What are descriptive studies? Descriptive studies are observational studies which describe the patterns of disease occurrence in relation to variables such as person, place and time. They are often the first step or initial enquiry into a new topic, event, disease or condition.
What is the purpose of a descriptive study?
[2] To put it simply, descriptive studies are used to describe various aspects of the phenomenon. In its popular format, descriptive research is used to describe characteristics and/or behaviour of sample population. It is an effective method to get information that can be used to develop hypotheses and propose associations.
What are some examples of observational studies?
Observational Study in Statistics: Definition & Examples
- Examples of Observational Studies. As we said, an observational study is one in which the researcher doesn't manipulate anything. ...
- Non-Example of an Observational Study. Consider our organic foods example of an observational study. ...
- Advantages and Disadvantages. There are advantages and disadvantages to any type of study. ...
What is the objective of descriptive research?
Advantages of Descriptive Research
- Effective to analyse non-quantified topics and issues
- The possibility to observe the phenomenon in a completely natural and unchanged natural environment
- The opportunity to integrate the qualitative and quantitative methods of data collection
- Less time-consuming than quantitative experiments
What are the types of descriptive research?
Descriptive, or qualitative, methods include the case study, naturalistic observation, surveys, archival research, longitudinal research, and cross-sectional research. Experiments are conducted in order to determine cause-and-effect relationships.
What are descriptive observational studies?
Descriptive studies are observational studies which describe the patterns of disease occurrence in relation to variables such as person, place and time. They are often the first step or initial enquiry into a new topic, event, disease or condition.
What are the 3 types of observational study?
Three types of observational studies include cohort studies, case-control studies, and cross-sectional studies (Figure 1).
What is an example of a descriptive study?
Descriptive research is also used to compare how different demographics respond to certain variables. For example, an organization may study how people with different income levels react to the launch of a new Apple phone.
What is the difference between descriptive and observational research?
The term descriptive research then refers to research questions, design of the study, and data analysis conducted on that topic. We call it an observational research method because none of the research study variables are influenced in any capacity.
What is the most common type of observational study?
The most common are cohort studies and case-control studies. Cohort Studies: They are used to study incidence, causes and prognosis. Because they measure events in chronological order they can be used to distinguish between cause and effect. Cross-sectional studies are used to determine prevalence.
What are the 4 types of observation in research?
There are several different approaches to observational research including naturalistic observation, participant observation, structured observation, case studies, and archival research.
What type of research design is a descriptive study?
Descriptive research is usually defined as a type of quantitative research, though qualitative research can also be used for descriptive purposes. The research design should be carefully developed to ensure that the results are valid and reliable.
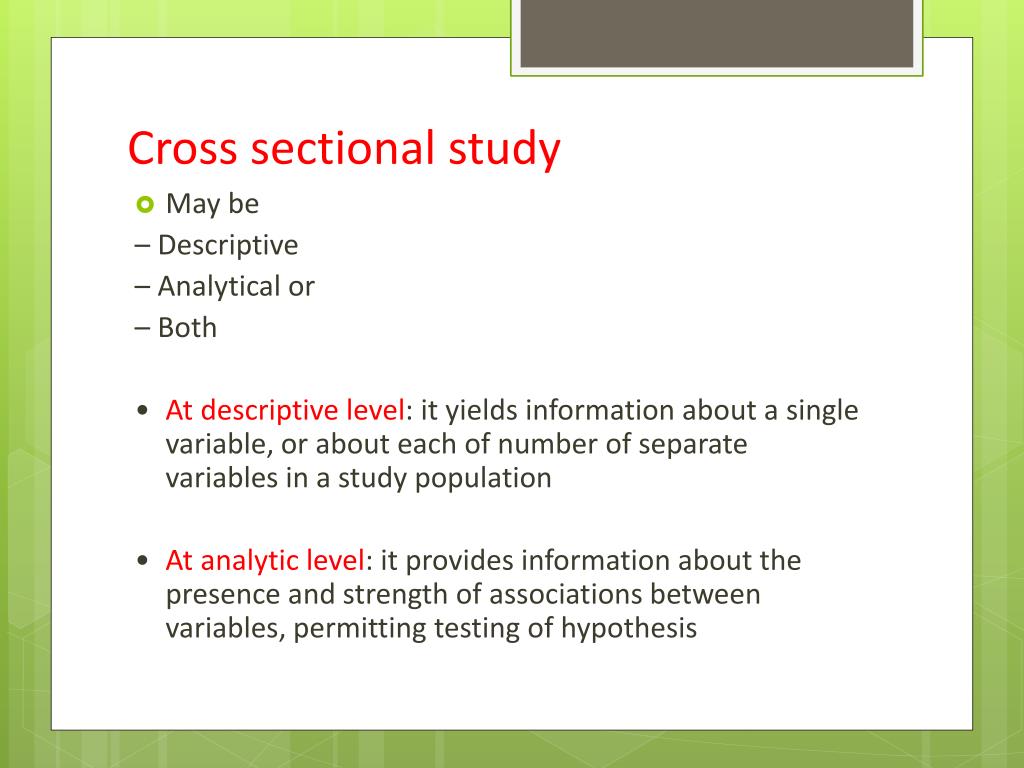
What is a descriptive study design?
