
Microlaryngoscopy is a procedure in which the larynx is visualized through a microscope. It thus allows a magnified view of the larynx which is not possible on direct or indirect laryngoscopy.
What is a microlaryngoscopy?
A microlaryngoscopy is a surgical procedure that allows a provider to view your vocal cords (also called vocal folds) with a microscope. During this procedure, your provider may also remove lesions (growths) from your vocal folds or correct movement disorders of your larynx (voice box).
What is direct laryngoscopy used for?
Direct laryngoscopy allows visualization of the larynx. It is used during general anesthesia, for surgical procedures of the larynx, and during resuscitation. This tool is useful in multiple hospital settings, from the emergency department to the intensive care unit and the operating room.
What is operative direct microlaryngoscopy (ODM)?
Operative direct microlaryngoscopy remains the gold standard for the assessment of the laryngeal epithelium and can be an invaluable tool in the assessment of certain voice disorders.
What is microlaryngoscopy and removal of lesions of vocal cords?
Microlaryngoscopy and Removal of Lesions. When there are lesions on the vocal cord that need to be removed, such as polyps or cysts, this is performed during a surgery called “microlaryngoscopy”, which literally means to view the vocal cords using a microscope.
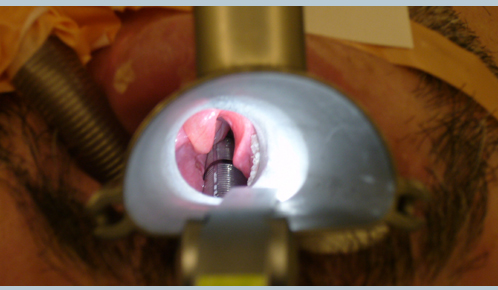
What is the difference between laryngoscopy and Microlaryngoscopy?
Problems involving the vocal cords result in varying degrees of hoarseness, breathing or speech abnormalities, and laryngoscopy is commonly used to evaluate these symptoms. Microlaryngoscopy gives the surgeon the ability to view the larynx in detail.
What does a Microlaryngoscopy mean?
A microlaryngoscopy is a procedure that allows your provider to view your vocal folds with a microscope. If you have any growths or vocal cord lesions, your provider may remove them with small instruments or a laser.
What is direct suspension Microlaryngoscopy?
In suspension microlaryngoscopy, the laryngoscope is suspended to allow the surgeon to work with both hands. A surgical microscope is used to provide magnification, better visualization and to deliver a LASER beam.
What is the difference between direct and indirect laryngoscopy?
Direct Laryngoscopy: Insertion of the endotracheal tube by a method of directly visualizing the vocal cords. Examples: Macinotosh blade, Miller Blade. Indirect Laryngoscopy: Insertion of the endotracheal tube by a method of indirectly visualizing the vocal cord, either using a video camera or optics (mirrors).
How long is Microlaryngoscopy surgery?
Microlaryngoscopy with Excision This procedure typically lasts 30 to 60 minutes and takes place in the operating room. General anesthesia is required. During a microlaryngoscopy, your surgeon accesses your vocal cords through the mouth using a laryngoscope.
Can I talk after Microlaryngoscopy?
Recovery from Microlaryngoscopy with Excision Complete voice rest is a vital part of a full recovery. After the procedure, you should not speak for three to five days to allow your vocal cords to heal.
How is a direct laryngoscopy performed?
Direct laryngoscopy. Your doctor uses a laryngoscope to push down your tongue and lift up the epiglottis. That's the flap of cartilage that covers your windpipe. It opens during breathing and closes during swallowing. Your doctor can do this to remove small growths or samples of tissue for testing.
How is a direct laryngoscopy done?
Laryngoscopy can be used to take biopsy samples of the vocal cords or nearby parts of the throat (to find out if an abnormal area is cancer, for example). This is done by passing long, thin instruments down the laryngoscope, such as small forceps (tweezers) to collect the samples.
