What is the life cycle of a parasite?
Parasites with direct life cycles spend most of their adult lives in one host, known as the parasitic stage, with their progeny transmitted from one host to another, known as the free-living stage. Direct parasites often lack an intermediate stage and must leave their host.
What are some examples of parasites with an indirect life cycle?
Some filarial nematodes, Plasmodium, and Leishmania are examples of parasites with indirect life cycles. Reservoir hosts typically tolerate parasites with no ill effects; however, the introduction of a new host into a population of reservoir hosts will often result in severe disease in the newly introduced host.
Which of the following is an example of direct life cycle?
Simple parasite reproduce and live inside single host, this is an example of direct life cycle. In direct life cycle, parasite lives its entire life inside the host and reproduce inside it. Such animals or organisms that harbor parasites are suppose to provide shelter and food to the parasite and such a host is called definitive host.
What is the difference between simple and complex parasites?
Simple parasites have direct life cycle while complex parasites have indirect life cycle. Parasite is known to complete its whole life in just one host in direct life cycle but it switch hosts in indirect life cycle.
What is direct and indirect life cycle in parasite?
The key difference between direct lifecycle and indirect lifecycle is that, in the direct lifecycle, the simple parasite lives their lifespan and reproduces within one host while in the indirect lifecycle, the complex parasites live in many numbers of hosts during the completion of their life cycle.
What is called indirect cycle of a parasite?
An indirect life cycle is a type of a life cycle wherein a parasite is transmitted from one host to another by using a vector or by an intermediate host of another species. A parasite with an indirect life cycle would therefore require more than one type of host species to complete their life cycle.
What is simple life cycle parasite?
Monoxenic or homoxenous parasite species with simple life cycles only use a single host species in their life. The single host species is entered by infective stages of the parasite, and then the parasite grows and develops in the host before switching to reproducing within the host.
What is direct transmission of parasite?
Direct contact transmission occurs when there is physical contact between an infected person and a susceptible person. Indirect contact transmission occurs when there is no direct human-to-human contact.
What are the different forms of life cycles?
In regard to changes of ploidy, there are 3 types of cycles:haplontic life cycle — the haploid stage is multicellular and the diploid stage is a single cell, meiosis is "zygotic".diplontic life cycle — the diploid stage is multicellular and haploid gametes are formed, meiosis is "gametic".More items...
What is the difference between definitive and intermediate host?
The definitive host is the one which harbors the adult parasite and where the parasite reproduces sexually. The intermediate host is the host which harbors the larval stage or the asexual forms of the parasite. Few parasites require two different intermediate hosts in addition to a definitive host.
Why is the life cycle of a parasite important?
The respective effect of individual parasite species was roughly proportional to the number of host species they affected, and thus the life cycle characteristics of parasites determine to a large extent their impact on food web structure.
Why is life cycle of parasite complex?
Parasitic worms (helminths) frequently have complex life cycles in which they are transmitted trophically between two or more successive hosts. Sexual reproduction often takes place in high trophic-level (TL) vertebrates, where parasites can grow to large sizes with high fecundity.
Why should we study the life cycle of parasites?
Finally, knowledge of parasite life cycles is also essential for parasite control. Each stage in the life cycle of a parasite earmarked for eradication is a potential target for control measures. Elucidation of the life cycle of human pathogens such as Plasmodium spp.
What is indirect mode of transmission?
Indirect transmission refers to the transfer of an infectious agent from a reservoir to a host by suspended air particles, inanimate objects (vehicles), or animate intermediaries (vectors).
What are the different mode of transmission of parasites?
Parasitic infections can be spread in a number of ways. For example, protozoa and helminths can be spread through contaminated water, food, waste, soil, and blood. Some can be passed through sexual contact. Some parasites are spread by insects that act as a vector, or carrier, of the disease.
What are the 3 types of parasitic infection?
