A dissecting aneurysm is a tear in one of an artery’s several linings. It can leak blood into the other layers and balloon out or block the artery. What causes a brain aneurysm? Some events encourage the development or rupture of an aneurysm in the brain.
What is an aneurysm and how is it caused?
An aneurysm occurs when part of an artery wall weakens, allowing it to abnormally balloon out or widen. The causes of aneurysms are sometimes unknown. Some people are born with them. They can also be hereditary. Aortic disease or an injury may also cause an aneurysm. A family history of aneurysm may increase your risk for developing an aneurysm ...
What is considered a large ventricular aneurysm?
Aneurysms range in size, from small – about 1/8 inch – to nearly one inch. Aneurysms larger than one inch are called giant aneurysms, pose a particularly high risk and are difficult to treat. The exact mechanisms by which cerebral aneurysms develop, grow and rupture are unknown.
Does aneurysm require surgery?
Some patients benefit most from repair using a stent, others need traditional open surgery, and still others benefit from hybrid procedures that blend open repair with the use of stent grafts. If an aneurysm is very small, it may not require surgery initially. In fact, most patients who are evaluated for aneurysms do not need surgery.
What are the symptoms of a carotid aneurysm?
- slight facial drooping
- excessive tiredness or sleeping
- slight muscle weakness in one side of the body
- slurred speech or difficulty speaking
- dizziness
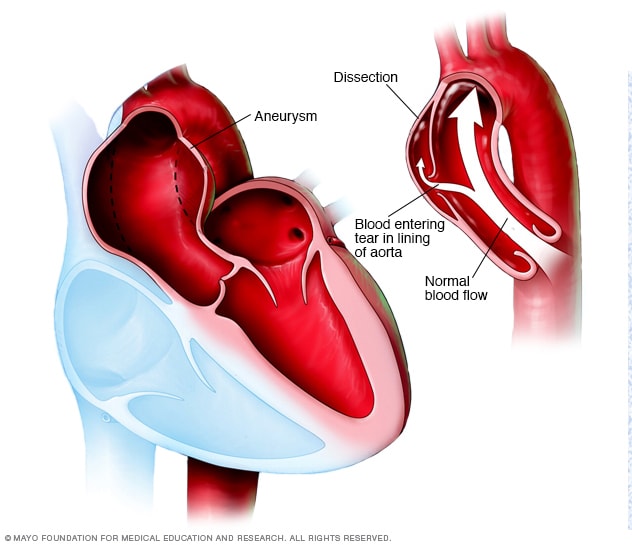
What causes a dissecting aortic aneurysm?
It's believed that most aortic dissections are caused by an underlying vulnerability that may be inherited. In others, the stress to the aortic wall from constant high blood pressure can weaken the aorta wall in susceptible people, resulting in a tear and dissection.
What is the difference between an aneurysm and a dissection?
Aneurysms can occur in any vessel, most notably in the brain, heart, thoracic aorta, and abdominal aorta. A dissection is a tear of the inside layer of a blood vessel wall that allows blood to flow between the layers that make up the vessel wall and separate these layers.
What is a dissecting aneurysm in brain?
Dissecting aneurysm. This type is caused by a tear along the length of the artery in the inner layer of the artery wall. Blood leaks in between the layers of the wall. It may cause 1 side of the artery wall to balloon out. Or it may block blood flow through the artery.
Is a dissecting aneurysm an emergency?
Aortic dissection involving the ascending aorta is a cardiac surgical emergency. Aortic dissection limited to the descending thoracic and/or the abdominal aorta can often be managed medically, unless there is evidence of end-organ ischemia, progression, or rupture.
How is a dissecting aneurysm treated?
TreatmentSurgery. Surgeons remove as much of the dissected aorta as possible and stop blood from leaking into the aortic wall. ... Medications. Medications are given to reduce heart rate and lower blood pressure, which can prevent the aortic dissection from worsening.
What are the symptoms of a dissecting aneurysm?
Signs and symptoms that a thoracic aortic aneurysm has ruptured or dissected include:Sharp, sudden pain in the upper back that spreads downward.Pain in the chest, jaw, neck or arms.Difficulty breathing.Low blood pressure.Loss of consciousness.Shortness of breath.Trouble swallowing.
