
Fair Value Hedging – Portfolio Layer Method
- Background. A fair value hedge protects an entity from changes in the value of recognized assets, liabilities, and unrecognized firm commitments that are attributable to a particular risk.
- Main Provisions. ...
- Effective Dates and Transition. ...
What are the disadvantages of hedge funds?
Quick Summary of Hedge Fund Disadvantages
- Higher Fee Structure
- Increased Volatility and Investment Risks
- Additional Performance Fee
What do hedge fund managers typically get paid?
Management Fees: This fee is calculated as a percentage of assets under management. Typically this equates to 2% but can range from 1% to 4% depending on the fund. These fees are generally paid monthly or quarterly and help pay overhead and daily expenses of running the hedge fund.
How do you value a hedge fund?
- asset price
- strike price
- time to maturity
- risk-free rate of return
- price volatility of the underlying asset (i.e., risk)
What is hedging, and how does a hedge fund operate?
What is a hedge fund?
- Relative freedom from regulation. Highly regulated traditional investment vehicles like mutual funds typically use pooled funds to invest in shares and fixed-income securities like bonds.
- The mitigation of market risk. Market risk is a measure of the systemic risk of the aggregate stock market. ...
- High minimum-entry criteria. ...
What is a fair value hedge example?
Fair value hedge example Imagine that Company A has an asset with a value of $10,000, though management are concerned that the asset's fair value may go down to $8,000. In order to offset this, Company A would enter into an offsetting position through a derivative contract which has a value of $10,000.
What is difference between fair value hedge and cash flow hedge?
As you can see, the key difference between a cash flow hedge and a fair value hedge is the hedged item. With a cash flow hedge, you're hedging the changes in cash inflow and outflow from assets and liabilities, whereas fair value hedges help to mitigate your exposure to changes in the value of assets or liabilities.
What is the objective of a fair value hedge?
Fair value hedges are hedges that reduce the risk of loss from declines in an asset's value. A fair value hedge is paired with the underlying asset it is protecting. When the value of the underlying asset falls, the value of the hedge goes up and reduces the loss in value to the asset owner.
What are the three types of hedging?
There are also three types of hedges that qualify for hedge accounting:Cash flow hedge. This reduces the risk of changes in fair value of future cash flows.Fair value hedge. This reduces the risk of changes in fair value of existing assets and liabilities or firm commitments.Net investment hedge.
How do you record fair value hedges?
0:496:41Accounting for Fair Value Hedges | Steps | Journal Entries - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipValue you know hedge instrument you need to record any changes lastly recognize the hedging gain orMoreValue you know hedge instrument you need to record any changes lastly recognize the hedging gain or loss on the hedged. Items as in the carrying amount.
Is an interest rate swap a fair value hedge?
Fair Value Hedge Example Therefore, you enter into interest rate swap to receive 2% fixed / pay LIBOR12M + 0.5%. This is a fair value hedge – you tied the fair value of your interest payments to market rates.
What is effective hedge?
Hedge effectiveness is defined as the extent to which changes in the fair value or cash flows of the hedging instrument offset changes in the fair value or cash flows of the hedged item.
How should gains or losses from fair value hedges be recognized?
A fair value hedge is reported at its fair market value with unrealized gains or losses recognized in earnings in the period of change. An offsetting amount of loss or gain related to the hedged risk will be recognized in the same period.
What is effective hedge and ineffective hedge?
A hedge is considered effective if the changes in the cash flow of the hedged item and the hedging instrument offset each other. Conversely, if the cash flow of the two items do not offset each other, the hedge is considered ineffective.
What is an example of hedging?
A classic example of hedging involves a wheat farmer and the wheat futures market. The farmer plants his seeds in the spring and sells his harvest in the fall. In the intervening months, the farmer is subject to the price risk that wheat will be lower in the fall than it is now.
What is the major disadvantage of hedging?
Disadvantages of Hedging Hedging involves a cost that tends to eat up the profit. Risk and reward are usually proportional to one other; thus, reducing risk will lead to reduced profits. For most short term traders, e.g., for a day trader, Hedging is a complex strategy to follow.
Who benefits from hedging?
Advantages of Hedging Futures and options are very good short-term risk-minimizing strategy for long-term traders and investors. Hedging tools can also be used for locking the profit. Hedging enables traders to survive hard market periods.
How is cash flow hedge calculated?
2:2212:25Cash Flow Hedge Explained - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn a planned transaction since it did not occur yet it's gonna require cash flow well guess what youMoreIn a planned transaction since it did not occur yet it's gonna require cash flow well guess what you can protect that cash flow. So cash flow is hedging the exposure to the cash flow.
