What are the different specialties of duodenoscopes?
Reviewer specialties include internal medicine, gastroenterology, oncology, orthopedic surgery and psychiatry. Duodenoscopes are hollow, flexible, lighted tubes that allow doctors to see the top of a patient’s small intestine, or duodenum. Doctors use them in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedures.
What is a duodenoscopy (endoscopy)?
1What is a Duodenoscopy (Endoscopy)? Upper endoscopyis a procedure to examine the esophagus (swallowing tube), stomach, and duodenum (first portion of small bowel) using a thin, flexible tube through which the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum can be viewed using a TV monitor.
What age is a duodenoscope used for?
Standard adult side-viewing endoscopes (duodenoscopes) are used in children older than 1 year of age and in adolescents.
Which duodenoscopes have a disposable cap?
In September 2017, the FDA cleared the first duodenoscope with a disposable cap. The Pentax Model ED34-i10T features a single-use cap that the company claims will prevent bacteria and other contaminates from spreading from patient to patient.
Why are duodenoscopes so complex?
Where do they put the duodenoscope?
How many duodenoscopes are used in ERCP?
What is ERCP in medical terms?
When did the FDA investigate the duodenoscope outbreak?
Why do we collect samples from tips of scopes?
Who found a link between duodenoscopes and infections?
See 2 more

What is the purpose of an ERCP?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, or ERCP, is a procedure to diagnose and treat problems in the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas. It combines X-ray and the use of an endoscope—a long, flexible, lighted tube.
What is the purpose of the elevator in a duodenoscope?
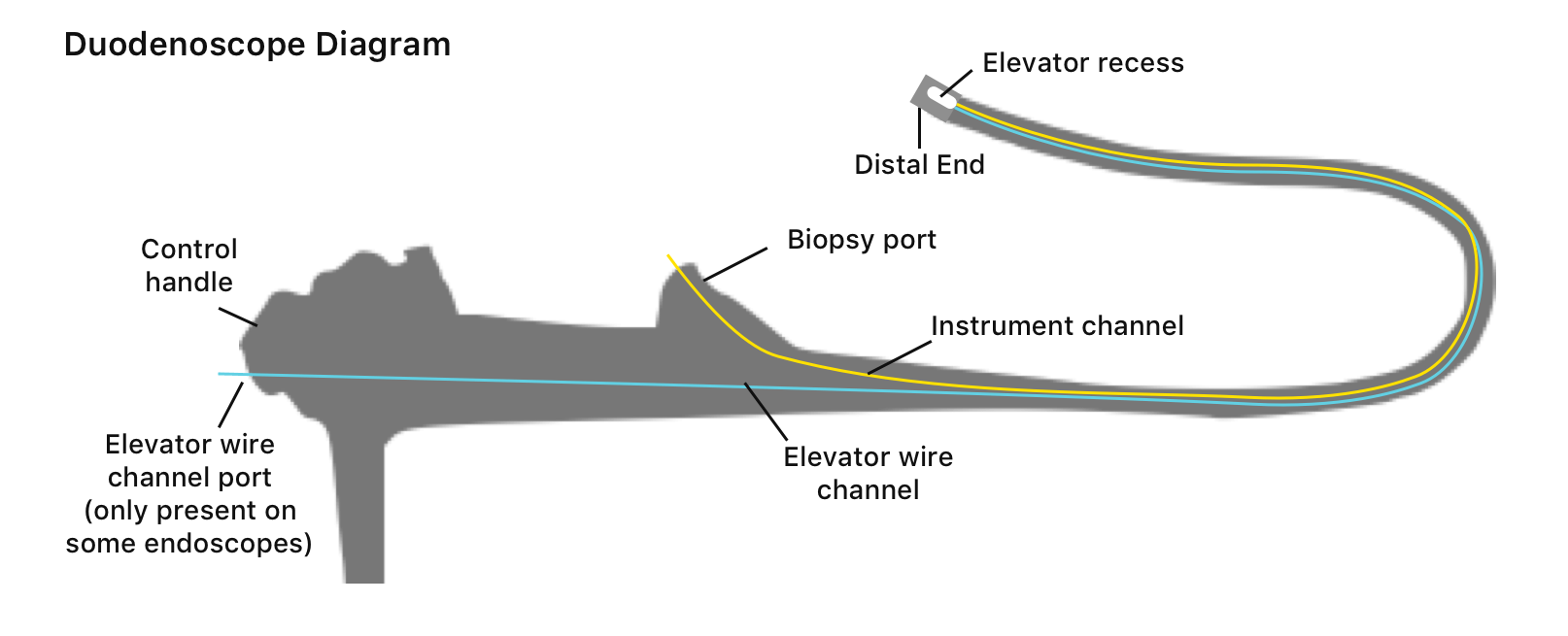
The elevator part of the duodenoscope facilitates access to the bile and pancreatic ducts, and is used to position endoscopic instruments during the procedure.
