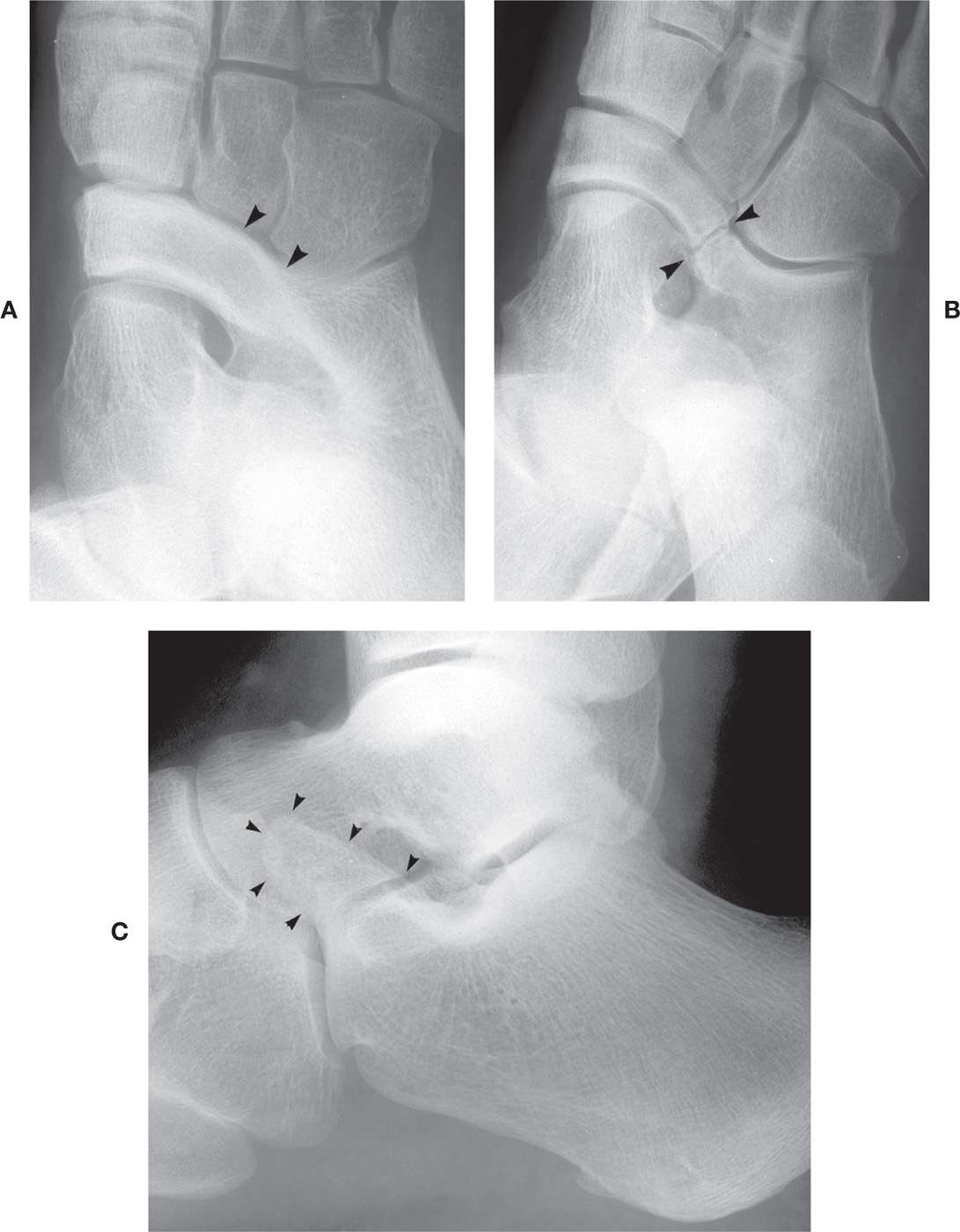
Calcaneonavicular coalition. Calcaneonavicular coalition is one of the two most common subtypes of tarsal coalition, the other being talocalcaneal coalition . As with any coalition it may be osseous (synostosis), cartilaginous (synchondrosis) or fibrous (syndesmosis).
