrical problems will be a regular thing to face.
What is a slow blow fuse?
Slow blow fuses come with a built-in delay, which allows for excessive inrush currents – however, they are designed to cut power in the event of an ongoing, sustained overload. Ideal uses for time delay fuses include:
What's the difference between a fuse and a time delay fuse?
A FAST ACTING fuse used on a motor with a high starting current will blow before the motor can start running. TIME –DELAY fuses will not blow unless an over- load condition exists for an extended period of time, typically 10 seconds. The time delay is usually required when a motor has high starting currents.
What is a time delay fuse used for?
Time delay fuses allow for a temporary current surge without going above the fuse's current rating. Because of this, time delay fuses are most commonly used to protect motor circuits.
Can I replace a normal fuse with a time delay fuse?
Fast-acting fuses are generally used to protect sensitive components from damage so replacing fast-acting fuses with a time-delay fuse could result in damage to your equipment.
Is a time delay fuse better?
There are many advantages to using these fuses. Unlike single-element fuses, the Cooper Bussmann dual-element, time-delay fuses can be sized closer to provide both high performance short circuit protection and reliable overload protection in circuits subject to temporary overloads and surge currents.
How do you know if a time delay fuse is blown?
Look at the fuse wire. If there is a visible gap in the wire or a dark or metallic smear inside the glass then the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced.
How can you tell if a fuse is time delay?
Look through the tube of the fuse glass and check the wire filament within. If there is a thin wire, you have a fast-blow fuse. If you see a thick wire that has a very small spring at one end, you will know it is a slow-blow fuse.
How long do time delay fuses last?
They are similar in function as they delay the time for 10 seconds at 500% of rated current.
What is the slowest burning fuse?
Green fuse is the most common fuse sold in the consumer market. It's the slowest burning of the fuses at approximately 25 seconds per foot. Often times it is coated with wax or a type of lacquer, making it water resistant.
How do you size a time delay fuse?
The type of protection used determines the maximum allowable rating with these exceptions, (a) Non-time delay fuses rated 600A or less can be sized up to 400% of the motor full-load current, (b) Time-delay fuses can be sized up to 225% of the full-load current, (c) Inverse time circuit breakers can be sized up to 400% ...
What does the T mean on a fuse?
The 'T' stands for 'Time lag'. This is the same as anti-surge. The. fuse can withstand brief surges in current such as you get when a. power supply starts up and its filters stabilise.
What are the different types of fuses?
Different Types of Fuses – Constriction, Working & CharacteristicsDC Fuses.AC Fuses.Cartridge Fuses.D – Type Cartridge Fuse.HRC (High Rupturing Capacity) Fuse or Link Type Cartridge Fuse.High Voltage Fuses.Automotive, Blade Type & Bolted Type Fuses.SMD Fuses (Surface Mount Fuse), Chip , Radial, and Lead Fuses.More items...
What is TLF fuse?
The time delay or 'time limiting' fuse links are used in conjunction with circuit breaker overcurrent releases. The time delay fuse link is connected in parallel with the trip coil and is fed via a current transformer on the primary side of the circuit breaker.
What are the 3 types of fuses?
Classification of Fuses Fuses can be classified as “One Time Only Fuse”, “Resettable Fuse”, “Current limiting and non – current limiting fuses” based on the usage for different applications.
What is a time delay circuit breaker?
Circuit breaker short-time-delay (STD) mechanisms allow an intentional delay to be installed on low voltage power circuit breakers. Short-time-delays allow the fault current to flow for several cycles, which subjects the electrical equipment to unnecessarily high mechanical and thermal stress.
How does a time delay relay work?
Upon application of input voltage, the time delay relay is ready to accept a trigger. When the trigger is applied, the time delay (t1) begins. At the end of the time delay (t1), the output is energized. When the trigger is removed, the output contacts remain energized for the time delay (t2).
What's a time delay safe?
Unlike the time lock, which unlocks at a preset time (as in the case of a bank vault), time-delay locks operate each time the safe is unlocked, but the operator must wait for the set delay period to elapse before the lock can be opened. Time delay safes are most commonly used in businesses with high cash transactions.
What is a time delay fuse?
A time delay fuse is a special kind of fuse that allows electrical surge for a short time before it actually blows. Due to its special design, it can bear electricity overload in a repeated cycle for a short period without blowing. Its ability to carry momentary overloads makes it an integral part of many systems that use a high inrush ...
How Does a Time Delay Fuse Work?
You will find the standard ones in particular circuits and appliances. Exposure to more electrical current than they are rated for will burn them out. By making a circuit dead, they protect devices and power lines from short circuits and damage.
What happens when a fuse is overloaded?
