Full Answer
What is a documentary collection?
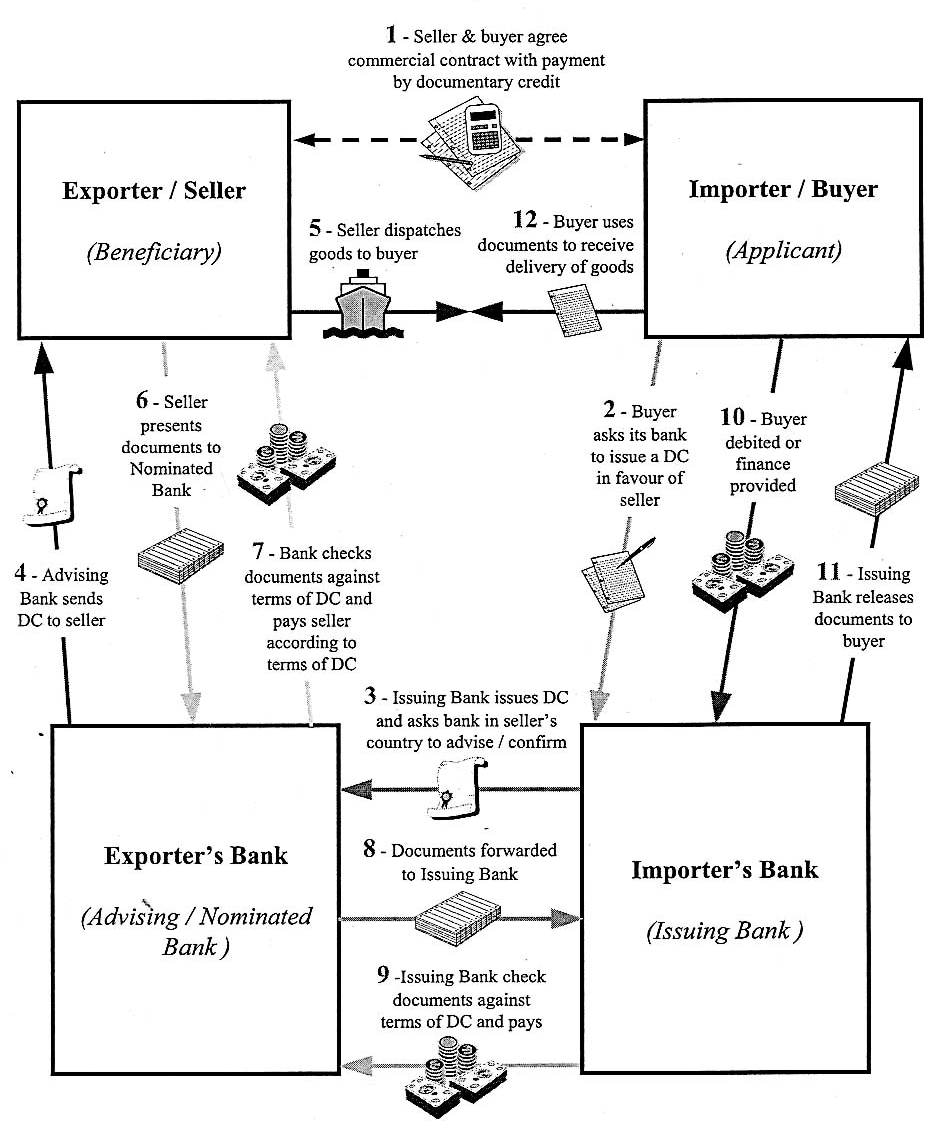
A procedure that allows a seller to give their bank instructions to forward trade-related documents to the bank of a buyer What is Documentary Collection? Documentary collection is a procedure that allows a seller to give their bank instructions to forward trade-related documents to the bank of a buyer.
What is a'documentary collection'?
What is a 'Documentary Collection'. A documentary collection is a trade transaction in which the exporter hands over the task of collecting payment for goods supplied to his or her bank, which sends the shipping documents to the importer’s bank together with payment instructions.
What is document collection and document against payment?
Documents against payment require the importer to pay the face amount of the draft at sight. In other words, the payment must be made to the bank when the buyer is presented with the draft, and before any shipping documents are released. This is the most common form of documentary collection because of the reduced risk for the seller.
How does documentary collection work in international trade?
Documentary collection does not provide sellers or exporters many options in case buyers or importers are unable to meet payment obligations. The process begins with a buyer making an order or a purchase of goods. The exporter or seller then makes arrangements to send the goods to the buyer or importer.
