The term fibro-osseous lesion is largely descriptive, limited and diagnostically non-specific. They represent—replacement of normal bone by fibrous tissue composed of collagen fibers, fibroblasts and certain varying amounts of mineralized substance, which may be bone or cementum like in appearance.
What are the three types of bone lesions?
What are the three types of bone lesions? The British Institute of Radiology classifies bone lesions in three basic categories: malignant (cancerous), benign (non-cancerous) and non-neoplastic (general bone cysts). The malignant and benign classifications are further divided into tumor types.
What are the causes of lytic bone lesions?
- Hypercalcemia. When your bones break down quickly, a lot of calcium gets released into your blood. A high calcium blood level is called hypercalcemia. ...
- Limping. If a bone with a tumor breaks, it can make you limp. ...
- Low blood cell counts. As myeloma cells crowd out your regular blood cells in the bone marrow, you could get conditions like: Anemia. ...
What is a fibroosseous lesion in a hip?
Liposclerosing myxofibrous tumors (LSMFT), also known as polymorphic fibro-osseous lesions of bone, are rare benign fibro-osseous lesions that have a predilection for the intertrochanteric region of the femur. It is slightly more common in males with mean age of 30-40 years.
What is a benign lytic lesion?
Benign lytic lesions. A benign, bubbly lytic lesion of bone is probably one of the most common skeletal findings a radiologist encounters. The differential diagnosis can be quite lengthy and is usually given on an “Aunt Minnie” basis (I know that’s Aunt Minnie because she looks like Aunt Minnie); in other words, the differential diagnosis is structured on how the lesion looks to the ...
What is a FOL?
Is B6C3F1 a lesion?
About this website

Are fibro-osseous lesions benign?
The benign fibro-osseous lesions (BFOL) are a poorly defined group of lesions that share the same evolutive mechanism [1,2]. They are characterized by replacement of the normal bone by an often cellular fibrous tissue containing various forms of ossification [1,2].
What is the most common fibro-osseous lesion?
Although their classification has been reviewed multiple times in the past, the most common benign fibro-osseous lesions are fibrous dysplasia, osseous dysplasia and ossifying fibroma.
What is fibro-osseous dysplasia?
Fibrous dysplasia is a bone disorder wherein during skeletal growth normal bone is replaced by a dysplastic proliferation of fibrous tissue and woven bone. This disorder can occur focally or multifocally anywhere in the skeleton. It usually is first recognized in the second decade.
WHO classification Fibroosseous lesions?
Furthermore, it introduced “fibro-osseous lesion” (FOL) as a lesion group for the first time in the WHO classification of odontogenic and maxillofacial bone tumors. There are 3 recognized FOLs; fibrous dysplasia (FD), cemento-ossifying fibroma (COF), and cemento-osseous dysplasia (COD).
What is a focal osseous lesion?
Abstract. Focal osseous dysplasia (FOD) is one of the benign fibro-osseous lesions of the jaw bones and the most commonly occuring benign fibro-osseous lesion. This entity occurs more commonly in females and has a predilection for African Americans.
Is fibrous dysplasia genetic?
What causes fibrous dysplasia? The exact cause of fibrous dysplasia is not known. It is believed to be due to a chemical defect in a specific bone protein. This defect may be due to a gene mutation present at birth, although the condition is not known to be passed down in families.
How many people are affected by fibrous dysplasia?
Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is one of those conditions. With an estimated prevalence of 1 in 15000-30000 individuals , it is unsurprising that I had never come across it.
What causes periapical osseous dysplasia?
Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia (COD) is a very rare benign lesion arising from a group of disorders which are known to originate from undifferentiated cells of the periodontal ligament tissue. Essentially, these underlying disorders all involve the same pathological process.
What is periapical osseous dysplasia?
Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia (PCOD) is a rare benign lesion, often asymptomatic, in which fibrous tissue replaces the normal bone tissue, with metaplasic bone and neo-formed cement.
Is Paget's disease a fibro osseous lesion?
Classic Paget Disease of Bone (CPDB) is an osseous dysplasia with late adult onset. It is characterized by rapid turnover of bone resulting in osseous expansion with progressive skeletal deformities [46–56]. Tubular bones show bowing and spinal curvature with vertebral collapse occur in the later stages of the disease.
What is dysplasia of the spine?
Introduction. Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a rare genetic disease characterized by development of dysplastic bone tissue leading to pain, deformities and compressive complications. Spinal involvement is rare particularly for the polyostotic form.
What is a fibrous cortical defect?
