
Muscle fascicle A muscle fascicle is a bundle of skeletal muscle fibers surrounded by perimysium, a type of connective tissue.
What is the connective tissue covering of a muscle fascicle?
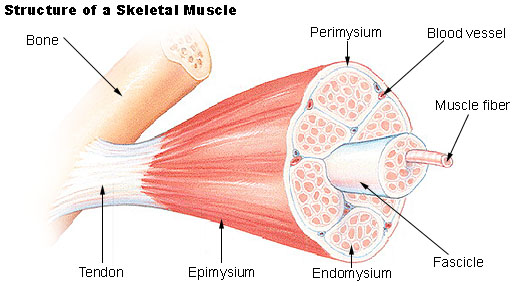
When a group of muscle fibers is “bundled” as a unit within the whole muscle it is called a fascicle. Fascicles are covered by a layer of connective tissue called perimysium (see Figure 10.3). Fascicle arrangement is correlated to the force generated by a muscle and affects the muscle’s range of motion.
What is a fascia of a muscle?
Muscle fascia is areolar connective tissue with loosely arranged collagen and elastin fibers. It surrounds each layer of muscle tissue and is continuous with the components of a muscle.
Are muscle fibers and myofibrils the same thing?
Are muscle fibers and myofibrils the same thing? Muscle fibers are composed of thousands of myofibrils. The key difference between myofibril and muscle fiber is that myofibril is the basic rod-like unit of a muscle fiber while muscle fiber is the tubular cells of the muscle.
What is the fascial covering of the entire muscle?
Fascia or myofascia is the dense, tough tissue which surrounds and covers all of your muscles and bones. This outer fascial covering is very strong and very flexible. In fact, it has a tensile strength of over 2000 pounds.
Where is the fascicle of a muscle?
Beneath the fascia in skeletal muscle is another layer of connective tissue termed the epimysium which is closely associated with the fascia. It extends inwards and becomes the perimysium, then into the muscle separating muscle fibers into small bundles termed fascicles.
What is the definition of fascicle?
1 : a small or slender bundle (as of pine needles or nerve fibers) 2 : one of the divisions of a book published in parts.
What are muscle fascicles made of?
A skeletal muscle fascicle consists of 20 to 60 fibers surrounded by a connective tissue sheath. A single muscle fiber is innervated by only one motor unit, but there may be two to three motor units within a fascicle. The muscle fibers of one motor unit may be distributed over 100 fascicles.
What does a muscle fascicle look like?
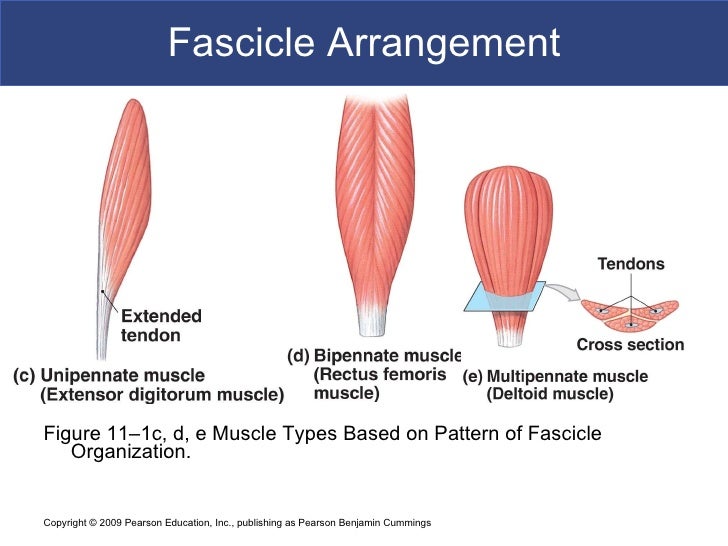
Fascicles can be parallel, circular, convergent, pennate, fusiform, or triangular. Each arrangement has its own range of motion and ability to do work.
What is another word for fascicle?
In this page you can discover 12 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for fascicle, like: group, bundle, cluster, installment, bunch, collection, fasciculus, fiber bundle, fibre-bundle, fascicule and graecorum.
How many fascicles does a muscle have?
The number of fascicles in a muscle ranged from 61 to 101 fascicles per whole muscle. During dissection it was observed that the fascicles did not always run from distal to proximal tendon, that some fascicles were in series, and that they were not the same length as the whole muscle.
What is a bundle of muscle fascicles called?
