
What is discontinuous data? Alternatively, discontinuous data collection systems are those that capture only a sample of behavior during an observation. These systems involve dividing an observation into equal duration intervals, and scoring the occurrence or nonoccurrence of behavior within each interval (Mudford, Taylor, & Martin, 2009).
What is discontinuous data collection?
Discontinuous data collection systems measure only a sample of behavior that occurs by breaking the session down into small increments of time. Although these data are potentially less accurate than continuous data collection methods, they are easier to collect in busy environments.
What is the difference between continuous and discontinuous methods?
Continuous methods provide the most accurate data, although they can be difficult to utilize in busy environments. Discontinuous methods offer an estimate of the occurrence of behavior, but can be used even when staff can’t attend to the learner’s behavior throughout the entire session.
What is continuous data collection in psychology?
Continuous Data Collection Continuous data collection methods measure every occurrence of a behavior. These methods either count each instance of the behavior or the specific amount of time a behavior occurs. These methods allow you to measure behavior along the basic dimensions and accurately detect change in the behavior.
What is discontinuous behavior analysis?
Discontinuous methods offer an estimate of the occurrence of behavior, but can be used even when staff can’t attend to the learner’s behavior throughout the entire session. The help you need! Download this infographic to help you keep this information fresh! See below to download data sheet templates!
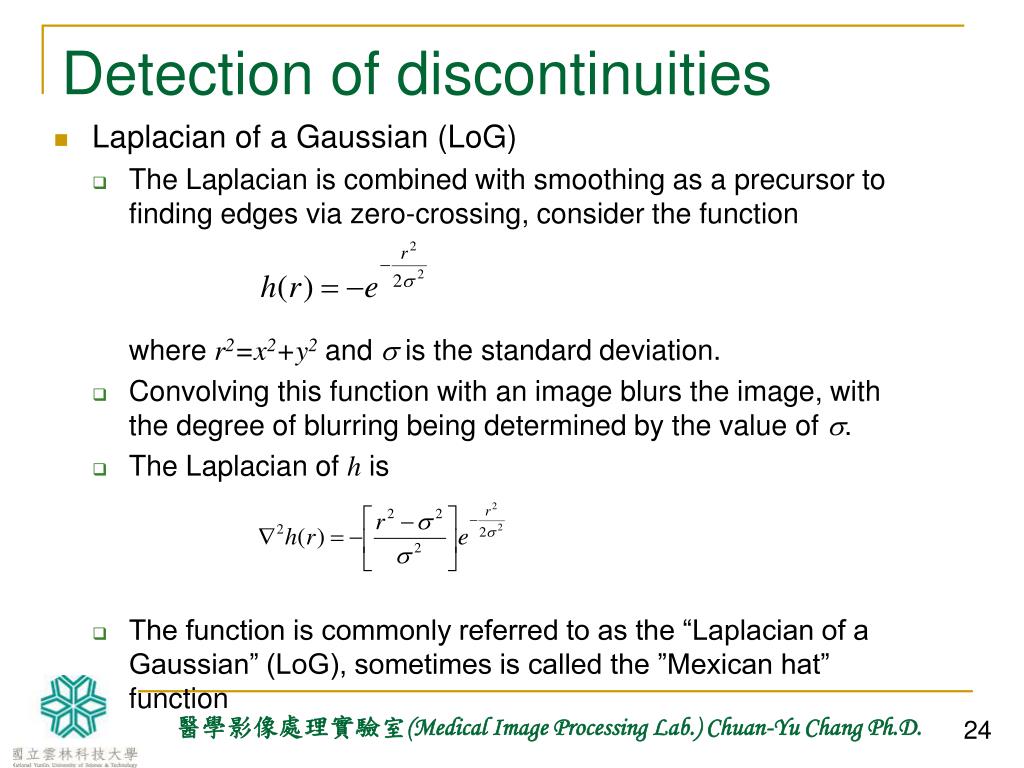
What are the 3 types of discontinuous measurement?
A form of time sampling measurement that does not catch every instance of behavior. There are three types of time sampling procedures: partial interval time sample, whole interval time sampling, and momentary time sampling.
What is a discontinuous data measurement?
Discontinuous measurement involves dividing an observation into intervals and recording whether a behavior occurred during some or all of each interval (i.e., interval recording) or at the exact time of observation (i.e., momentary time sampling; MTS).
What does discontinuous data collection require?
Discontinuous data collection systems measure only a sample of behavior that occurs by breaking the session down into small increments of time. Although these data are potentially less accurate than continuous data collection methods, they are easier to collect in busy environments.
What is discontinuous measurement ABA examples?
Some examples are as follows: 1) a 1-hour session may be broken down into 3 minute intervals; 2) a 10 minute observation may be broken down into 1 minute intervals; and 3) a 5 minute observation may be broken down into 30 second intervals.
What is discontinuous data example?
Some discrete data examples are: The number of customers who bought different items. The number of computers in each department. The number of items you buy at the grocery store each week.
What is the difference between continuous and discontinuous data?
The primary difference, though, between discrete and continuous data is that discrete data is a finite value that can be counted whereas continuous data has an infinite number of possible values that can be measured.
What is the difference between discrete and discontinuous?
A relation is said to be discrete if there are a finite number of data points on its graph. Graphs of discrete relations appear as dots. Infinite discontinuities occur when a function has a vertical asymptote on one or both sides. This will happen when a factor in the denominator of the function is zero.
What makes function discontinuous?
A discontinuous function is a function that has a discontinuity at one or more values mainly because of the denominator of a function is being zero at that points. For example, if the denominator is (x-1), the function will have a discontinuity at x=1.
What are examples of continuous measurements?
A continuous measurement can be meaningfully divided into finer levels. It can be measured on a scale or continuum and can have any numeric value. For example, you can measure your height at very precise scales — meters, centimeters, millimeters, etc. The amount of time required to complete a project.
What are the continuous measurement systems ABA?
2:066:26Continuous and Discontinuous Measurement EXPLAINED by a ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThis continuous measurement is a sample of how often behavior occurs in a given observation. ThisMoreThis continuous measurement is a sample of how often behavior occurs in a given observation. This consider which measurement systems are popular in both practice. And an applied research in the mud
What is discontinuous interval?
Discontinuities may be classified as removable, jump, or infinite. A function is continuous over an open interval if it is continuous at every point in the interval. It is continuous over a closed interval if it is continuous at every point in its interior and is continuous at its endpoints.
What are the types of discontinuous measurement?
3 Types of Discontinuous measurement (aka, time sampling) Momentary time sampling and partial and whole-interval recording are discontinuous methods. These methods all either over or underestimate the rate of the target behavior because of the way that it is measured.
What is the difference between discontinuous and discrete?
A relation is said to be discrete if there are a finite number of data points on its graph. Graphs of discrete relations appear as dots. Infinite discontinuities occur when a function has a vertical asymptote on one or both sides. This will happen when a factor in the denominator of the function is zero.
What is a continuous data measurement?
Continuous data is data that can be measured on an infinite scale, It can take any value between two numbers, no matter how small. The measure can be virtually any value on the scale.
What are examples of continuous measurement?
A continuous measurement can be meaningfully divided into finer levels. It can be measured on a scale or continuum and can have any numeric value. For example, you can measure your height at very precise scales — meters, centimeters, millimeters, etc. The amount of time required to complete a project.