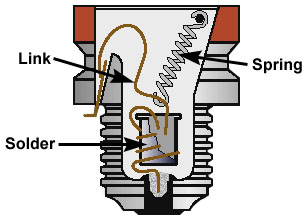
Also, a prolonged overload will build up the heat in the fuse to the point of melting the solder joint. It will open the connector by releasing the spring. The result will be the melting of the fuse wire, just what happens in case of a standard fuse.
How long does a fuses delay time?
They are similar in function as they delay the time for 10 seconds at 500% of rated current. These high-performance fuses have the capability of repeated cycling with superior time-delay for carrying surges without affecting the circuit.
How much more current can a time delay fuse handle?
A time delay fuse, on the contrary, can handle 100 or 200% more electrical current than a regular type because it has an extra spring-attached short connector. The connector is attached to the fuse wire with a low melting point solder.
What is a midget fuse?
Midget Fuses. Like the CC Class, they also provide a 12-second of time delay. These have a tube-like dual-element construction. It allows the surges pass through from one end to another without affecting the fuse wire. These are used in solenoids, transformers, small motors, and other high inrush electronic circuits.
Why are regular amps useless?
Regular models are useless in this case because they do not allow any power surge beyond their amp rating.
What is a time delay fuse?
A time delay fuse has the capacity to sustain transient pulse currents, which is not the strong suit of a fast-acting model. The slow-blow version can withstand the electrical surge in a repeated cycle upon switching the power on/off.
Why are time delay fuses less effective?
Protection. Many people think that time delay fuses are less effective because they allow current overloads pass through the circuits. Well, it’s not true. They are used only for those tools and appliances that need a high voltage current to start their operation.
What Is a Fast Acting Fuse?
It gives a quick response to electric spikes and then protects the devices by breaking the circuit.
What is the main function of a fuse?
The main function of a fuse is to melt the wire inside during overloads, and disconnect the electricity flow into that circuit. All types of fuses will blow out, but the differences lie in how and what leads to that blowing. Take a look at the time delay fuse vs fast acting fuse analysis to know how they actually differ in functions.
Why does a fuse wire melt?
Their fuse wire will melt because of the initial excess supply of electricity. However, replacing the fast acting fuses with the time delay versions will not be cost-effective because the latter is more expensive.
How long does it take for a slow blow fuse to melt?
But, a slow-blow one will melt its fuse wire after a specific period, within 10 or 15 seconds.
What is a fuse?
A fuse is a protective device that keeps electrical appliances safe in the event of a surge of electrical current. They come in various types. One category differs from the other in terms of functions and response time to a peak of electricity. Depending on these features, you can divide them into time delay and fast acting fuses.
What is a time delay fuse?
Generally, fuses are an integral part of a house’s electrical system. They serve to protect people from electrical fires and shocks by cutting power to a circuit if certain limits are exceeded. Time delay fuses, which are also called slow blow fuses, are different in that they temporarily allow excessive current to pass through them. Although something like a power surge can blow a time delay fuse, these components are still ideal for certain types of appliances.
What is slow blow fuses?
Slow blow fuses come with a built-in delay, which allows for excessive inrush currents – however, they are designed to cut power in the event of an ongoing, sustained overload. Ideal uses for time delay fuses include:
Is it safe to use a slow blow fuse?
Without slow blow fuses, you would be forced to use a fuse that's rated for higher loads. This means the fuse you utilize will ultimately be too big for the appliance’s normal load, which in turn means that an overloaded circuit won’t blow the fuse – a huge safety risk.
What happens when a fuse blows?
So, when the fuse opens (blows), it stops the flow of current through the components by opening the entire circuit. However, connecting the fuse in one branch of a parallel circuit won’t affect the flow of current in other branches.
How to identify fuses?
You can identify fuses by two letters according to your applications (more details later). For low voltage applications, we have gG and aM fuses.
Why does a fuse have a melting point?
As current flows into the element, it creates a tiny voltage drop across the element (small enough not to affect the circuit downstream). This process dissipates some power as heat. Thus, increasing the resistive element’s temperature.
How much power can a high breaking capacity fuse limit?
The higher the breaking capacity, the stronger the fuse. Furthermore, high breaking capacity fuses can limit short circuits reaching up to 100 000 A RMS.
Why is DC fuse bigger than AC fuse?
The DC fuse is different from the AC fuse when it comes to size. It’s bigger because of the constant values of direct current circuits. When the current rating goes past the maximum current limit, the metallic fuse wire melts and disconnects the rest of the circuit from the power supply. So, here are the different types of DC fuse:
Why do you put fuse wires in safety sheaths?
Additionally, you’ll find that manufacturers place fuse wires within a safety sheath to minimize the hazards of the wire burning up with violent force. When this happens, it creates an Electric arc blast. Usually, this occurs during severe overcurrents.
What is circuit safety?
Circuit safety is the specialty of a fuse. A fuse is an electrical safety device. It has a conductive strip that melts and separates whenever there’s an overflow of current. It would help if you always connected a fuse in series with the electrical components—you want to protect.