WHAT IS A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY? A descriptive study is one that is designed to describe the distribution of one or more variables, without regard to any causal or other hypothesis.
What are the 7 types of descriptive research?
We have explained these seven types in brief with examples to help you better understand them.Cross-sectional: A descriptive method of studying a particular section of people at a given point in time. ... Longitudinal: ... Normative: ... Relational/Correlational: ... Comparative: ... Classification: ... Archival:
What kind of study is an observational study?
Observational studies are ones where researchers observe the effect of a risk factor, diagnostic test, treatment or other intervention without trying to change who is or isn't exposed to it. Cohort studies and case control studies are two types of observational studies.
What are the 3 types of research methods?
Types of researchQualitative Research.Quantitative Research.Mixed Methods Research.
What's the difference between descriptive and experimental research?
Descriptive research is a method that describes a study or a topic. It defines the characteristics of the variable under research and answers the questions related to it. Whereas experimental research is a scientific approach to testing a theory or a hypothesis using experimental groups and control variables.
What type of observational study are there?
There are three main types of observational studies: cohort studies, case–control studies, and cross-sectional studies.
What kind of study is an observational study?
Observational studies are ones where researchers observe the effect of a risk factor, diagnostic test, treatment or other intervention without trying to change who is or isn't exposed to it. Cohort studies and case control studies are two types of observational studies.
What are examples of observational studies?
In an observational study, researchers study how participants perform certain behaviors or activities without telling them what methods or behaviors to choose. For example, if a scientist wants to study how the amount of water humans drink affects their diets, they might choose an observational study.
What are the types of observation?
When it comes to observational research, you have three different types of methodologies: controlled observations, naturalistic observations, and participant observations.
How do you define an observational study?
An observational study is a great choice for you if your research question is based purely on observations. If there are ethical, logistical, or...
What is the difference between an observational study and an experiment?
The key difference between observational studies and experimental designs is that a well-done observational study does not influence the respon...
What is a quasi-experiment?
A quasi-experiment is a type of research design that attempts to establish a cause-and-effect relationship. The main difference with a true expe...
What’s the difference between exploratory and explanatory research?
Exploratory research aims to explore the main aspects of an under-researched problem, while explanatory research aims to explain the causes and...
What is experimental design?
Experimental design means planning a set of procedures to investigate a relationship between variables . To design a controlled experiment, you ne...
When does a prospective study result?
Prospective studies –the Result occur after the study start (cohort) Retrospective studies - the Result occur before the start of study (case-control, cohort - as a component)
What is the basis for dividing the study population into two groups?
Based on symptoms or syndromes, results of laboratory and functional examinations This allows to divide the study population in two groups: cases and control Sources:
What is primary in research?
1. Primary –made by the researcher from a practical point of view.
Why are CS studies important?
CS are the design of choice for studying the causes of a condition, the course of the disease, or the risk factors because they are longitudinal and follow a group of subjects over a period of time 2. Allow the direct measure of incidence 3. They possess the correct time sequence to provide strong evidence for possible causes and effects. 4. In well- designed CS, investigators can control many sources of bias related to patient selection and recorded measurements 5. Can be identified different effects of one exposure 6. Very useful in rare expose –cohort type 2.
What is a snapshot shot?
one point in time like a photo “snap shot” •Analyze data collected from a group of subject at one time rather that over a period of time
What is the observational method used for?from formpl.us
The observational method allows researchers to collect data based on their view of the behaviour and characteristics of the respondent, with the respondents themselves not directly having an input. It is often used in market research, psychology, and some other social science research to understand human behaviour.
What is quantitative observation?from formpl.us
Quantitative observation involved the objective collection of numerical data, whose results can be analyzed using numerical and statistical methods.
What is Descriptive Research?from formpl.us
Descriptive research is a type of research that describes a population, situation, or phenomenon that is being studied. It focuses on answering the how, what, when, and where questions If a research problem, rather than the why.
What are the Data Collection Methods in Descriptive Research?from formpl.us
There are 3 main data collection methods in descriptive research, namely; observational method, case study method, and survey research.
What is correlational research?from formpl.us
Correlational research is a type of descriptive research, which is used to measure the relationship between 2 variables, with the researcher having no control over them. It aims to find whether there is; positive correlation (both variables change in the same direction), negative correlation (the variables change in the opposite direction), or zero correlation (there is no relationship between the variables).