There are three main classes of parasites that can cause disease in humans: protozoa, helminths, and ectoparasites.
What is indirect life cycle in nematode?
The indirect life cycle involves an intermediate host. The first two moults usually occur in the intermediate host. Infection of the definitive host is either via ingestion of the intermediate host or by inoculation of the L3 by an intermediate host such as an insect.
What is an intermediate host of a parasite?
Definition of intermediate host 1 : a host which is normally used by a parasite in the course of its life cycle and in which it may multiply asexually but not sexually — compare definitive host.
What is Heteroxenous life cycle?
Definition of heteroxenous : infesting more than one kind of host especially : requiring at least two kinds of host to complete the life cycle —used of various parasites (as the malaria parasites or the liver flukes)
What is monoxenous life cycle?
The life cycle of Eimeria is considered monoxenous, meaning that the cycle occurs in one host. The three stages of its life cycle include oocyst, sporozoite, and merozoite. The oocyst stage can be seen in Figure 1. This stage is mostly powered by the mannitol cycle that Eimeria use as metabolism.
What are the two types of life cycles of parasites?
Life cycles of parasites can be further divided into two categories: direct (monoxenous) and indirect (heteroxenous). Further discussion would depend on the specific parasite. Some such as parasitic worms can be rather disgusting as we examine how they live. Other parasites are external and more easily seen and countered.
What is the life cycle of a malaria parasite?
Others have their own specialized life cycle such as the malarial parasite. The malaria parasite life cycle involves two hosts. During a blood meal, a malaria -infected female Anopheles mosquito inoculates sporozoites into the human host . Sporozoites infect liver cells and mature into schizonts , which rupture and release merozoites .
What is customer life management?
Needless to say, customer life management provides marketers a detailed framework for interacting with the clients at every touchpoint for seamless communication. Start personalizing your brand for your customers and see how to stick around. These are the stages of how one can delve into the same.
What is customer lifecycle?
The customer lifecycle outlines the steps undertaken by a customer as they progress with the company through sales or marketing. Having said that, it draws a clear-cut picture of the customer’s journey with you. It describes the various stages a customer goes through during their course of interaction with your brand.
Who provided a lot of good information about parasites?
Richard Greco provided a lot of good information about parasites, but as he explained there are too many different parasitic organisms to be able to answer your general question.
Do parasites have a direct or indirect life cycle?
Parasites have either a direct life cycle , in which they require only one . Host , or an indirect cycle , in which one or more intermediate hosts are required . An intermediate host is the one in which the young parasite , undergoes development leading to the stage which is infective to the final .👍
What is the direct life cycle of a parasite?
What is Direct Life Cycle? Parasites are small microscopic organisms that keep inside a quantity cell. Some parasites are obligate parasites, that is they keep and reproduce inside a quantity cell whereas some might even reproduce outdoor a quantity cell.
What is the time interval for a parasite?
The time interval direct and indirect life cycle is used to point the life cycles of a parasite. The foremost between direct and indirect life cycle is, in direct life cycle the parasite lives and reproduce contained within the host. But some parasites are sophisticated and they need a variety of hosts to breed, such a life cycle is known as indirect life cycle.
What is Indirect Life Cycle?
In this type of life cycle of a parasite, it might probably’t survive inside one host solely. They must have a variety of hosts so that they will reproduce further. A complicated type of parasite have this type of life cycle. They infect many host and are that is the rationale further virulent than straightforward parasites. For their meals and shelter, they depend upon host cell. If parasites would not have been able to harm the host cell they they could have died, their existence would have gotten right here to an end. Some parasites are moreover acknowledged to set off good diploma of harm to the host cell, finally killing it. Such parasites depend upon the destruction of many host cells. Main goal of these parasites for having an indirect life cycle is commonly copy.
Why do parasites depend on host cells?
For their meals and shelter, they depend upon host cell. If parasites would not have been able to harm the host cell they they could have died , their existence would have gotten right here to an end. Some parasites are moreover acknowledged to set off good diploma of harm to the host cell, finally killing it.
