
What is a forerun in chemistry?
This lower boiling distillate is called the forerun. Watch the thermometer, and when the temperature rises to the boiling point of the expected distillate, replace the receiving flask with another flask. Depending on the experiment, you may collect several fractions of distillate at different boiling ranges.
What is the liquid at the end of distillation?
The liquid and/or solid that remains in the pot at the end of distillation is called the pot residue; the condensed liquid is called the distillate. Figure 16-2 shows the temperature versus volume curves for two successful distillations.
What is the purpose of distillation?
Exp 3 - Distillation - F17 Experiment 3 – Distillation pg. 1 3. Distillation A. Background Distillation is the second general method we have encountered for separating and purifying organic molecules. The purpose of distillation is to separate the components of a mixture of liquids by taking advantage of differences in their boiling points.
Can the ethanol produced during fermentation be distilled to greater than 96%?
Therefore, the ethanol produced during fermentation cannot be distilled to greater than 96% purity. Distillation of an ethanol-water mixture cannot be used to obtain absolute (200 proof) ethanol. When an azeotrope has a lower boiling point than that of the pure components, it is referred to as a minimum-boiling azeotrope.
What are the 3 stages of distillation?
The distillation process generally involves three main steps: The conversion of the desired liquid from a mixture into vapour. The condensation of the purified liquid. The collection of the condensed liquid.
What do distillations do?
Distillation is used to separate liquids from nonvolatile solids, as in the separation of alcoholic liquors from fermented materials, or in the separation of two or more liquids having different boiling points, as in the separation of gasoline, kerosene, and lubricating oil from crude oil.
How distillations can be used to separate mixtures?
Distillation is a physical separation based on the vaporization of the different components of the mixture to be separated. Typically, a mixture is heated, vapors are produced, separated, and then condensed back into a liquid. As a result, each component can be separately recuperated in different fractions.
What happens if you distill too quickly?
Slow, gradual distillation essentially allows the best equilibration and heat transfer. If you heat too fast, vapors may not condense as quickly as desired, and may waste some of the column. Packing material is also crucial. High surface area packing material provides surface on which condensation can occur.
How do you separate salt and water from distillation?
Separating the solvent from a solution – simple distillationSalt solution is heated.Water evaporates and its vapours rise. The water vapour passes into the condenser, where it cools and condenses. Liquid water drips into a beaker.All the water has evaporated from the salt solution, leaving the salt behind.
Why should a distilling flask be filled 2 3?
Fill the distillation flask. The flask should be no more than two thirds full because there needs to be sufficient clearance above the surface of the liquid so that when boiling commences the liquid is not propelled into the condenser, compromising the purity of the distillate.
What are the 5 separation techniques?
The Different Types of Separation TechniquesHandpicking.Threshing.Winnowing.Sieving.Sedimentation.Decantation.Filtration.Evaporation.More items...
What are the two basic methods of distillation?
Types of distillation include simple distillation (described here), fractional distillation (different volatile 'fractions' are collected as they are produced) and destructive distillation (usually, a material is heated so that it decomposes into compounds for collection) (http://www.chemistry.about.com/cs/5/f/ ...
How can you separate two liquids from each other?
Fractional distillation is a method for separating a liquid from a mixture of two or more liquids. For example, liquid ethanol can be separated from a mixture of ethanol and water by fractional distillation.
Why is it necessary to discard the first few drops of distillate?
The first few drops collected are the forerun that contains low boiling impurities and should be discarded. If, after you heat your distillation pot for a while and you notice no distillate, you may need to insulate your fractionating column and distillation pot with cotton and aluminum foil.
Which of the following are common mistakes made during distillation?
Common distillation mistakes. Water entering the condenser at the wrong end. It should enter at the bottom. If it enters at the top there are likely to be air pockets which result in poor condensation.
What are three important safety rules for distillation?
Distillation Safety TipsNever Rush The Process. It never pays to rush the process. ... Never Leave The Distiller Unattended. ... No Smoking or Drinking. ... Temperature. ... Avoid Math Mistakes. ... Label Your Containers. ... Never Use Plastic In Your Homemade Still.
What is the purpose of fractional distillation?
Fractional Distillation is used for both oil refining and purification of reagents and products. Fractional distillation is used in oil refineries (Figure 5.41) to separate the complex mixture into fractions that contain similar boiling points and therefore similar molecular weights and properties.
How is distillation used in everyday life?
Examples of uses of distillation include purification of alcohol, desalination, crude oil refining, and making liquefied gases from air.
What is the most common purpose of simple distillation?
The most common purpose for simple distillation is to purify drinking water of unwanted chemicals and minerals such as salt.
What are 5 distillation examples?
6 Fractional Distillation Examples in Everyday LifeOil Refining.Alcohol Manufacturing.Air Separation.Perfume Manufacturing.In the Manufacturing of High-Purity Silicon Semiconductors.Pharmaceutical Industry.
How is distillation made?
Wine or beer is first produced from a fruit or grain base, respectively, that has been fermented with yeast prior to distillation. The wine or beer is then placed into a still where a heat source is applied. There are two types of stills: column stills (Image 1) and pot stills (Image 2) (Berglund, 2004). Each uniquely separates ethanol from other organic compounds.