What is a Microlaryngoscopy biopsy?
A microlaryngoscopy is performed under brief anesthesia and involves the insertion of an endoscope through the nose and into the throat. If swelling is present, the surgeon will perform a biopsy (take a tissue sample) inside the larynx. Since only a tiny piece of tissue is removed, stitches are not necessary.
How do you prepare for a laryngoscopy?
Preparing for the procedure Do not eat or drink for 8 hours before the procedure. Rigid laryngoscopy is done with a general anesthetic. Be sure you have someone to take you home. Anesthesia and pain medicine will make it unsafe for you to drive or get home on your own.
Is a laryngoscopy painful?
Direct flexible laryngoscopy It may feel strange to have the doctor put the scope up your nose. But it should not hurt. You will still be able to breathe. If a spray anesthetic is used, it may taste bitter.
How long does a laryngoscopy last?
Laryngospasm (luh-RING-o-spaz-um) is a condition in which your vocal cords suddenly spasm (involuntarily contract or seize). As a result, your airway becomes temporarily blocked, making it difficult to breathe or speak. Laryngospasms are rare and typically last for fewer than 60 seconds.
How long does it take for vocal cords to heal?
You need to allow time for your vocal folds to heal before returning to full voice use. If you are a singer or do use your voice a lot, you may need four to six weeks of careful voice use for a full recovery, he says.
What is Microlaryngoscopy and biopsy?
A microlaryngoscopy is performed under brief anesthesia and involves the insertion of an endoscope through the nose and into the throat. If swelling is present, the surgeon will perform a biopsy (take a tissue sample) inside the larynx. Since only a tiny piece of tissue is removed, stitches are not necessary.
How long does it take for vocal cords to heal after surgery?
For the First Few Weeks Continue to drink plenty of fluids, avoid irritants, and use the humidifier at night. While your vocal cords are coming back to health and you are relearning how to use your voice in healthy ways, it will take a full 6 to 8 weeks to recover.
Can I drink alcohol after Microlaryngoscopy?
You must have an adult with you on the night after surgery. You should not be alone in case you need help or have an emergency. For the first 24 hours after your surgery: o Do not drive a motor vehicle, operate machinery or sign legal papers. o Do not drink any alcohol.
What is the purpose of a microlaryngoscopy?
Microlaryngoscopy and rigid bronchoscopy are performed with the primary goal of identifying anatomic levels of airway obstruction from the larynx to the carina. The supraglottis is evaluated with attention given to the possibility of supraglottic obstruction such as laryngomalacia and supraglottic stenosis. The vocal fold level is then evaluated for posterior glottic stenosis, anterior glottic web, and laryngeal cleft. If vocal fold immobility is suspected or seen on the fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) or on voice evaluation, the cricoarytenoid joints should be palpated to determine if there is any fixation of the joint.
What type of laryngoscope is used for a microlaryngoscopy?
Microlaryngoscopy is performed with a rigid anterior commissure-type laryngoscope such as a Benjamin or Parsons placed in the vallecula (Fig. 2) and used to expose the endolarynx and subglottic airway.
What is a ML&B?
Direct rigid telescope microlaryngoscopy and rigid bronchoscopy (ML&B) can be useful as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool for upper airway and subglottic pathology (Fig. 13-1 ). In contrast to bedside flexible laryngoscopy, general anesthesia is required. Evaluation with ML&B should be considered when a need for surgical intervention is determined based on findings during NPL or when better visualization of the airway is required.
Why is a posterior commissure laryngoscope important?
A posterior commissure laryngoscope can be quite helpful in providing appropriate visualization and exposure, because the laryngoscope has a notch to secure the ETT in anterior position. As in the rest of the larynx, angled telescopes can also be quite beneficial in helping to determine the extent of the RRP lesions.
What is the gold standard for laryngoscopy?