What is the difference between correlational and descriptive research?from formpl.us
Below are some of the differences between correlational and descriptive research: Definitions: Descriptive research aims is a type of research that provides an in-depth understanding of the study population, while correlational research is the type of research that measures the relationship between 2 variables.
What is descriptive comparative research?from formpl.us
In descriptive-comparative research, the researcher considers 2 variables which are not manipulated, and establish a formal procedure to conclude that one is better than the other. For example, an examination body wants to determine the better method of conducting tests between paper-based and computer-based tests.
What is descriptive study?
A descriptive study is one that is designed to describe the distribution of one or more variables, without regard to any causal or other hypothesis. TYPES OF DESCRIPTIVE STUDIES. Descriptive studies can be of several types, namely, case reports, case series, cross-sectional studies, and ecological studies. In the first three of these, data are ...
Why are descriptive studies important?
Descriptive studies are useful for estimating the burden of disease (e.g., prevalence or incidence) in a population. This information is useful for resource planning. For instance, information on prevalence of cataract in a city may help the government decide on the appropriate number of ophthalmologic facilities.
Why are cross sectional studies important?
Cross-sectional studies can be thought of as providing a “snapshot” of the frequency and characteristics of a disease in a population at a particular point in time. These are very good for measuring the prevalence of a disease or of a risk factor in a population. Thus, these are very helpful in assessing the disease burden and healthcare needs.
What are the two types of study designs?
Study designs are primarily of two types – observational and interventional, with the former being loosely divided into “descriptive” and “analytical.”. In this article, we discuss the descriptive study designs.
What is a study design?
In our previous article in this series,[1] we introduced the concept of “study designs”– as “the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data on variables specified in a particular research question.” Study designs are primarily of two types – observational and interventional, with the former being loosely divided into “descriptive” and “analytical.” In this article, we discuss the descriptive study designs.
What are the steps of a research study?
One of the first steps in planning a research study is the choice of study design. The available study designs are divided broadly into two types – observational and interventional. Of the various observational study designs, the descriptive design is the simplest. It allows the researcher to study and describe the distribution ...
What are the limitations of ecological studies?
However, the ecological study design has some important limitations.First, an association between exposure and outcome at the group level may not be true at the individual level (a phenomenon also referred to as “ecological fallacy”).[10] Second, the association may be related to a third factor which in turn is related to both the exposure and the outcome, the so-called “confounding”. For instance, an ecological association between higher income level and greater cardiovascular mortality across countries may be related to a higher prevalence of obesity. Third, migration of people between regions with different exposure levels may also introduce an error. A fourth consideration may be the use of differing definitions for exposure, outcome or both in different populations.
What type of study is an observational study?
Observational studies are ones where researchers observe the effect of a risk factor, diagnostic test, treatment or other intervention without trying to change who is or isn't exposed to it. Cohort studies and case control studies are two types of observational studies.
What types of studies are descriptive?
The three main types of descriptive studies are case studies, naturalistic observation, and surveys.
What is an example of a descriptive study?
Some examples of descriptive research are: A specialty food group launching a new range of barbecue rubs would like to understand what flavors of rubs are favored by different people.
Is a descriptive observational study qualitative or quantitative?
The data that are collected in observational research studies are often qualitative in nature but they may also be quantitative or both (mixed-methods).
Why is descriptive research called observational research?
We call it an observational research method because none of the research study variables are influenced in any capacity. Some distinctive characteristics of descriptive research are: Quantitative research: Descriptive research is a quantitative researchmethod that attempts to collect quantifiable information for statistical analysis ...
What is qualitative observation?
Qualitative observation doesn’t involve measurements or numbers but instead just monitoring characteristics. In this case, the researcher observes the respondents from a distance. Since the respondents are in a comfortable environment, the characteristics observed are natural and effective. In a descriptive research design, the researcher can choose to be either a complete observer, an observer as a participant, a participant as an observer, or a full participant. For example, in a supermarket, a researcher can from afar monitor and track the customers’ selection and purchasing trends. This offers a more in-depth insight into the purchasing experience of the customer.
What is the basis of further research?
The basis for further research:Researchers further research the data collected and analyzed from descriptive research using different research techniques. The data can also help point towards the types of research methods used for the subsequent research.
Why do organizations use descriptive research?
Conduct comparisons: Organizations also use a descriptive research design to understand how different groups respond to a specific product or service. For example, an apparel brand creates a survey asking general questions that measure the brand’s image. The same study also asks demographic questions like age, income, gender, geographical location, etc. This consumer research helps the organization understand what aspects of the brand appeal to the population and what aspects do not. It also helps make product or marketing fixes or even create a new product line to cater to high growth potential groups.
How many distinct methods are there for conducting descriptive research?