What is a single use duodenoscope?
Single-use duodenoscopes, disposable distal ends, or distal end cap sealants could eliminate or reduce exogenous patient-to-patient infection associated with ERCP. Methods: This document reviews technologies that have been developed to help reduce or eliminate exogenous infections because of duodenoscopes.
What is the difference between endoscopy and ERCP?
The main difference between the two is that endoscopic ultrasound utilizes high-frequency sound waves to generate a virtual image and ERCP procedure uses a video camera. These two techniques are commonly used for examining organs like the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas.
Is a duodenoscope an endoscope?
Duodenoscopes are specialized endoscopes that are used primarily for ERCP. They are side-viewing (rather than forward-viewing) endoscopes that have the advantage of looking at the major duodenal papilla en-face. Duodenoscopes have a lever that is used to manipulate an elevator located at the tip of the endoscope.
Is Upper GI and EGD the same?
An upper GI endoscopy or EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) is a procedure to diagnose and treat problems in your upper GI (gastrointestinal) tract. The upper GI tract includes your food pipe (esophagus), stomach, and the first part of your small intestine (the duodenum).
Is ERCP a high risk procedure?
An ERCP is considered a low-risk procedure; however, complications can occur. These can include pancreatitis, infections, bowel perforation, and bleeding.
Why is ERCP high risk?
Biliary sphincterotomy presents increased ERCP risk factors such as bleeding and hemorrhage. Many patients who undergo a biliary sphincterotomy are also statistically more likely to develop pancreatits after ERCP.
Is ERCP a major surgery?
An ERCP is a minimally invasive interventional procedure that is part of the diagnostic and treatment plan for a number of gastrointestinal conditions. Your ERCP will require that you dedicate about a day to the procedure and recovery. You may experience substantial relief as a result of this intervention.
What is a gastroscopy procedure?
A gastroscopy is a test to check inside your throat, food pipe (oesophagus) and stomach, known as the upper part of your digestive system. This test can help find what's causing your symptoms.
How is an endoscopic ultrasound performed?
Your endoscopist will use a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope that has a built-in miniature ultrasound probe. Your doctor will pass the endoscope through your mouth or anus to the area to be examined. Your doctor then will use the ultrasound to use sound waves to create visual images of the digestive tract.
Where is an EGD performed?
EGD is done in a hospital or medical center. The procedure uses an endoscope. This is a flexible tube with a light and camera at the end.
What is endoscopy procedures?
An endoscopy procedure involves inserting a long, flexible tube (endoscope) down your throat and into your esophagus. A tiny camera on the end of the endoscope lets your health care provider examine your esophagus, stomach and the beginning of your small intestine (duodenum).
What is a duodenoscope used for?
Duodenoscopes used for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and linear echoendoscopes have an additional dial for controlling the elevator.
How does a duodenoscope work?