What is the life expectancy after surviving a brain aneurysm?
As more time passes with a ruptured aneurysm, the likelihood of death or disability increases. About 75% of people with a ruptured brain aneurysm survive longer than 24 hours. A quarter of the survivors, though, may have life-ending complications within six months.
What is the most common site for a dissecting aneurysm?
The most common location of an aneurysm is the aorta, which carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the body. The thoracic aorta is the short segment of the aorta in the chest cavity.
Can you live a normal life after a brain aneurysm?
With rapid, expert treatment, patients can often recover fully. An unruptured brain aneurysm may cause zero symptoms. People can live with them for years before detection. If a brain aneurysm is unruptured, no blood has broken through the blood vessel walls.
What type of aneurysm is fatal?
Cerebral Aneurysm While cerebral aneurysms can be tiny and not cause any problems, larger ones can rupture causing bleeding in the brain and potentially becoming fatal.
What is life expectancy after aortic dissection surgery?
Acute type A aortic dissection (AAD) is a life-threatening emergency that carries a high mortality rate without surgical treatment [1,2]. Surgical mortality has been estimated to range from 9% to 30%, and survival rates of 51–82% at 5 years have been reported [3–9].
How big does an aneurysm have to be before they do surgery?
If the aneurysm is more than 5.5 centimeters in size, or if it's rapidly getting larger, your doctor may recommend surgery to repair the aneurysm. In many cases, doctors will run a catheter through the patient's femoral artery in the groin to the site of the aneurysm in the aorta, then implant a stent graft.
Is an aortic dissection the same as an aneurysm?
An aortic dissection is a life-threatening condition that develops when there is a split in one or more layers of the aortic artery wall, which can be caused by a ruptured aneurysm.
Is dissection a type of aneurysm?
Dissecting aneurysms are not true aneurysms but rather hematomas within the arterial media that occur almost exclusively in the aorta. An intimal tear allows access of blood to the media, and luminal blood pressure causes propagation of the thrombus through the arterial media over the course of hours to days (Fig.
Does dissection lead to aneurysm?
An aortic dissection may also cause abnormal widening or ballooning of the aorta (aneurysm). The exact cause is unknown, but more common risks include: Aging. Atherosclerosis.
What are the 3 types of aneurysms?
There are three types of aneurysms: abdominal aortic, thoracic aortic, and cerebral.
What is the name of the dissection of the aorta?
WALES: Maira's killers are locked up; PENSIONER DIED AFTER 'CALLOUSLY EXECUTED' BURGLARY. Aortic dissection, also called dissecting aneurysm of the aorta, is a localized dilatation of the aorta characterized by a longitudinal dissection between the outer and middle layers of the vascular wall. [1] .
What is dissecting aneurysm?
dissecting aneurysm one resulting from hemorrhage that causes lengthwise splitting of the arterial wall, producing a tear in the inner wall (intima) and establishing communication with the lumen of the vessel. It usually affects the thoracic aorta (see aortic dissection) but can also occur in other large arteries.
Why is it important to be alert to an aneurysm?
One should be particularly alert to the possibility of an aneurysm in persons with a history of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, or peripheral vascular disease. Aneurysms tend to increase in size, presenting a problem of increasing pressure against adjacent tissues and organs and a danger of rupture.
How to tell if an aneurysm is a tumor?
The chief signs of an arterial aneurysm are the formation of a pulsating tumor, and often a bruit (aneurysmal bruit) heard over the swelling. Sometimes there are symptoms from pressure on contiguous parts. The most common site for an arterial aneurysm is the abdominal aorta.
What is the term for the thinning of the wall of the left ventricle?
cardiac aneurysm thinning and dilatation of a portion of the wall of the left ventricle, usually a consequence of myocardial infarction. cerebral aneurysm berry aneurysm. cirsoid aneurysm dilatation and tortuous lengthening of part of an artery; called also racemose aneurysm.