What is a documentary collection transaction?
A documentary collection (D/C) is a transaction whereby the exporter entrusts the collection of payment to the exporter's bank (remitting bank), which sends documents to the importer's bank (collecting bank), along with instructions for payment.
What are the difference between clean payments and documentary payments?
Using documentary collections seller ships the goods and provides draft and documents to the bank. Using clean collection seller provides only draft without transport documents. Clean collection can serve the main documentary transaction or financial transaction.
What are the types of documentary collection?
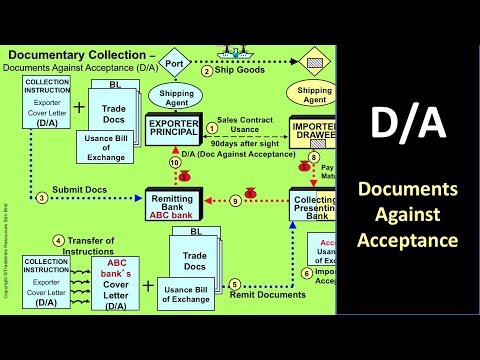
There are two types of Documentary collections: Documents against Payment Collection (D/P): The importer receives the delivery documents only against payment. Documents against Acceptance Collection (D/A):
What is a downside of documentary collection?
The role of the bank is limited and they do not guarantee payment. 2. No verification of the accuracy of the documents. 3. Seller does not get the benefit of a bank guarantee of the payment provided by documentary credit.
WHO issues documentary collection?
A documentary collection refers to apayment collected by a bank at the seller's request against handover of documents to the buyer. (the seller's bank) together with the collection order. The remitting bank sends the documents, together with the necessary instructions, to a bank in the buyer's country.
What is the difference between letter of credit and documentary collection?
A letter of credit is a legally binding document that guarantees payment to a seller. A documentary collection allows a buyer to refuse a shipment if it does not match the standards of excellence. The importer's bank issues the letter of credit, while the exporter's bank issues a documentary collection.
What is the time of payment for documentary collection?
Two Types of Documentary Collection Documents against payment require the importer to pay the face amount of the draft at sight. In other words, the payment must be made to the bank when the buyer is presented with the draft, and before any shipping documents are released.
What is difference between open account and documentary collection?
Open Account Payment – after goods are shipped or received. Documentary Credits – payment is guaranteed by a bank subject to the fulfilment of certain terms and conditions by the importer and exporter. Documentary Collections – payment is handled by banks acting as agents for the importer and exporter.
What is a documentary bill?
Definition of documentary bill : a bill of exchange drawn on a consignee of goods and having appended to it the shipment documents by way of collateral security for its payment.
What is the steps of documentary collection?
What are the steps in documentary collection? The buyer (importer) and seller (exporter) agree on the. ... The exporter, through a freight forwarder, arranges for the. ... The forwarder delivers the goods to the point of departure. ... Export documents and instructions are delivered to the.More items...
Who bears the documentation risk in documentary collection?
If the buyer and seller agree to a delay in payment, the transaction becomes a Time Draft, Documents Against Acceptance, or simply D/A, as illustrated in this lesson. In a documentary collection method of payment, both the buyer and seller bear some risk, and, likewise, both have a measure of security.
What are the types of documentary bills?
Documentary Bills can be in the form of Sight Bill and Acceptance Bill. Method of payment depends on the form of bill used.
What is clean payment?
A payment of cash for which there is no directly associated countervalue.
What is difference between open account and documentary collection?
Open Account Payment – after goods are shipped or received. Documentary Credits – payment is guaranteed by a bank subject to the fulfilment of certain terms and conditions by the importer and exporter. Documentary Collections – payment is handled by banks acting as agents for the importer and exporter.
What is the difference between UCP 500 and 600?
Under UCP 500, banks may not be justified to pay after using up full seven banking days, considering the requirement for reasonable time; whilst under UCP 600, banks may be justified to pay after using up full five banking days.
What is the meaning of a documentary credit?
A Documentary Credit (“D/C”) also known as Letter of Credit (“L/C”) is a method of payment where the buyer's bank guarantees payment to the seller with the condition that the seller has to fulfil the terms specified in the L/C.
Why is it important to use documentary collections?
When to Use Documentary Collections. Documentary collections do not provide sellers or exporters many options in case buyers or importers are unable to meet payment obligations. That’s why it is important for documentary collections to be used under certain conditions.
What is a document against payment collection?