Duodenoscopes have a lever that is used to manipulate an elevator located at the tip of the endoscope. By maneuvering the elevator, the endoscopist can raise and lower accessories passed through the working channel into the field of view (Fig. 3.8 ).
Why do we need a guidewire for cannulation?
Cannulation with a sphincterotome is recommended because most cases of biliary tract infection require a sphincterotomy. A guidewire is essential for selective cannulation of the intrahepatic ducts and the cystic duct and for accessing the biliary tree proximal to a stricture.
Why do endoscopists use a sphincterotome instead of a can?
Most endoscopists use a sphincterotome instead of a cannula as a primary bile duct cannulation device because it has the ability to be bowed, increasing the likelihood of cannulating the biliary tree. Selected fluoroscopic images are saved, and therapeutic maneuvers are performed as required.
How to pass through the stomach?
Immediately upon entering the stomach, leftward endoscope torque and brief tip extension (large wheel forward) combined with endoscope advancement and air insufflation will allow visualization of the fundus and a portion of the gastric body. A lowering of the left hand to the level of the table and simultaneous partial extension of the left elbow (“dropping the left hand”) will also facilitate this initial maneuver. Once the gastric body has been identified the endoscope is advanced, following the direction of the gastric folds, allowing it to pass along the surface of the greater curvature of the stomach towards the antrum. During this advancement, the endoscopist should slowly raise the left hand back to the vertical position so that the endoscopic image rotates in a clockwise manner and the incisura, when seen, appears to be horizontal. The posterior gastric wall will be rightward in the endoscopic field. Identification of the pylorus often occurs at this time. Advancement at this point with the endoscope tip in a neutral position will bring the pylorus (and a limited view of the post-bulbar duodenum) into full view. This image will be replaced with further advancement with the classic “setting sun” as the endoscope approaches and ultimately traverses the pylorus, resulting in a close view of the duodenal bulb with its characteristic mucosa. During attempts at traversal through the pylorus, some upward tip deflection combined with lateral tip deflection can be helpful if the tip of the endoscope repeatedly “rolls” off of the pylorus.
Why do you flex the tip of a duodenoscope?
The tip flexion helps to help bow the duodenal wall and position the duodenoscope “under” the papilla. In some patients, only a “long” endoscope position (with the endoscope shaft following the greater curvature of the stomach) will allow adequate alignment and orientation to the major papilla to be obtained.
What is the purpose of cholangioscopy?
Diagnostic cholangioscopy may be used to evaluate indeterminate biliary strictures and filling defects. Similarly, diagnostic pancreatoscopy may be used to evaluate pancreatic strictures and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.
What is a duodenoscope?
Duodenoscopes are flexible, lighted tubes that are threaded through the mouth, throat, and stomach into the top of the small intestine (duodenum). They are used during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), a potentially life-saving procedure to diagnose and treat problems in the pancreas and bile ducts.
Why are duodenoscopes important?
Duodenoscopes are critical to diagnosing and treating severe, often life-threatening diseases. While the overwhelming proportion of procedures with these devices are carried out safely and effectively, the FDA takes the risk of infection very seriously and is working intensively to address it.
What companies make duodenoscopes?
On March 9, 2018, the FDA issued Warning Letters to all three manufacturers (Fujifilm Medical Systems USA, Inc, Olympus Medical Systems Corporation, and Pentax of America), who make duodenoscopes sold in the U.S. for failure to provide sufficient data to address the postmarket surveillance studies requirements under Section 522 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the Act). All three manufacturers responded to the warning letters and submitted plans that outlines how study milestones will be achieved including enrolling new sites and collecting samples.
What is the FDA 522 study?
In October 2015, the FDA ordered each U.S. duodenoscope manufacturer (Olympus, Fujifilm and Pentax) to conduct postmarket surveillance studies ("522 study") to better understand how these devices are reprocessed in real-world settings and their impact on duodenoscope transmitted infections. Postmarket surveillance studies are important tools ...