Each bundle of muscle fiber is called a fasciculus and is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the perimysium. Within the fasciculus, each individual muscle cell, called a muscle fiber, is surrounded by connective tissue called the endomysium.
What are the 3 types of muscles?
The three main types of muscle include:Skeletal muscle – the specialised tissue that is attached to bones and allows movement. ... Smooth muscle – located in various internal structures including the digestive tract, uterus and blood vessels such as arteries. ... Cardiac muscle – the muscle specific to the heart.
What are fascicles held together by?
Solution : Muscle bundles or fascicles held together by collagenous tissue layer called fascia.
What connects muscle to bone?
Listen to pronunciation. (TEN-dun) Tough, fibrous, cord-like tissue that connects muscle to bone or another structure, such as an eyeball. Tendons help the bone or structure to move.
What are fascicles quizlet?
fascicle. A bundle of muscle fibers.
What is a bundle of muscle fibers called?
Each bundle of muscle fiber is called a fasciculus and is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the perimysium. Within the fasciculus, each individual muscle cell, called a muscle fiber, is surrounded by connective tissue called the endomysium.
What are tendons Definition?
Listen to pronunciation. (TEN-dun) Tough, fibrous, cord-like tissue that connects muscle to bone or another structure, such as an eyeball. Tendons help the bone or structure to move.
What is the Definition of muscle fiber?
Muscle tissue contains something called muscle fibers. Muscle fibers consist of a single muscle cell. They help to control the physical forces within the body. When grouped together, they can facilitate organized movement of your limbs and tissues.
Which muscle has circular fascicles?
A circular pattern of fascicles is characteristic of sphincter muscles that surround openings (e.g., the mouth or the anus). Sign in to download full-size image. Figure 2.
What is the fascicle of the musculoskeletal system?
Fascicle. A fascicle consists of thousands of muscle cells, called fibers, which are likewise surrounded by a connective tissue layer, termed the endomysium. From: Computational Modelling of Biomechanics and Biotribology in the Musculoskeletal System (Second Edition), 2021. Download as PDF.
What type of muscle is a spindle?
The differing ways in which fascicles attach to tendons creates a variety of skeletal muscle sizes and shapes ( Figure 2 ). As mentioned earlier, fusiform muscles have parallel fibers that run the length of the muscle and narrow at each end, forming a spindle shape. The tendons that attach fusiform muscles to bones are restricted to the ends ...
What are the four shapes of skeletal muscles?
Shapes of Skeletal Muscles. Four distinct patterns of fascicles are seen within the whole of the muscle: parallel, convergent, pennate, and circular (Figure 2 ). Parallel fascicles lie parallel to one another along the longitudinal axis of the muscle. Parallel muscles may narrow to a tendon at each end, forming a fusiform muscle, ...
Where are the tendons located in the fusiform muscle?
The tendons that attach fusiform muscles to bones are restricted to the ends of the muscle. The thickest part of the muscle is usually near its middle. Pennate muscles are flattened, and either or both of the tendons extend for some distance along the length of the belly.
What happens when a muscle has multiple tendinous intersections?
As pennation increases (unipennate to multipennate), the muscle fibers become shorter, the number of fibers increases and, thus, the cross-sectional area of the fibers increases. This results in a decreased shortening of the muscle as a whole upon contraction ...
What is convergent pattern in abdominal muscles?
A convergent pattern is found in triangular-shaped muscles, in which fascicles attach along a broad tendon at one end of the muscle and converge ...
What is a muscle fascicle?
(Fascicle labeled at bottom right.) Not to be confused with Nerve fascicle. A muscle fascicle is a bundle of skeletal muscle fibers surrounded by perimysium, a type of connective tissue.
Which muscle fascicle is narrower?
Myocytes towards the edges of the muscle fascicle are typically narrower, while those at the centre of the muscle fascicle are a normal thickness. Muscle fascicles may be involved in myokymia, although commonly only individual myocytes are involved.
How are myocytes grouped into muscle fascicles?
Myocytes are grouped into muscle fascicles by enveloping perimysium connective tissue. Fascicles are bundled together by epimysium connective tissue. Muscle fascicles typically only contain one type of muscle cell (either type I fibres or type II fibres ), but can contain a mixture of both types.
What are structural changes that occur at the muscle fascicle level?
Structural changes that occur at the muscle fasciclelevel may include lengthening or shortening of the fascicle or a change in the orientation (i.e. , pennation angle) of the muscle fibers as theyspan the muscle belly.