Operative direct microlaryngoscopy remains the gold standard for the assessment of the laryngeal epithelium and can be an invaluable tool in the assessment of certain voice disorders. Operative laryngoscopy allows for examination of the larynx through palpation of the laryngeal epithelium and the cricoarytenoid joint as well as offers the opportunity to perform diagnostic biopsy or phonomicrosurgery. Difficult laryngeal exposure may limit the utility of direct laryngoscopy in certain patients, especially in the population with head and neck cancer, although angled telescopes and curved or flexible instrumentation may help overcome these challenges.43
How to remove internal laryngocele cyst?
Internal laryngocele/saccular cysts should be removed by direct suspension microlaryngoscopy and CO2 laser.
How is rigid bronchoscopy performed?
Rigid bronchoscopy is performed using a combination of Hopkins rod telescopes and rigid bronchoscopes. The subglottis is evaluated initially. If subglottic stenosis is present, it is classified by the Cotton-Myer scale 1 and sized using appropriate endotracheal tubes ( Table 69-1 ). Additionally, the length of stenosis and the proximity to the vocal folds is assessed and documented. If a tracheotomy is in place, attention is paid to the evaluation of the suprastomal area, considering the possibility of suprastomal collapse, granuloma, intratracheal skin tract, and high tracheotomy. The trachea is evaluated to the level of the carina, looking for additional pathology, including tracheal stenosis, complete tracheal rings, tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF), TEF pouches, vascular compression, and tracheomalacia.
Which laryngoscope expands both proximally and distally to provide excellent exposure for supraglo?
Weerda laryngoscope: Expands both proximally and distally to provide excellent exposure for supraglottic surgery
Which laryngoscope is best for laser surgery?
Dedo laryngoscope: The "workhorse" provides adequate exposure of the glottis in most patients; limited for laser surgery by absence of smoke evacuation port. Ossoff-Karlan laryngoscopes: Good exposure but cannot be used in all patients because of larger size; best for laser surgery because of smoke evacuation port.
Can you purchase a dental protector for a suspension laryngoscopy?
Less expensive dental protectors may be purchased and prepared by the patient - see Custom Dental Guards for Micro Direct Laryngoscopy (Suspension Laryngoscopy)
Is a biopsy of a suspected cancer more likely to result in dysphonia than a small biopsy?
A large biopsy of a cancer to be treated with irradiation is more likely to result in greater dysphonia than a small biopsy. A small biopsy of a suspected cancer does not sample the lesion as well as an excisional biopsy.
Does videotroboscopic imaging of the larynx decrease the use of microlaryngoscopy?
Use of videostroboscopic equipment with improved imaging of the larynx in the clinical setting has decreased the use of microlaryngoscopy for diagnostic purposes. The capacity to evaluate the undersurface of the vocal folds and to palpate, manipulate, and possibly offer a temporary (trial) injection maintains the value of microdirect laryngoscopy as a diagnostic tool.
What is the vertical segment of a microlaryngeal probe?
The vertical segment on this probe is 4 millimeters in length and is shown here next to a penny for a sense of scale.
How many instruments are used in microlaryngeal surgery?
In general, microlaryngeal surgery is performed with two instruments at a time, one in each of the surgeon’s hands.
What are the distal ends of laryngoscopes used for?
The distal ends of several different laryngoscopes used in microlaryngeal surgery in adult patients. Note the various sizes and shapes, which are necessary to accommodate the variety of voice boxes (larynges) that exist across the anatomical spectrum.
What does the red arrow on the laryngoscope mean?
Red arrows indicate the breathing (endotracheal) tube, yellow arrows indicate the laryngoscope, and the green arrow shows the illuminated but unmagnified view of the vocal cords. An magnified view through the laryngoscope (see below) is necessary to provide maximal operative precision.
Why is the laryngoscope fixed?