When did the FDA release the duodenoscope protocol?
On February 26, 2018, the FDA, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and American Society for Microbiology (ASM), together with other endoscope culturing experts, released voluntary standardized protocols for duodenoscope surveillance sampling and culturing. These protocols are an update to the Interim Duodenoscope Surveillance Protocol ...
Can duodenoscopes be used on a patient?
Duodenoscopes are complex instruments that contain many small working parts. If not thoroughly cleaned and disinfected, tissue or fluid from one patient can remain in a duodenoscope when it is used on a subsequent patient. In rare cases, this can lead to patient-to-patient transmission of infection.
Who is responsible for reprocessing medical devices?
Ensuring the safety of reprocessed medical devices for use in multiple patients is a shared responsibility among the FDA and other federal agencies, public health systems, state and local health departments, medical device manufacturers, health care facilities, professional societies and others. The FDA is actively engaged with many ...
What is the upper endoscopy?
Upper endoscopy is a procedure to examine the esophagus (swallowing tube), stomach, and duodenum (first portion of small bowel) using a thin, flexible tube through which the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum can be viewed using a TV monitor.
What is FindATopDoc?
FindATopDoc is a trusted resource for patients to find the top doctors in their area. Be visible and accessible with your up to date contact information, certified patients reviews and online appointment booking functionality.
Is endoscopy safe?
Endoscopy is a safe procedure, and the complications are extremely rare when it is performed by a physician with specialized training.
Is upper endoscopy more accurate than X-ray?
The advantage of upper endoscopy over X-ray is that is more accurate for detecting inflammation or smaller abnormalities such as ulcers or tumors within the reach of the instrument and biopsies (obtain small pieces of tissue) or cytology (obtain some cells with a fine brush) can be performed to determine the nature of the abnormality and whether the abnormality is benign or malignant (cancerous).
Why are duodenoscopes so complex?
Because duodenoscopes allow direct access to bile or pancreatic ducts, they are more complex than other endoscopes. In addition to a small, lighted camera in the tip, duodenoscopes have a lever with a hinge called an elevator mechanism, explain researchers Divyanshoo R. Kohli and John Baillie in Clinical Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. This added feature makes it possible for a doctor to raise or lower accessories from the scope’s tip to perform biopsies and other delicate procedures in bile and pancreatic ducts.
Where do they put the duodenoscope?
Doctors insert flexible, snake-like duodenoscopes into the mouth and pass them through the throat, stomach and into the top of the small intestine — also called the duodenum. These scopes are different from typical endoscopes used in procedures such as colonoscopies and are specifically for ERCP procedures.
How many duodenoscopes are used in ERCP?
Each year, Americans undergo more than 500,000 ERCP procedures using duodenoscopes, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s website. Though, the biggest manufacturer of duodenoscopes — Japan-based Olympus — told the Los Angeles Times that the number was closer to 700,000.
What is ERCP in medical terms?
Doctors use them in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedures. The instruments help doctors diagnose and treat severe, often life-threatening, diseases such as cancer or gallstones in the pancreas and bile ducts.
When did the FDA investigate the duodenoscope outbreak?
The FDA investigated the outbreaks in 2013 but did not take significant action until 2015 when it ordered scope makers to conduct further studies. These postmarket surveillance studies were supposed to gather data on how health care workers cleaned duodenoscopes in “real-world settings” and how this affected infection transmission.
Why do we collect samples from tips of scopes?
The guidelines called for collecting samples from the tips of scopes and testing them to monitor the quality of reprocessing. It also pointed out that other countries already did this type of testing.
Who found a link between duodenoscopes and infections?
Dutch researcher Arjan W. Rauwers and his colleagues at the Erasmus MC University Medical Center in the Netherlands published a 2018 study in the BMJ’s Gut journal. They found a link between duodenoscopes and infections.