What is a fibrous coalition?
A coalition occurs whenever bone cartilage or fibrous tissue grows across the joints in your foot. Most commonly, this occurs between your talus (ankle bone) and calcaneus (heel) bones or your calcaneus and navicular bones.
How is Calcaneonavicular coalition treated?
Calcaneonavicular coalition Initial conservative treatment of calcaneonavicular coalitions may include soft shoe inserts or a trial of walking-cast immobilization. These treatments have been described in the literature to extend from 3 to 6 weeks each.
How common is Calcaneonavicular coalition?
The two most common sites of tarsal coalition are between the calcaneus and navicular bones, or between the talus and calcaneus bones. However, other joints can also be affected. It is estimated that one out of every 100 people may have a tarsal coalition. In about 50% of cases, both feet are affected.
Is Calcaneonavicular coalition painful?
The pain is usually gradual in onset. Patients may complain of multiple sprains. This may be due to the increased stiffness of the subtalar joint leading to abnormal stresses thru the ankle. Walking on uneven ground may prove to be problematic.
What is Calcaneonavicular coalition in adults?
Introduction. Calcaneonavicular coalition is an abnormal union bridge between the calcaneus and the navicular or tarsal scaphoid bone, and may be osseous (synostosis), cartilaginous (synchondrosis) or fibrous (synfibrosis or syndesmosis).
Is surgery needed for tarsal coalition?
Treatment for tarsal coalition is only necessary if the condition is causing symptoms. Nonsurgical treatment options are often quite effective at managing symptoms long-term. However, if the pain and stiffness do not improve with conservative treatments, Dr. Katchis may recommend surgery.
Is Calcaneonavicular coalition hereditary?
Causes of Calcaneonavicular Coalition The condition is usually inherited. It occurs when the bones in the foot do not develop properly in the womb.
How painful is tarsal coalition?
Sometimes no symptoms are present during childhood. However, pain and symptoms may develop later in life. The symptoms of tarsal coalition may include one or more of the following: Pain (mild to severe) when walking or standing.
Is a tarsal coalition a disability?
Tarsal coalitions may cause altered foot biomechanics leading to patient disability from osteoarthritis and other sequelae. While some types of coalition are common, isolated talonavicular coalitions are relatively rare.
How successful is tarsal coalition surgery?
Treatment of tarsal coalitions can be considered good to excellent as well as safe, with an overall clinical success rate of 79% for TCCs and 81% for CNCs. Arthroscopic resection of the coalition appears to be non-inferior to open resection of TCCs and CNCs.
What does the calcaneonavicular ligament do?
The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament helps to maintain the medial longitudinal arch of the foot and by providing support to the head of the talus bears the major portion of the body weight. It is the main part of the spring ligament complex.
What are the two most common types of tarsal coalition?
The most common coalitions occur either: across a joint between the talus and calcaneus bones (talocalcaneal coalition, also referred to as a TC bar) between the calcaneus and navicular bones (calcaneonavicular coalition, also referred to as a CN bar)
How successful is tarsal coalition surgery?
Treatment of tarsal coalitions can be considered good to excellent as well as safe, with an overall clinical success rate of 79% for TCCs and 81% for CNCs. Arthroscopic resection of the coalition appears to be non-inferior to open resection of TCCs and CNCs.
How painful is tarsal coalition?
Sometimes no symptoms are present during childhood. However, pain and symptoms may develop later in life. The symptoms of tarsal coalition may include one or more of the following: Pain (mild to severe) when walking or standing.
Is a tarsal coalition a disability?
Tarsal coalitions may cause altered foot biomechanics leading to patient disability from osteoarthritis and other sequelae. While some types of coalition are common, isolated talonavicular coalitions are relatively rare.