A document against payment collection is initiated with the exporter shipping goods to a buyer. The seller or exporter supplies their bank with the shipping (and other relevant) documentation, which then forwards the documents to the importer or buyer’s bank.
What is an extension of credit?
The extension of credit is done through a time draft, which means that the documents related to the sale of goods are availed to the buyer or importer once he or she has accepted and signed the time draft.
How does a collection order work?
The process begins with a buyer making an order or a purchase of goods. The exporter or seller then makes arrangements to send the goods to the buyer or importer. The seller submits a collection order to his or her bank. The seller’s bank then submits the collection order to the bank of the buyer. The buyer’s bank presents a “presentation document” ...
What is a bill of lading?
Lading is the action of loading a ship or vessel with cargo. A negotiable bill of lading is. Balance of Payments. Balance of Payments The Balance of Payments is a statement that contains the transactions made by residents of a particular country with the rest of the world.
What makes a documentary collection ideal?
The conditions that make documentary collections ideal include the presence of a long-standing and well-established relationship between the seller and the buyer, a time when the country of the buyer is economically and politically sound, and in cases when a letter of credit is not acceptable to the buyer.
What happens to the buyer's bank after payment is made?
After payment completion, the buyer’s bank (also known as the collecting bank) transfers the funds to the bank of the exporter, who then transmits the funds to the exporter/seller.
What is documentary collections payment method?
The Documentary Collections payment method is an approach used for merchandise and commodity exports. Generally recommended in situations where there is an established and ongoing trade relationship with a trusted buyer, this method can simplify your export transaction, offer faster payment, and reduce costs when compared to Letters of Credits.
What is a documentary collection?
In a Documentary Collections transaction, the exporter’s and the importer’s banks facilitate the export sale by exchanging shipping documents for payment. However, the banks do not verify that the documents are accurate and do not guarantee payment as they do with Letters of Credit. As a result, Documentary Collections are only recommended for established trade relationships in economically and politically stable markets.
What if they don’t pay?
If the importer does not pay, the exporter typically needs to find another buyer, pay for return transportation, or abandon the merchandise.
What happens if an importer doesn't pay?
If the importer does not pay, the exporter typically needs to find another buyer, pay for return transportation, or abandon the merchandise.
What is a draft bill?
3. The Bill of Exchange - also known as a draft - provides instructions to the bank about the required documents, payment amount due, the terms of payment, and when title transfers for the goods
Is Documentary Collections a unique transaction?
While there are several benefits to the Documentary Collections payment method, each export transaction is unique. We recommend you consult with your bank before moving forward.
What is a documentary collection?
A documentary collection (D/C) is a transaction where the exporter entrusts the collection of payment to the exporter's bank (remitting bank), which sends documents to the importer's bank (collecting bank) along with instructions for payments.
How many steps are there to get paid for documentary collections?
There are typically seven steps that occur in order to get paid using documentary collections:
What happens to the collecting bank at maturity?
At maturity, the collecting bank contacts the importer for payment. Upon receipt of payment, the collecting bank transmits the funds to the remitting bank for payment to the exporter. Table 2 shows an overview of this type of collection:
What is a document against payment collection?
With a document against payment collection, the exporter ships the goods and then gives the documents to the bank, which will forward the documents to the importer's collecting bank along with instructions on how to collect the money from the importer.
What is the purpose of the importer's documents?
The importer uses the documents to obtain the goods and to clear them at customs. Once the collecting bank receives payment, it forwards the proceeds to the remitting bank. The remitting bank credits the exporter's account.
Who sends documents to the importer's collecting bank?
The exporter's remitting bank sends the documents to the importer's collecting bank.
What is the role of the exporter's bank in a D/C?
The exporter's bank (remitting bank) and the importer's bank (collecting bank) play an essential role in D/Cs. Although the banks control the flow of documents, they neither verify with the documents nor take any risks. They can, however, influence the mutually satisfactory settlement of a D/C transaction.
What is documentary collection?
Therefore, documentary collection can be defined as the “treatment” by banks of commercial and/or financial documents to obtain payment or acceptance of drafts ( Bill of Exchanges) or to deliver documents against payment (D/P: Documents against Payment for payment at sight) or the acceptance of drafts (Bill of Exchanges) (D/A: Documents against Acceptance for payment at sight with a “demand draft” or expiring with a “usance draft”) or deliver documents under other terms and conditions.
How many parties are involved in a documentary collection?
In the context of a documentary collection operation, there are five parties potentially involved in the operation:
What does "clean collection" mean?