Do parasites get revenue from a positive parasite?
In some circumstances, host cell even will get revenue from a positive parasite. Some parasites are acknowledged to set off harm to the host. Simple parasite reproduce and keep inside single host, that’s an occasion of direct life cycle. In direct life cycle, parasite lives its full life contained within the host and reproduce inside it.
Is there a single host in the direct life cycle?
In direct life cycle, there could also be usually single host. In indirect life cycle, there are a variety of hosts.
Do parasites have a direct or indirect life cycle?
Simple parasites have direct life cycle whereas sophisticated parasites have indirect life cycle. Parasite is known to complete its full life in just one host in direct life cycle nevertheless it swap hosts in indirect life cycle.
What is direct life cycle?
Direct life cycles are characterized by direct penetration of the spider host through the integument by the infective stage larva following emergence from the egg.
How many hosts are involved in a direct life cycle?
Direct life cycles involve only one definitive host, whereas indirect life cycles involve a definitive host and one or more intermediate hosts.
How do capillaria spread?
Capillaria species have direct life cycles and can spread from one fish to another by ingestion of infective larvae.
Is a mermithid a life cycle?
The large number of non-web spinning, cursorial Lycosidae (Table 1; 38% of all species, excluding nomina dubia) with undescribed mermithids, suggests that a direct life cycle may be involved in some instances.
Do spiders eat fly insects?
For example, winged, flying insects are more likely to be consumed by web spinning or foliage/flower hunting spiders than they are by non-web spinning, ground hunters or burrowing, sit and wait predators, which can be expected to feed primarily on non-flying, mainly fully terrestrial prey and are thus, more likely to be hosts to mermithids with a direct life cycle. Interestingly, the ecology of all but one of the spiders reported by Poinar & Benton (1986) as hosts of A.
What is the life cycle of a parasite?
Parasites are small microscopic organisms that live inside a host cell. Some parasites are obligate parasites, that is they live and reproduce inside a host cell while some can even reproduce outside a host cell. In some cases, host cell even gets benefit from a certain parasite. Some parasites are known to cause harm to the host. Simple parasite reproduce and live inside single host, this is an example of direct life cycle. In direct life cycle, parasite lives its entire life inside the host and reproduce inside it. Such animals or organisms that harbor parasites are suppose to provide shelter and food to the parasite and such a host is called definitive host.
What is Direct Life Cycle?
In some cases, host cell even gets benefit from a certain parasite. Some parasites are known to cause harm to the host. Simple parasite reproduce and live inside single host, this is an example of direct life cycle. In direct life cycle, parasite lives its entire life inside the host and reproduce inside it. Such animals or organisms that harbor parasites are suppose to provide shelter and food to the parasite and such a host is called definitive host.
Why do parasites depend on host cells?
For their food and shelter, they depend upon host cell. If parasites would not have been able to harm the host cell they they would have died, their existence would have came to an end. Some parasites are also known to cause great degree of harm to the host cell, eventually killing it.
What is the difference between direct and indirect life cycles?
Key Differences between Direct Life Cycle and Indirect Life Cycle 1 In direct life cycle, there is usually single host. In indirect life cycle, there are multiple hosts. 2 In direct life cycle parasites are not as virulent as in indirect life cycle. 3 The main purpose for having multiple hosts in indirect life cycle of a parasite is reproduction. 4 Simple parasites have direct life cycle while complex parasites have indirect life cycle. 5 Parasite is known to complete its whole life in just one host in direct life cycle but it switch hosts in indirect life cycle.
Why do parasites need multiple hosts?
They need to have multiple hosts so that they can reproduce more. A complex type of parasite have this type of life cycle. They infect many host and are that is why more virulent than simple parasites. For their food and shelter, they depend upon host cell.
How many hosts does a parasite have?