It is typically then temporarily fixed into position in order to free the surgeon’s hands. The laryngoscope contains a light source, which illuminates the inner part of the laryngoscope, since room light is insufficient to view beyond the very outer portions of even the mouth.
What is a binocular microscope?
A binocular operating microscope provides high-powered magnification when working through the laryngoscope. Notice that it is crucial for the surgeon’s arms and wrists to be supported, in order to maximally stabilize the long instruments when performing laryngeal surgery.
What microscope do you use for vocal cord surgery?
At present, microlaryngoscopy (and, in particular, surgery on the vocal cords) is generally performed with either the use of: (1) a binocular operating microscope, or (2) a magnified, rigid telescope.
What is the purpose of laryngoscopy?
Direct laryngoscopy to perform endotracheal intubation is indicated in the emergent setting in perioperative settings or the intensive care setting. In the emergency room, the indications for direct laryngoscopy to perform endotracheal intubation include acute respiratory failure, impending airway collapse indicated by hypoxia or hypercapnia, and airway protection in patients with altered or depressed mental status, upper gastrointestinal bleeding or hematemesis secondary to bleeding from esophageal varices.[4] In the perioperative setting, endotracheal tubes can be placed using direct laryngoscopy for patients receiving general anesthesia, surgeries involving the airway or areas adjacent to it, or surgeries involving unusual positioning, such as spinal surgery, which requires prone positioning.[5] In the intensive care unit, direct laryngoscopy for endotracheal intubation is performed for impending airway collapse, or short-term hyperventilation of patients with increased intracranial pressures in the setting of intracranial hemorrhage, tumors or masses. Intubations in the intensive care unit are also performed to manage copious secretions. [6]
What equipment is used for direct laryngoscopy?
Equipment for direct laryngoscopy also includes adjunct airway management devices such as a "Bougie," which is an ETT introducer, oral and nasal airways, and rescue airway devices such as a Combitube or supraglottic airway tubes. An end-tidal carbon dioxide monitor (capnography) is required to help confirm the appropriate placement of the ETT. Lastly, all direct laryngoscopy equipment includes back-up devices to access the airway, such as video laryngoscopes[13], rescue airway devices (laryngeal mask airway) and if nothing works, a cricothyrotomy or tracheostomy tray. If a difficult airway is known or suspected, the instruments for a surgical airway should be opened and ready before beginning laryngoscopy.
What size ETT for tracheal intubation?
Direct laryngoscopy and subsequent endotracheal intubation require a laryngoscope handle, blades (Macintosh or curved, Miller, or straight with a curved end, Jackson-Wisconsin or straight), appropriate sized ETT with a stylet and an ETT one size bigger and one smaller. Most tracheal intubations in an emergency or perioperative setting in adults can be accomplished with 7.5 mm cuffed tubes. In the intensive care setting, larger tubes are preferred as these make tracheal suctioning and flexible bronchoscopy possible through the ETT; in addition, larger tubes cause less resistance to flow of air through a ventilator, but the tube must not be so large as to increase risk of arytenoid injury or subglottic stenosis. In addition to a laryngoscope, blade, and ETT, appropriate equipment includes sterile lubricant for the ETT cuff and balloon and at least a 10 cc syringe to inflate the ETT balloon after successful placement. [12]
What is the importance of a suctioning device before a laryngoscopy?
Before direct laryngoscopy can begin, it is important to place the patient on cardiac monitoring and a continuous pulse oximeter, the suctioning device should be prepared and accessible for immediate use, appropriate lighting and positioning of the patient as successful preparation of patient and equipment are equally important to the procedure. [11]
Where is the laryngoscope inserted?
The laryngoscope is then inserted in the right side of the mouth, and the blade is then used to sweep the tongue to the left, then the blade is smoothly advanced to the epiglottis. If a Macintosh blade is used, it is advanced to the vallecula, and if a Miller blade is used, it is advanced over the epiglottis to the entrance of the trachea proximal to the vocal cords.
Is laryngoscopy contraindicated?