The URC 522 ICC regulation also defines the meaning of “Clean” and “Documentary Collection”: “Clean collection” means collection of financial documents not accompanied by commercial documents. Commercial documents not accompanied by financial documents.
What are the details of a drawee?
Details of the drawee including full name, postal address, or the domicile at which presentation is to be made and if applicable, email, telephone and facsimile numbers;
What is a collecting/presenting bank?
The “collecting/presenting bank” presents the documents to the importer/drawee, delivering them against payment or acceptance;
What is CAD in finance?
Definition of the contractual agreement between the parties who identify , as a form of regulation of the supply price, documentary collection (D/P, more commonly known as CAD – Cash Against Documents or D/A)
Who is the drawee in a document?
The “drawee” which is the person to whom the presentation of the documents is made, in accordance with the “collection instructions”.
How does a documentary trade payment work?
A documentary trade payment is issued as the payment method supporting the purchase order with terms and conditions of payment . The DTP is issued in the format of a MT700 SWIFT message normally used for a documentary letter of credit; however, the availability of funds for the DTP found in paragraph 41D of the MT700 format is with the seller instead of a commercial bank.
What are the benefits of using a DTP documentary trade payment?
Universal guidelines – A DTP follows eUCP 600, International Chamber of Commerce Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits Supplement for Electronic Presentation (eUCP v2.0) effective 1 July 2019.
What is the UCP 600?
The documentary trade payment uses UCP 600 (letter of credit guidelines ) to add the negotiation function to the collection process. These guidelines are universally accepted in all 200 trading countries and have become Internet compatible with the publication of UCP 600 Supplement 2.0 providing for electronic records to be equivalent with paper. The UCP has never been a “bank regulation”; it was first published in 1933 and adopted by the banking industry as universal guidelines for managing documentary letters of credit.
How long does it take to pay a DTP?
A DTP is payable to the seller within five days or less (UCP 600, Article 14.b).
How many weekly shipments of 100 CTNs?
For example, 100 CTNs with a value of $1,000,000 can be divided into ten weekly shipments of $100,000 each. Since the payment time for electronic records is less than 5 days, the seller can receive payment for the first shipment before the second shipment is due to be shipped. Indeed, this is probably the most important benefit that the Internet brings to trade transactions using ICC eRules.
Is DTP a financial instrument?
Any company that trades with another company. The DTP is not a financial instrument, it is a collection instruction. The DTP is managed under UCP 600 guidelines (the International Chamber of Commerce Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits) instead of URC 522 guidelines (the International Chamber of Commerce Uniform Rules for Collections).
Is a documentary trade credit a credit?
No. The documentary trade payment is defined as funds available with the buyer. However, a documentary trade credit (DTC) is defined as funds available in escrow under contract with a commercial finance company that are allocated to the transaction by the buyer to the seller.
What is a documentary collection?
A documentary collection is a trade transaction in which the seller (or exporter) instructs his bank to forward documents related to the export of goods to a buyer’s bank with a request to present these documents to the buyer (or importer) for payment, indicating when and on what conditions these documents can be released to the buyer. In the process, the exporter hands over the task of collecting payment for goods supplied to his bank.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a documentary collection?
A documentary collection presents three main advantages: It is simple and easy to handle administratively compared to letters of credit. The exporter can retain title to the goods until payment or acceptance is made.
What is CAD in banking?
Documents against payment (D / P) also known as Sight Draft or Cash against Documents (CAD): The bank releases the documents to the importer only after immediate payment. This type of documentary collection is safe for the exporter but if the buyer refuses documents and merchandise, he has little recourse and can not do much.
What is a presenting bank?
The presenting / collecting bank is the bank that , in a documentary collection, presents the documents received from the remitting bank to the buyer and collects the payment from him. It is called collecting bank primarily because it collects the funds.
What is financial document?
financial documents: commercial paper and other instruments used to obtain the payment of a sum of money. All documents in the instruction letter must be given to the bank. Otherwise, it may refuse to be in charge of the payment collection. 4. Sending of documents.
What is the delivery of documents?
Delivery of documents. Once the goods have been dispatched, the exporter collects all the documents mentioned in the contract and hands them over to his bank with a letter of instructions. The documents that make up the documentary collection are called shipping documents. There are among others:
Who pays the invoice amount?
It is the buyer of the goods shipped. He pays the invoice amount or signs a bill of exchange. In exchange, his bank gives him the documents that will allow him to clear and take possession of the goods.