Parasite is known to complete its whole life in just one host in direct life cycle but it switch hosts in indirect life cycle.
Is there a single host in a direct life cycle?
In direct life cycle, there is usually single host. In indirect life cycle, there are multiple hosts.
Other versions of this article
Please review our Terms and Conditions of Use and check box below to share full-text version of article.
Abstract
Parasites must reach new hosts and have evolved a variety of strategies to achieve this. For some there is a direct life cycle, with the parasite passing from one member of the host species to another via the infective stage of the life cycle.
Key Concepts
Finding a new host is a formidable challenge for a parasite: variety of strategies evolved to achieve this end.
Where do parasites spend their life cycle?
Some parasites spend most or all of their life cycle in the bloodstream, such as Babesia and Plasmodium species. Parasites, such as Trypanosoma cruzi, might be found in the blood early in an infection (the acute phase) and then at much lower levels later (the chronic phase of infection).
What are some examples of factors that affect whether parasites that can be found in the bloodstream might be spread by?
Blood Transfusions. Many factors affect whether parasites that can be found in the bloodstream might be spread by blood transfusion. Examples of some of the factors include. how much of the parasite’s life cycle is spent in the blood;
What are the most common foodborne parasites?
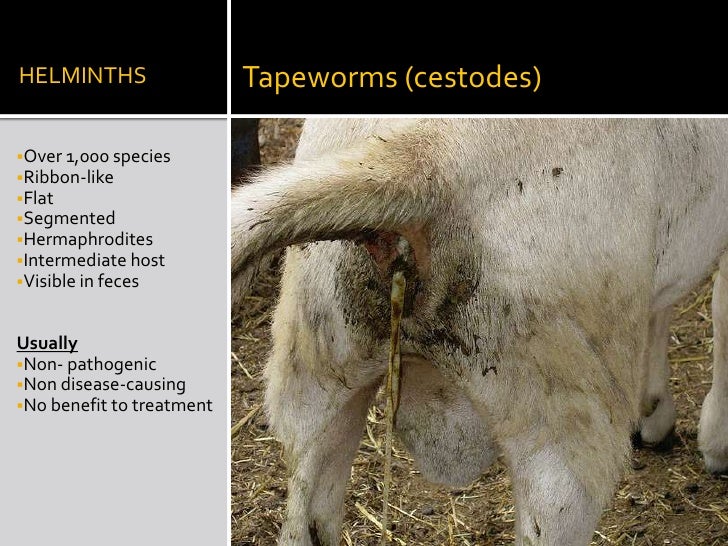
In the United States, the most common foodborne parasites are protozoa such as Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia intestinalis, Cyclospora cayetanensis, and Toxoplasma gondii; roundworms such as Trichinella spp. and Anisakis spp.; and tapeworms such as Diphyllobothrium spp. and Taenia spp.
How does vector-borne disease occur?
Vector-borne transmission of disease can take place when the parasite enters the host through the saliva of the insect during a blood meal (for example , malaria), or from parasites in the feces of the insect that defecates immediately after a blood meal (for example, Chagas disease ).
How to protect your pet from parasites?
Regular veterinary care will protect your pet and your family. There are simple steps you can take to protect yourself and your family from zoonotic diseases caused by parasites. Make sure your pet is under a veterinarian’s care to help protect your pet and your family from possible parasite infections.
What is a zoonotic disease?
A zoonotic disease is a disease spread between animals and people. Zoonotic diseases can be caused by viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi. Some of these diseases are very common. For zoonotic diseases that are caused by parasites, the types of symptoms and signs can be different depending on the parasite and the person.
How are helminths transmitted?
Many of these organisms can also be transmitted by water, soil, or person-to-person contact. Occasionally in the U.S., but often in developing countries, a wide variety of helminthic roundworms, tapeworms, and flukes are transmitted in foods such as. raw vegetables that have been contaminated by human or animal feces.