What is a Calcaneonavicular coalition resection?
Summary. Calcaneonavicular coalition is a common source of pain and more or less severe flat and stiff foot in children. Classically, treatment consists in resecting the coalition using a dorsolateral approach. Good quality resection and interposition can prevent recurrence.
What is the Calcaneonavicular coalition?
Calcaneonavicular coalition. Calcaneonavicular coalition is one of the two most common subtypes of the tarsal coalition, the other being talocalcaneal coalition . As with any coalition it may be osseous (synostosis), cartilaginous (synchondrosis) or fibrous (syndesmosis).
Can tarsal coalitions be surgically treated?
As with any tarsal coalition, non-operative management may allow some improvement in symptoms initially, but they usually return. Usually, surgical treatment with excision of the coalition is required.
What is the calcaneonavicular coalition?
Calcaneonavicular coalition refers to the fusing of two bones in the foot: the calcaneus (heel bone) and the navicular bone. The navicular is an important bone because it joins with many other bones ...
How old is a child when ankles are calcaneonavicular?
When calcaneonavicular coalition occurs, the affected individual (usually a child between the ages of eight to 12 years old) reports ankle pain with loss of motion. They are no longer able to point the foot down all the way.
Does coalition grow back after surgery?
The problem is that in some patients, the coalition grows back. And even for those whose bone doesn ’t grow back, the bump that’s left after surgery is unsightly and rubs against the shoes. In this study, they tried using a fat graft instead of the muscle and tendon, thinking it would fill the hole more completely and prevent regrowth. But even with more than enough fat to fill the area, there were still a fair number of recurrences.
Is fat a good filler for tendon interposition?
The use of fat as a filler has several advantages over tendon interposition. For one thing, the tendon really isn’t long enough to fill the entire hole. Fat is always plentiful. For another, it’s easier to shape the results with fat, avoiding cosmetic disasters, such as obvious lumps and bumps that rub against shoes and sandals.
What is the Calcaneocuboid coalition?
Calcaneocuboid coalition, talonavicular coalition, and cubonavicular coalition: Calcaneocuboid coalition involves the calcaneus and the cuboid (located on the bottom of the foot) bones; talonavicular coalition involves the talus and the navicular bones; and cubonavicular coalition involves the cuboid and navicular bones. These forms of tarsal coalition are very rare.
What type of surgery is used to remove the calcaneonavicular coalition?
Excision surgery: In this type of surgery, the connecting tissue between the bones is removed, and replaced with muscle or fat tissue. The muscle or fat forms a physical barrier that prevents the bones from connecting again. This type of surgery is generally very successful in calcaneonavicular coalition.
What Is Tarsal Coalition?
Tarsal coalition affects the bones in the midfoot and heel, which are called the tarsal bones. There are several different forms of tarsal coalition.
How Is Tarsal Coalition Diagnosed?
In adolescents, tarsal coalition is sometimes discovered because their bones are ossifying.
What is a talocalcaneal coalition?
Talocalcaneal coalition (or talocalcaneal bar): In this form of tarsal coalition, the calcaneus bone and the talus bone (the ankle bone) are involved. As in calcaneonavicular coalition, the connection between the calcaneus and the talus could be partial or complete, and could be made of bone, cartilage, or fibrous tissue.
What percentage of people have tarsal coalition?
It’s estimated that anywhere from 1 to 3 percent of the population have this condition, which is typically diagnosed in children and adolescents. In tarsal coalition, two or more bones in the heel or the midfoot do not separate properly during fetal development, which can lead to a painful, flat foot. In about half of all cases, both feet are ...
What is the procedure to fuse bones together?
Fusion surgery: In cases in which excision would not be successful, such as where the tarsal coalition is too extensive, surgery may be performed to fuse the bones together. It may also be done when there is damage to the joints, when the patient is older, or if prior excision surgery was not successful.