Direct laryngoscopy has few absolute contraindications. Such absolute contraindications involve supraglottic and glottic lesions that would prohibit the advancement of the endotracheal tube (ETT) such as high-grade subglottic or glottic stenosis or complete obstruction by supraglottic or glottic tumors. Additionally, blunt trauma to larynx resulting in laryngeal fracture or disruption of the laryngotracheal junction can become worse in the setting of traction from laryngoscope blade, placement of the ETT or pressure from the ETT stylet, which can promote the creation of a false lumen in the trachea or cause perforation through the trachea.[7] In these patients, a surgical airway is required.
Can cricoid pressure be applied to the anterior airway?
In the cases of very anterior airways, mild-to-moderate cricoid pressure can be applied by an assistant while lifting the laryngoscope to help visualize the airway.
What is the procedure to remove vocal cords?
When there are lesions on the vocal cord that need to be removed, such as polyps or cysts, this is performed during a surgery called “microlaryngoscopy”, which literally means to view the vocal cords using a microscope. With the patient completely asleep in the operating a “laryngoscope” or hollow metal tube is placed into the mouth to open ...
Why is vocal cord surgery so delicate?
This is a very delicate surgery because the vocal cords are less than two inches in length. It is critical during this surgery to leave the uninvolved layers of the vocal cord alone to prevent scar. After surgery patients are asked to minimize voice use to allow the vocal cords to heal.
What are the complications of laryngoscopy?
It’s rare to have problems after a laryngoscopy, but it can still happen. Some of these complications include: 1 Pain or swelling in the mouth, tongue, or throat 2 Bleeding 3 Hoarseness 4 Gagging or vomiting 5 Infection
How long does it take to gag with a laryngoscopy?
Many doctors now do this kind, sometimes called flexible laryngoscopy. They use a small telescope at the end of a cable, which goes up your nose and down into your throat. It takes less than 10 minutes.
What is the procedure called when you have a cough?
What Is Laryngoscopy ? Doctors sometimes use a small device to look into your throat and larynx, or voice box. This procedure is called laryngoscopy. They may do this to figure out why you have a cough or sore throat, to find and remove something that’s stuck in there, or to take samples of your tissue to look at later.
What is the procedure to open your nasal passages?
Sometimes a decongestant is used to open your nasal passages as well. Gagging is a common reaction with this procedure as well. Direct laryngoscopy. This is the most involved type. Your doctor uses a laryngoscope to push down your tongue and lift up the epiglottis. That’s the flap of cartilage that covers your windpipe.
How long does it take to see a doctor in the mirror?
The doctor shines a light into your mouth to see the image in the mirror. It can be done in a doctor’s office in just 5 to 10 minutes.
How does a doctor look at your throat?
This is the simplest form. Your doctor uses a small mirror and a light to look into your throat. The mirror is on a long handle, like the kind a dentist often uses, and it’s placed against the roof of your mouth. The doctor shines a light into your mouth to see the image in the mirror.
How long does it take to see a doctor in the mirror?
The doctor shines a light into your mouth to see the image in the mirror. It can be done in a doctor’s office in just 5 to 10 minutes.
What type of laryngoscope is used to open the windpipe?
Direct laryngoscopy. This is the most involved type. Your doctor uses a laryngoscope to push down your tongue and lift up the epiglottis. That’s the flap of cartilage that covers your windpipe. It opens during breathing and closes during swallowing.
Where is the larynx located?
Laryngoscopy is a visual examination below the back of the throat, where the voice box (larynx) containing the vocal cords is located. ... The procedure is relatively painless, but the idea of having a scope inserted into the throat can be a little scary, so it helps to understand how a laryngoscopy is done.
Can you feel pain after microlaryngoscopy?
Most people who have microlaryngoscopy return home on the day of surgery. You may experience minor discomfort in your throat or soreness in your jaw, but pain is rarely severe.