What are the two architectural parameters that can influence how a muscle generates force?
Muscle fasciclelength and pennation angle (i.e., the angle in which the fascicles insert themselves into the aponeuroses of the muscle) are two architectural parameters that can influence how a muscle generates force.
Which layer of subcutaneous tissue is muscle?
muscle layer in fatty layer of subcutaneous tissue
What is Fascia?
If you have ever had Plantar fasciitis, a painful condition that is also called jogger’s heel, then you know something about your fascia.
What is the structure of the fascia?
It is also a fluid system that every cell in your body relies on for proper functioning. It is the crystalline structure that literally holds all the information of your life!
Why does fascia help with overstretching?
Protects you from injury. Your fascia stretches and moves to support your body, and actually protects you from overstretching. But, if you hurt yourself, your fascia adapts to protect your body from further injury. Likewise, if you sit all day slumped over a computer, you put abnormal stress on your fascia.
Why is my fascia tight?
The most common reasons for tight fascia are prolonged sitting or standing and lack of stretching. In addition, any type of intense physical training, such as marathon running, chronic inflammation, and poor posture can also cause your fascia to be tight.
Why do fascia fibers thicken?
But, when you are sedentary your fascia fibers can become like cement. Also, if you are under chronic stress or have an injury, your fascia fibers can thicken in an attempt to protect the underlying muscle or bone. This can even result in adhesions.
How to make your fascia feel better?
Be sure to drink enough pure water and replace fluids after exercise. However, you need to take it one step further because, unlike blood that is pumped by your heart, there is no other organ pumping fluid to your fascia. That’s where stretching comes in. This gets fluid moving into your fascia.
How to tell if your fascia is healthy?
To see this for yourself, sit at a desk for an hour or longer then stand up. Notice how your hips feel. If they feel tight or you need to rise slowly due to pain in another part of your body, this is your fascia telling you that it needs attention.
What is the fascia of a muscle?
Muscle fascia is areolar connective tissue with loosely arranged collagen and elastin fibers. It surrounds each layer of muscle tissue and is continuous with the components of a muscle. Because muscles are not separate from the fascia that encases them and each of their components, we reflect the reality of this integrated arrangement by referring ...
Why is muscle fascia important?
Fascia is the tissue that connects everything into one big interconnected whole. With this in mind then, you could imagine that tension or length experienced in the muscle is in a relationship with the tension or length in the fascia. Fascia is an important component of maintaining the tensional patterns of the body and can be a part of allowing or restricting movements.
What is the term for connective tissue that has a specific arrangement, type, and amount of protein fibers?
We can refer to specific types of fascia, such as “muscle fascia” when we want to talk about connective tissue proper that has a particular arrangement, type, and amount of protein fibers and has a specific role in the body. Muscle fascia is areolar connective tissue with loosely arranged collagen and elastin fibers.
What is the protein fiber?
Protein fibers: a mixture of collagen, elastin, and sometimes reticulin fibers. A ground substance called hyaluronic acid, in which the protein fibers are found. The specific type of connective tissue proper or fascia is determined by:
What is a bundle of muscle fibers called?
Groups of muscle fibers are arranged together in a bundle. Multiple bundles of muscle fibers grouped together are called a fascicle. A bundle of fascicles together make up a whole muscle, for example, the triceps brachii. Each of these components of a muscle is surrounded by a thin sheet of muscle fascia. Each of the muscle fibers is surrounded by ...
What is the arrangement of protein fibers?
the arrangement of protein fibers. Connective tissue proper, or fascia, is divided into loose connective tissue proper (when there are fewer protein fibers) and dense connective tissue proper (when there are more protein fibers).
What is the term for the thin sheet of muscle fibers?
Each of these components of a muscle is surrounded by a thin sheet of muscle fascia. Each of the muscle fibers is surrounded by fascia (known as endomysium). Each bundle of fibers (a fascicle) is surrounded by fascia (known as perimysium).
What is the cuneate fasciculus of the spinal cord?
cuneate fasciculus of spinal cordthe lateral portion of the dorsal funiculus of the spinal cord, composed of ascending fibers that end in the nucleus cuneatus.
What is PCSA muscle?
PCSA is a function of the muscle volume, fasciclelength, and pennation angle and was estimated using . Differences in plantar flexor fascicle length and pennation angle between healthy and poststroke individuals and implications for poststroke plantar flexor force contributions.
What is a bundle of fibers?