What is the difference between hedging and hedge accounting?
Hedging is an economic concept designed to reduce risk. Hedge accounting is designed to ensure economic results are reflected in the accounts, when normal accounting rules would not give that result.
What are cash flow derivatives?
The main variable used in this study is derivative cash flows (Dercashflow). Dercashflow is the cash settlement of outstanding commodity hedge contracts. Firms typically report the total derivative gain or loss (GL), including unrealized GLs, in net income.
What is the effective portion of a cash flow hedge?
When is a cash flow hedge effective? A hedge is considered effective if the changes in the cash flow of the hedged item and the hedging instrument offset each other. Conversely, if the cash flow of the two items do not offset each other, the hedge is considered ineffective.
Example
Assets and liabilities which are commonly fair value hedged are as follows −
Understanding the fair value of hedge by example
Let’s say the company has an asset of 500000 a n d t h e y m a y b e c o n c e r n e d d u e t o f a i r v a l u e h e d g e a s s e t v a l u e m a y d e c r e a s e u p 10000.
What is fair value hedge?
A fair value hedge is used to manage an exposure to changes in the fair value of a recognized asset or liability (e.g., fixed-rate debt) or an unrecognized firm commitment (e. g., the commitment to buy a fixed quantity of gold at a fixed price at a future date). A fair value hedge can be of either a financial or nonfinancial item, ...
What happens to the value of a LIBOR investment when the interest rate increases?
All else being equal, as LIBOR decreases, the value of its investment will increase because the contractual fixed interest payments will be above market. Similarly, all else being equal, if LIBOR increases, the value of its investment will decrease.
Is a fair value hedge a financial asset?
A fair value hedge can be of either a financial or nonfinancial item, but fair value hedges of financial assets and liabilities are more common. If a derivative qualifies as a fair value hedging instrument, the portion of the gain or loss on the derivative designated as a fair value hedge will still be recognized in earnings currently.
Does a reporting entity recognize hedged assets?
However, a reporting entity would also recognize in earnings the changes in the value of the hedged asset, liability, or firm commitment due to the hedged risk through a basis adjustment to the hedged item.
What is fair value hedge?
A fair value hedge is a type of financial strategy that involves using a financial product, usually a derivative, to hedge against risk from price changes in an asset. Investors and traders use fair value hedges to hedge against changes in fair value, or market value, of assets or liabilities.
What is hedge in finance?
Sometimes, a company can issue debt, and use the hedge to balance out changes in the value of that debt. Various financial professionals refer to bonds or other debts and their corresponding hedge instruments, as “balancing each other out” on a ledger.
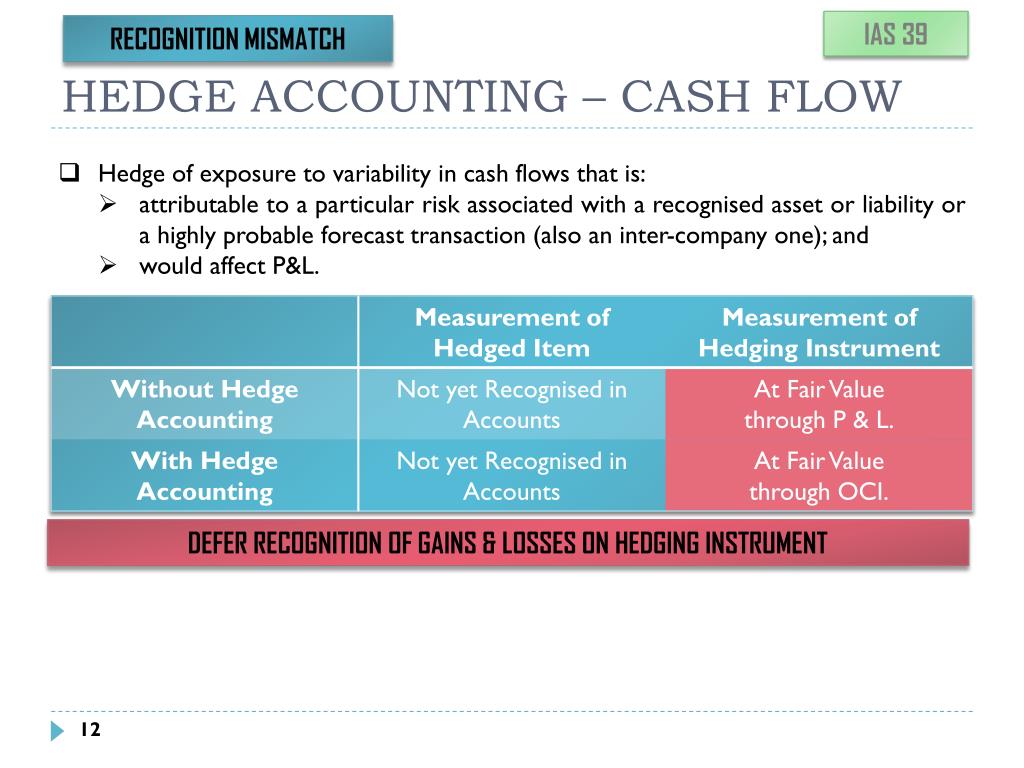
What is a cash flow hedge?