Why is distillation important?
When faults occur in wine, it is ideal to rework the product rather than to throw the product away at an economical loss. The identification of wine faults is necessary first before remediation techniques can be applied.
What temperature does ethanol boil?
As wine and beer are not pure compounds, their boiling temperatures will vary. Pure water boils at 100oC and pure ethanol boils at 78.5°C (Ackland, 2012). There are other compounds present in the mixtures that will boil at varying temperatures below 78.5°C , between 78.5°C and 100°C , and above 100°C (Table 1). The first compounds to boil, condense and be collected are often low molecular weight organic compounds such as methanol. These compounds are undesirable in the collected distillate. This portion of the distillate that is collected in the beginning of a still run is referred to as the "heads" or "forerun" (Berglund, 2004). Once the low molecular weight compounds have boiled off, ethanol is vaporized. This portion of the distillate is referred to as the "hearts." This is the part of the distillate that can be consumed and used in production of spirits. Following ethanol, the end distillate is called the "tails" and is also an undesirable portion of the distillation because it contains higher alcohols and esters that can dull the character of the spirit (Berglund, 2004).
Why does ethanol separate from water?
The separation of ethanol occurs because ethanol boils at a lower temperature than water. When heat is applied to the wine or beer base, ethanol boils before the water in solution. The ethanol vaporizes, rising to the top of the still, where it collects and then is sent to a condenser where it is quickly cooled.
What is the cause of wine oxidation?
Oxidation of wine is caused by oxygen exposure and carried through enzymatically or chemically (Gardner, 2013). A byproduct of wine oxidation is acetylaldehyde. The presence of acetylaldehyde smells like sherry or bruised apples, but it also reduces the perception of freshness and fruitiness of the wine.
What is a VA in wine?
Such faults include volatile acidity, oxidation, sulfur compounds, Brettanomyces contamination and cork taint. Volatile Acidity (VA) refers to the volatile acids that are found in wines, which is primarily acetic acid. VA includes acetic acid (AA) and other volatile acids.
What is cork taint?
Cork taint is a musty aroma that results from the impact compound 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole (TCA). TCA is formed in wine when wine comes in contact with phenols in wood (corks, pallets etc.) in addition to chlorine (Elias, 2012). The threshold for TCA in wine is 1 part per trillion (ppt), so extremely low levels of this compound in wine will reduce flavor and aromas in wine (Gardner, 2013). At higher concentrations, TCA smells like wet cardboard or a dank musty cellar.
What does "run in front of" mean?
to run in front of; come before; precede.
Does conscious aim forerun execution?
But the reflexes have a machine-like fatality, and conscious aim does not forerun their execution.
What is fractional distillation?
Fractional distillation is a separation technique that is used when the boiling point differences of the compounds in a mixture to be separated are not large enough to employ the simple distillation technique. The components to be separated are collected in different fractions, whose identity are usually then confirmed via spectroscopy or TLC (thin layer chromatography). The first fraction, (or the first mixture between fractions) usually just a few drops, is called the forerun. It contains any highly volatile substances that were present in the sample, and is a kind of first rinse of the distillation glassware. It may be combined with the next fraction if analysis warrants.
What is distillation used for?
Distillation is one of the most useful methods for the separation and purification of liquids. It is perhaps the oldest separation technique known. It is most commonly used to purify a liquid from either liquid or solid contaminants by exploiting differences in their boiling points.
Why is vacuum distillation important?
Vacuum distillation is used to purify compounds that can decompose before reaching their boiling point at atmospheric pressure. By lowering the gas pressure above a liquid, that liquid can be encouraged to boil at a lower temperature. This is important if it would break down at a higher one.
What is the first fraction of a mixture called?
The first fraction, (or the first mixture between fractions) usually just a few drops, is called the forerun.
What temperature does naphthalene boil?
For example, naphthalene, a solid at room temperature that boils at 218°C, can be melted and mixed with water. Because the two are immiscible, they will steam distill at a temperature around 90°C, less than 100°C (the boiling point of water) and well below 218 °C. In all steam distillations, the distillate collected will be a mixture ...
How to improve distillation?
Both batch and continuous distillations can be improved by making use of a fractionating column on top of the distillation flask. The column improves separation by providing a larger surface area for the vapor and condensate to come into contact. This helps it remain at equilibrium for as long as possible. The column can even consist of small subsystems ('trays' or 'dishes') which all contain an enriched, boiling liquid mixture, all with their own vapor–liquid equilibrium.
How does continuous distillation work?
Continuous distillation differs from batch distillation in the respect that concentrations should not change over time. Continuous distillation can be run at a steady state for an arbitrary amount of time. For any source material of specific composition, the main variables that affect the purity of products in continuous distillation are the reflux ratio and the number of theoretical equilibrium stages, in practice determined by the number of trays or the height of packing. Reflux is a flow from the condenser back to the column, which generates a recycle that allows a better separation with a given number of trays. Equilibrium stages are ideal steps where compositions achieve vapor–liquid equilibrium, repeating the separation process and allowing better separation given a reflux ratio. A column with a high reflux ratio may have fewer stages, but it refluxes a large amount of liquid, giving a wide column with a large holdup. Conversely, a column with a low reflux ratio must have a large number of stages, thus requiring a taller column.