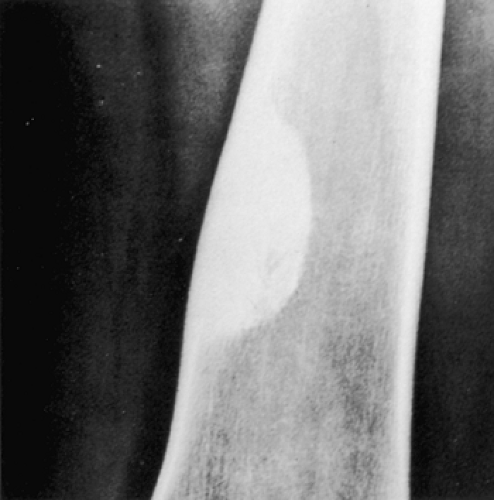
Non-ossifying fibroma (NOF) and fibrous cortical defect (FCD) are common bone lesions that are usually found in skeletally immature patients aged < 15 years [1]. These are usually asymptomatic and often discovered incidentally.
What causes Cemento-osseous dysplasia?
Periapical occurs most commonly in the mandibular anterior teeth while focal appears predominantly in the mandibular posterior teeth and florid in both maxilla and mandible in multiple quadrants....Cemento-osseous dysplasiaCausesCongenitalDiagnostic methodX-ray, CBCT scan, vitality testing of teeth10 more rows
What is focal Cemento-osseous dysplasia?
Focal cemento-osseous dysplasia (FCOD) is a benign fibro-osseous lesion of bone characterized by the replacement of normal bone by fibrous tissue and subsequently followed by its calcification with osseous and cementum-like material. It is mostly asymptomatic in nature and requires no treatment.
What is an ossifying fibroma?
Ossifying fibroma is defined as an encapsulated benign neoplasm composed of varying amounts of bone or cementum-like tissue in the fibrous tissue stroma. 1 It is a slow-growing benign neoplasm that occurs most often in the jaws, especially the mandible.
Fibro Osseous Lesions Classifications, Pathophysiology and Importance ...
Fibro Osseous Lesions 15 Int. Biol. Biomed. J. Winter 2016; Vol 2, No 1 embryonic life, the osteoblast, melanocyte and endocrine cells carry the mutation and express the
Benign Fibro-Osseous Lesions of the Head and Neck - PubMed
Benign fibro-osseous lesions (BFOLs) are a particularly challenging set of diagnoses for the pathologist. This diverse collection of diseases includes fibrous dysplasia, ossifying fibroma and cemento-osseous dysplasia. While all three conditions have similar microscopic presentations, their treatmen …
Benign fibro-osseous lesions: clinicopathologic features from 143 cases ...
The aim of this study was to report the clinicopathologic and radiologic features of 143 benign fibro-osseous lesions (BFOLs).Clinical and radiologic …
What are fibrogenic lesions?
These lesions represent a clinical spectrum ranging from very innocent lesions requiring no treatment at all to very aggressive and malignant neoplasms. All of these conditions have a common denominator, which is the fibroblast cell.
What is the common denominator of fibrous lesions?
All of these conditions have a common denominator, which is the fibroblast cell. In general, the fibrous lesions are composed of spindle cells (myofibroblasts and fibroclasts), which produce a collagenous matrix and so-called ground substance consisting of glucosaminoglycans, whereas the fibrohistiocytic lesions may or may not produce ...
What is the name of the disorder where a girl has a rough border?
Its polyostotic form may be associated with endocrine disturbances (leading to premature sexual development in girls) and skin pigmentation (café-aulait spots with rough border), known as McCune-Albright syndrome, or with benign soft-tissue myxomas, known as Mazabraud syndrome.
Which bones are most commonly affected by polyostotic form?
In monostotic form, about 35% involve the skull, 33% the tibia and femur, and 20% the ribs. In polyostotic form, the femur, pelvic bones, and tibia are most commonly affected.
What is a woven bone?
Woven and mature (lamellar) type of bone surrounded by cellular fibrous spindle cell growth in whorled or matted pattern; bone trabeculae rimmed by differentiated osteoblasts (“dressed trabeculae”)
What is angioma fibrous histiocytoma?
Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma, recently classified by WHO as a tumor of uncertain differentiation, is a rare lesion of low-grade malignancy, affecting predominantly children and young adults, involving mainly the soft tissues but occasionally seen in the bones.
How much of the bone is involved in pathologic fractures?
Most pathologic fractures develop through the lesions that involve more than 50% of the transverse diameter of the bone .
What is a FOL?
Historically, FOL has been referred to by a variety of names, including fibro-osseous dysplasia, fibrous dysplasia, focal osteodystrophy, osteodysplasia, osteofibrosis, and osteodystrophy, but the preferred term for these lesions is "fibro-osseous lesion.".
Is B6C3F1 a lesion?
Although this is a fairly common age-related background lesion in the B6C3F1 mouse, the incidence and severity of FOL may be influenced by treatment with compounds that possess estrogenic effects. Therefore, this lesion should be diagnosed, given a severity grade, and described in the narrative whenever present. Advanced FOL in mice is indistinguishable histologically from fibrous osteodystrophy. Therefore, when this lesion is observed in mice in an advanced state and in the absence of parathyroid or renal lesions, the diagnosis of FOL should be made. If the lesion occurs concurrently with chronic renal disease or proliferative parathyroid lesions, the diagnosis of fibrous osteodystrophy should be made (see Bone - Fibrous Osteodystrophy