What is an arteriosclerotic aneurysm?
arteriosclerotic aneurysm an aneurysm arising in a large artery, most commonly the abdominal aorta, as a result of weakening of the wall in severe atherosclerosis; called also atherosclerotic aneurysm.
How is varicose aneurysmone formed?
varicose aneurysmone formed by rupture of an aneurysm into a vein.
What causes aortic dissection?
Most patients under 40 years of age with dissecting aneurysms have Marfan syndrome or have been recently pregnant. Both of these conditions result in the accumulation of mucopolysaccharide ground substance within the media of the aorta, with loss and disorder of elastin fibers. In Marfan syndrome, this lesion (called cystic medial necrosis) is caused by point mutations in the fibrillin gene that prevent normal deposition of elastin in the extracellular matrix. These connective tissue abnormalities predispose patients to aortic dissection. In patients older than 40 years, typical risk factors for aortic dissection are hypertension and bicuspid aortic valve (which results in abnormal flow and endothelial injury).
Why is LVEDP higher in acute AR?
Because of the much higher left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) in the acute form. The acute development of a severe aortic valvular leak causes a much higher LVEDP in the normal-sized LV of patients with acute AR. Patients with chronic AR commonly have a dilated LV with increased compliance capable of accommodating large blood volumes without a significant rise of LVEDP.
What is MIP imaging?
1.6 ). In particular, maximum-intensity projection (MIP) images of the intracranial circulation provide an easy way to detect proximal arterial occlusions in stroke patients, for example, that may be amenable to catheter-based treatments. These MIP images depict the highest density along a particular imaging ray. For evaluation of the intracranial arteries, MIP images reformatted to 20–30 mm thickness with 3–5 mm overlap can be created in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes quickly at the scanner console by the CT technologist. More complex postprocessing techniques include curved reformats, multiplanar volume reformats, and volume-rendered images. Curved reformats depict the entire course of a particular vessel in a single two-dimensional image, and provide a good evaluation of arterial steno-occlusive disease in the neck, such as at the carotid bifurcation. The 3D volume-rendered and other surface techniques are less helpful for ischemic stroke evaluation, but are routinely used in aneurysm detection and treatment planning ( Fig. 1.7 ).
What is the most common artery that is affected by an aneurysm?
Entry of blood into this cavity can occlude branches of the aorta at that site. The thoracic aorta is the most common artery affected in this process. The most prominent symptom of this condition is a very sudden onset of excruciating pain which may radiate to the back and shoulder. If the condition occurs proximal to the origin of the left subclavian artery it can occlude the coronary arteries and the head and neck vessels.
What causes a diastolic rumble in AR?
A much shorter and softer diastolic rumble results from the rapid elevation of LVEDP in acute AR and its rapid equilibration with aortic pressure. Another ausculatory manifestation of the rapid rise of LVEDP is premature mitral valve closure that is also considered a reliable echocardiographic sign of acute AR.
What is the elephant trunk technique?
In some specific situations when the pathology of aortic arch (aneurysm, dissection), acute or chronic, extends into descending aorta, a “technique of elephant trunk,” described by Borst, is a procedure used to facilitate staged surgery for the aortic arch and the distal aortic segments [49].
What prostheses were used in the Hannover surgery?
The Hannover surgical team used three different prostheses (Chavan–Haverich, Jotec–Evita, and Thoraflex) for frozen “elephant trunk,” during 10 years, to treat aortic aneurysm, and dissection of aortic arch and descending aorta in a single-stage operation ( Fig. 31.9 ). They reported good results.
What is an aortic aneurysm?
Overview. An aortic aneurysm occurs when a weak spot in the wall of your aorta begins to bulge (left). This can occur anywhere in your aorta. Having an aneurysm increases the risk of rupture or an aortic dissection — a tear in the lining of the aorta, shown in the image on the right.
What is the most dangerous type of aortic dissection?
Aortic dissections are divided into two groups, depending on which part of the aorta is affected: Type A. This more common and dangerous type involves a tear in the part of the aorta where it exits the heart or a tear in the upper aorta (ascending aorta), which may extend into the abdomen. Type B.
What is a dissection of the aorta?