A band or bundle of fibers, usually of muscle or nerve fibers; a nerve fiber tract.
What is the median portion of the dorsal funiculus of the spinal cord?
gracile fasciculus of spinal cord the median portion of the dorsal funiculus of the spinal cord, composed of ascending fibers that end in the nucleus gracilis.
Definition of fascicle
Other Words from fascicle Did you know? Example Sentences Learn More About fascicle
Did you know?
Fascicle, which has been a part of our language since the 15th century, is one of a bundle of words derived from Latin fascis, meaning "bundle." In book publishing, "fascicle" and its variants "fascicule" and "fasciculus" can all be used for one of the installments of a voluminous work; "fasciculus" can also be used for a bundle of anatomical fibers.
Examples of fascicle in a Sentence
Recent Examples on the Web These grow from a little cup-like structure called a fascicle, which grows from a small bud on the pine twig shoot. — Tim Macwelch, Outdoor Life, 23 Dec.
Overview
A muscle fascicle is a bundle of skeletal muscle fibers surrounded by perimysium, a type of connective tissue.
Structure
Muscle cells are grouped into muscle fascicles by enveloping perimysium connective tissue. Fascicles are bundled together by epimysium connective tissue. Muscle fascicles typically only contain one type of muscle cell (either type I fibres or type II fibres), but can contain a mixture of both types.
Function
In the heart specialized cardiac muscle cells transmit electrical impulses from the atrioventricular node (AV node) to the Purkinje fibers – fascicles, also referred to as bundle branches. These start as a single fascicle of fibers at the AV node called the bundle of His that then splits into three bundle branches: the right fascicular branch, left anterior fascicular branch, and left posterior fascicular branch.
Clinical significance
Myositis may cause thickening of the muscle fascicles. This may be detected with ultrasound scans.
Muscle fascicle structure is a useful diagnostic tool for dermatomyositis. Myocytes towards the edges of the muscle fascicle are typically narrower, while those at the centre of the muscle fascicle are a normal thickness.
See also
• Connective tissue in skeletal muscle
• Endomysium
• Epimysium
External links
• Histology image: 77_04 at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center – "Slide 77 skeletal muscle"
• Anatomy Atlases - Microscopic Anatomy, plate 05.83 – "Smooth Muscle"
• Diagram at kctcs.edu
Overview
- Your muscle fascia is important to every move you make. And, when your fascia is tight or damaged you may suffer from any number of symptoms, including headaches, muscle pain, neck and back pain, general lack of flexibility, and poor posture. The most common reasons for tight fascia are prolonged sitting or standing and lack of stretching. If you h...
Causes
- In addition, any type of intense physical training, such as marathon running, chronic inflammation, and poor posture can also cause your fascia to be tight. Of course, trauma can also be a culprit this can be in the form of physical trauma, such as falls, injuries and surgery, or emotional trauma. Aging is in part due to dry, tight fascia. This is often at the center of chronic pain, illness, injury, a…
Results
- Better than X-rays, MRIs, and other scans, your fascia lets you know how healthy you are on a daily even hourly basis. To see this for yourself, sit at a desk for an hour or longer then stand up. Notice how your hips feel. If they feel tight or you need to rise slowly due to pain in another part of your body, this is your fascia telling you that it needs attention. Healthy fascia has a gel-like consisten…
Treatment
- Other patterns that can take their toll on your fascia include poor posture, lack of flexibility and repetitive movements. The good news is you can reverse any damage to your fascia with the proper techniques. And, caring for your fascia can be easy. Here are some ways you can improve your fascia and improve your health: Take a few minutes first thing in the morning to stretch out …
Symptoms
- When you stop moving for long periods of time, such as when you sleep at night, your fascia starts to get sticky. This is why you may feel stiff in the morning. In addition, if you get injured, adhesions can form in your fascia. Over time, these adhesions can become permanent, and can even inhibit your range of motion.
Prevention
- If you have a tight IT band, most likely the mid-thoracic area of your back is tight. When you work on releasing this area of your back, your IT band will also release. These external techniques for addressing fascia tension can help support your stretching or assisted stretching program.
Benefits
- Remember, you dont need to be injured to try these techniques. The benefits of facial release are numerous. From less pain to better posture, deeper breathing to increased energy, improved flexibility and coordination to better fitting clothes! In fact, many athletes, dancers, and musicians use fascial release techniques to keep themselves in peak condition for their profession.
Quotes
- Have you tried fascial work? If so, what have you tried? And, what improvements have you experienced?