An alternative kind of hedge to the fair value hedge is called a cash flow hedge. This kind of hedge is used differently from the fair value hedge in corporate accounting. The end result of a cash flow hedge is balancing the market rate changes into a fixed rate of interest expense.
Is derivatives a hedge?
Derivatives sold on Forex markets may be said to constitute a “Forex hedge,” and come under other rules. Those using hedges should understand how Forex, or foreign exchange, hedges are handled in a specific country or region of the world.
What is fair value hedge?
A fair value hedge is a hedge of the exposure to changes in the fair value of an asset or liability or any such item that is attributable to a particular risk and can result in either profit or loss. A fair value hedge relates to a fixed value item. Fair value hedge pertains to a fixed value item.
What is accounting for fair value hedges?
The accounting done by the company with respect to the hedge of exposure of fair value change of the item be it a asset for the company or it is a liability that is attributable to the particular risk and the same can result in profit or loss generation to the company is known as the Accounting for the Fair Value Hedges.
What is fair value in investing?
In investing, it refers to an asset's sale price agreed upon by a willing buyer and seller, assuming both parties are knowledgeable and enter the transaction freely. For example, securities have a fair value that's determined by a market where they are traded.
When is fair value used?
Fair value is also used in a consolidation when a subsidiary company’s financial statements are combined or consolidated with those of a parent company. The parent company buys an interest in a subsidiary, and the subsidiary’s assets and liabilities are presented at fair market value for each account.
What is the difference between fair value and market value?
What's the Difference Between Fair Value and Market Value? Fair value is a broad measure of an asset's intrinsic worth while market value refers solely to the price of an asset in the marketplace as determined by the laws of demand and supply . As such, fair value is most often used to gauge the true worth of an asset.
What happens to the value of XYZ stock if the price of the option increases?
If XYZ stock’s market price increases, the value of the option on the stock also increases. In the futures market, fair value is the equilibrium price for a futures contract—that is, the point where the supply of goods matches demand.
Can an accountant determine fair value?
This is often an issue when accountants perform a company valuation. Say, for example, an accountant cannot determine a fair value for an unusual piece of equipment.
Is market value the same as market value?
Although it infers an open marketplace, it is not quite the same as market value, which simply refers to the price of an asset in the marketplace (not intrinsic worth). In the investment world, a common way to determine a security's or asset's fair value is to list it in a publicly-traded marketplace, like a stock exchange.
What is fair value hedge?
What is a fair value hedge? Fair value hedges can be used to mitigate the risk of changes in the fair market value of liabilities, assets, or other firm commitments. Generally, fair value hedges move in the opposite direction of the hedged item so that they can be used to cancel out your losses.
What is the difference between cash flow hedge and fair value hedge?
As you can see, the key difference between a cash flow hedge and a fair value hedge is the hedged item . With a cash flow hedge, you’re hedging the changes in cash inflow and outflow from assets and liabilities, whereas fair value hedges help to mitigate your exposure to changes in the value of assets or liabilities.
What is fair value hedge?
Fair value hedge is a hedge of the exposure to changes in fair value of a recognized asset or liability or unrecognized firm commitment, or a component of any such item, that is attributable to a particular risk and could affect profit or loss. Special For You!
How to determine fair value of hedged instrument?
Step 1: Determine the fair value of both your hedged item and hedging instrument at the reporting date ; Step 2: Recognize any change in fair value (gain or loss) on the hedging instrument in profit or loss (in most cases).
How to calculate cash flow hedge?
Assuming your cash flow hedge meets all hedge accounting criteria, you’ll need to make the following steps: Step 1: Determine the gain or loss on your hedging instrument and hedge item at the reporting date; Step 2: Calculate the effective and ineffective portions of the gain or loss on the hedging instrument; Step 3:
What is variable item?
A variable item means that the expected future cash flows from this item change as a result of certain risk exposure, for example, variable interest rates or foreign currencies. When it comes to hedging variable items, you’re practically speaking of a cash flow hedge.