There are three distinctive methods to conduct descriptive research. They are:
What is descriptive research?
Descriptive research definition: Descriptive research is defined as a research method that describes the characteristics of the population or phenomenon studied. This methodology focuses more on the “what” of the research subject than the “why” of the research subject. The descriptive research method primarily focuses on describing the nature ...
What is survey research?
In survey research, respondents answer through surveys or questionnairesor polls. They are a popular market research tool to collect feedback from respondents. A study to gather useful data should have the right survey questions. It should be a balanced mix of open-ended questionsand close ended-questions. The survey method can be conducted online or offline, making it the go-to option for descriptive research where the sample size is enormous.
What is an observational design?
Observational : descriptive. An observational design for descriptive inference has an inquiry like a population mean, covariance, or distribution as the main research goal. In an observational research design, the data strategy includes sampling and measurement components, but no treatments are allocated. Put differently, in an observational design ...
How to study population?
One approach to studying a population is to conduct a census in which we record data on all N N units. A census has the clear advantage of being comprehensive, but it usually comes at an overwhelming and prohibitive cost.
Why do researchers reweight the responses of different units in a sample?
We declare a design in which researchers reweight the responses of different units in a sample in order to better estimate a population level quantity. Reweighting depends on how much units are thought to “represent” other nonsampled units and requires making decisions about how much units of different types should be pooled together. Design performance of a partially pooled model is compared against designs that involve no pooling and full pooling.
Why can't researchers randomly sample at the individual level?
Researchers often cannot randomly sample at the individual level because it may, among other reasons, be too costly or logistically impractical.
How to avoid missingness in data analysis?
Avoiding missingness often means adding extra effort and expense: monetary incentives for participation, multiple rounds of attempted contact, and a variety of modes of contact (phone, mail, email, direct message, text, canvass). The best way to allocate extra effort will vary from context to context, as will the payoff from doing so. Our recommendation is to reason about the plausible response rates that would result from different levels of effort, then to consider how to optimize the bias-effort tradeoff. Sometimes, achieving zero bias would be far too costly, so we would be willing to tolerate some bias because effort is too expensive.
What is the most critical step in research methodology?
The selection of a study design is the most critical step in the research methodology. Crucial factors should be considered during the selection of the study design, which is the formulated research question, as well as the method of participant selection. Different study designs can be applied to the same research question(s). Research designs are classified as qualitative, quantitative, and mixed design. Observational design occupies the middle and lower parts of the hierarchy of evidence-based pyramid. The observational design is subdivided into descriptive, including cross-sectional, case report or case series, and correlational, and analytic which includes cross-section, case-control, and cohort studies. Each research design has its uses and points of strength and limitations. The aim of this article to provide a simplified approach for the selection of descriptive study design.
What is cross sectional study?
The cross-sectional study examines the association between exposures and outcomes on a snap of time. The assessed associations are guided by sound hypotheses and seen as hypothesis-generating [17]. This design can be descriptive (when dealing with prevalence or survey) or analytic (when comparing groups) [17-18]. The selection of participants in a cross-sectional study design depends on the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria [18-19]. This method of selection limits randomization (Table 4).
What is the purpose of a correlational study?
Correlational studies (ecologic studies) explore the statistical relationships between the outcome of interest in population and estimate the exposures. It deals with the community rather than in individual cases. The correlational study design can compare two or more relevant variables and reports the association between them without controlling the variables. The aim of correlational study design or research is to uncover any types of systematic relationships between the studied variables. Ecological studies are often used to measure the prevalence and incidence of disease, mainly when the disease is rare. The populations compared can be defined in several ways, such as geographical, time trends, migrants, longitudinal, occupation, and social class. It should be considered that in ecological studies, the results are presented at the population (group) level rather than individuals. Ecological studies do not provide information about the degree or extent of exposure or outcome of interest for particular individuals within the study group (Table 3) [7, 15-16]. For example, we do not know whether those individuals who died in the study group under observation had higher exposure than those remained alive.
What is research design?
A research design is defined as the “set up to decide on, among other issues, how to collect further data, analyze and interpret them, and finally, to provide an answer to the question” [1]. The primary objective of a research design is to guarantee that the collected evidence allows the answering of the initial question(s) as clearly as possible [2]. Various study designs have been described in the literature [1-3]. Each of them deals with the specific type of research or research questions and has points of strength and weakness. Broadly, research designs are classified into qualitative and quantitative research and mixed methods [3]. The quantitative study design is subdivided into descriptive versus analytical study designs or as observational versus interventional (Figure (Figure1).1). Descriptive designs occupy the middle and lower parts of the hierarchy of evidence-based medicine pyramid. Study designs are organized in a hierarchy beginning from the basic "case report" to the highly valued "randomised clinical trial" [4-5].