An aortic dissection is a serious condition in which the inner layer of the aorta, the large blood vessel branching off the heart, tears. Blood surges through the tear, causing the inner and middle layers of the aorta to separate (dissect). If the blood-filled channel ruptures through ...
What are the symptoms of aortic dissection?
Typical signs and symptoms include: Sudden severe chest or upper back pain, often described as a tearing, ripping or shearing sensation, that radiates to the neck or down the back. Sudden difficulty speaking, loss of vision, ...
How to reduce risk of aortic dissection?
You can reduce your risk of an aortic dissection by preventing chest injury and taking steps to keep your heart healthy.
What is the term for a narrowing of the aorta at birth?
Hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) Weakened and bulging artery (pre-existing aortic aneurysm) An aortic valve defect (bicuspid aortic valve) A narrowing of the aorta at birth (aortic coarctation) Certain genetic diseases increase the risk of having an aortic dissection, including: Turner's syndrome.
What to do if you have a bicuspid aortic valve?
Wear a seat belt. This reduces the risk of traumatic injury to your chest area. Work with your doctor. If you have a family history of aortic dissection, a connective tissue disorder or a bicuspid aortic valve, tell your doctor.
What is an Aneurysm?
But first, we need to know what an aneurysm is in general! An aneurysm is an external bulge of a blood-containing structure, such as a blood vessel or ventricle of the heart, which expands when the heart contracts (during systole). In more simple terms, an aneurysm is often defined as the localized dilatation of the wall of a blood vessel or ventricle (chamber) of the heart.
What is dissecting aneurysm?
A dissecting aneurysm occurs when blood pierces the intima (inner layer of the blood vessel) and splits the media (middle layer) in a lengthwise manner. This results in blood flowing in between the layers of the blood vessel as well as within the normal lumen (open space) of the blood vessel itself. If that's hard to imagine, then think of ...
Why is aortic dissection considered an emergency?
The reason the aortic dissection is an emergency is because it can rupture. A ruptured aneurysm refers to an aneurysm that has burst open. In other words, the hose has sprung a leak or completely ripped apart. This, as you might expect, is an emergency situation.
What happens when you dissect an aneurysm?
A dissecting aneurysm occurs when blood pierces the intima and tears the media in a lengthwise manner. This is often referenced to with respect to an aortic dissection, which can lead to: Acute chest pain. Dyspnea, or shortness of breath. The inability to speak properly. Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body.
What is the treatment for aortic dissection?
Treatment. An aortic dissection is a life threatening emergency and is treated with: Medications, like beta blockers, which can prevent the aortic dissection from getting any worse. Surgery, where the damaged section of the aorta is removed and replaced with artificial material. Ruptured Aneurysm.
What is a diffuse aneurysm?
A diffuse (fusiform) aneurysm of the abdominal aorta. There are also false aneurysms (pseudoaneurysms), where the internal vessel wall is breached but the blood spill, so to speak, is contained either by the outer layer of the blood vessel (the adventitia) or the tissue surrounding the blood vessel.
What degree does Artem have?
Artem has a doctor of veterinary medicine degree. This lesson is going to define ruptured aneurysms and dissecting aneurysms. You'll learn about other aneurysms in the process, as well as the signs, symptoms, and treatments related to the former two. Create an account.
What is the name of the aneurysm that occurs along the aorta?
Aortic aneurysms include: Abdominal aortic aneurysm. An abdominal aortic aneurysm occurs along the part of the aorta that passes through the abdomen. Thoracic aortic aneurysm. A thoracic aortic aneurysm occurs along the part of the aorta that passes through the chest cavity.
What is the term for a weak spot in the wall of the aorta?
Aortic dissection and aortic aneurysm. Aortic dissection and aortic aneurysm. An aortic aneurysm occurs when a weak spot in the wall of your aorta begins to bulge (left). This can occur anywhere in your aorta.
Where is the aortic aneurysm located?
Aortic aneurysms can occur anywhere in the aorta and may be tube-shaped (fusiform) or round (saccular).
Can an aortic aneurysm burst?
This causes one or more of the layers of the wall of the aorta to separate, which weakens the wall of the aorta. Having an aortic aneurysm also increases your risk that the aneurysm can burst (rupture).