Why is fractional distillation used?
Therefore, fractional distillation must be used in order to separate the components by repeated vaporization-condensation cycles within a packed fractionating column.
How is distillation kept constant?
In continuous distillation, the source materials, vapors, and distillate are kept at a constant composition by carefully replenishing the source material and removing fractions from both vapor and liquid in the system. This results in a more detailed control of the separation process.
What is the process of desalination?
Distillation is an effective and traditional method of desalination. In the petroleum industry, oil stabilization is a form of partial distillation that reduces the vapor pressure of crude oil, thereby making it safe for storage and transport as well as reducing the atmospheric emissions of volatile hydrocarbons.
How to boil a compound?
To boil such compounds, it is often better to lower the pressure at which such compounds are boiled instead of increasing the temperature. Once the pressure is lowered to the vapor pressure of the compound (at the given temperature), boiling and the rest of the distillation process can commence. This technique is referred to as vacuum distillation and it is commonly found in the laboratory in the form of the rotary evaporator .
What is distillation in chemistry?
Distillation may result in essentially complete separation (nearly pure components), or it may be a partial separation that increases the concentration of selected components in the mixture. In either case, the process exploits differences in the relative volatility of the mixture's components.
What is distillation in science?
Distillation is the process of heating a liquid until it boils, capturing and cooling the resultant hot vapors, and collecting the condensed liquid. Mankind has applied the principles of distillation for thousands of years. Distillation was probably first used by ancient Arab chemists to isolate perfumes. Vessels with a trough on the rim to collect distillate, called diqarus, date back to 3500 BC. In the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, alchemists developed distillation equipment known as retorts. In the 1800s, distilleries producing brandy, whisky, rum, gin, and vodka were established in Europe and America. The word “alcohol” derives from the Arabic “al-koh’l,” translated as “finely divided spirit.” Most of us are familiar with pictures of the moonshiner’s still: a large boiling pot with long coils of metal tubing used for condensing the alcohol vapors into moonshine, or illegal whisky.
How to make a distillation pot?
Turn on the water to the condenser to cool it down. Begin heating the distillation pot so that it boils smoothly and the distillate drips into the receiver at about 1–2 drops per second. Do not heat it too fast, or bumping (violent eruptions of large bubbles of liquid into the Y-adaptor) will occur. Bumping can cause impure liquid to be forced through the Y-adaptor and into the distilling pot.
What is steam distillation?
Steam distillation is the distillation of a mixture of water – steam – and an immiscible organic compound. The mixture will boil below 100°C because an immiscible mixture does not behave like an ideal solution (a mixture of miscible liquids). In a mixture of immiscible liquids, the total vapor pressure is the sum of the vapor pressures of the pure individual components. Thus for a steam distillation:
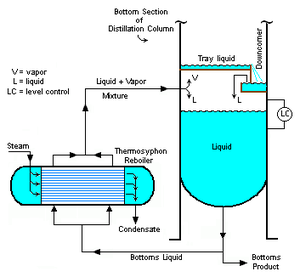
Introduction
- Wine is an alcoholic beverage made from the fermentation of grape must (Elias, 2012). It is a complex product that takes extreme care and caution throughout every stage of production. The overall quality of the final wine is a sum of each step in the process. Should a miscalculation or misstep occur along the production line, the final beverage can...
Faults in Wine
- Wine faults can appear anywhere in the production process. Such faults include volatile acidity, oxidation, sulfur compounds, Brettanomycescontamination and cork taint. Volatile Acidity (VA) refers to the volatile acids that are found in wines, which is primarily acetic acid. VA includes acetic acid (AA) and other volatile acids. Acetic acid's breakdown product, ethyl acetate (EA) ma…
Distillation of Wine For Wine Fault Remediation
- Distillation is used to produce many types of spirits, but in the wine industry, distilled wine can be used to produce brandy and port. Although the base beverage determines the neutrality and flavor of the distilled spirit, distillation can also be used to remediate some wine defects. The remainder of this paper will examine how faulted wine can be distilled for use in the wine industry. Volatile …
Conclusion
- Distillation of wine for the remediation of wine faults offers production choices for winemakers. When faults occur in wine, it is ideal to rework the product rather than to throw the product away at an economical loss. The identification of wine faults is necessary first before remediation techniques can be applied. With careful distillation techniques and understanding of the separati…
References
- Ackland, T. 2012. Home Distillation of Alcohol. 18 March 2013.
- Bavarian-Holstein Partners. Distilling. 18 March 2013.
- Berglund, Kris Arvid. 2004. Artisan Distilling: A Guide for Small Distillers. Michigan State University and Lulea University of Technology.
- Bisson, Linda F. 2013. Overview of the Biology of Brettanomyces: A New Look at an Old Probl…
- Ackland, T. 2012. Home Distillation of Alcohol. 18 March 2013.
- Bavarian-Holstein Partners. Distilling. 18 March 2013.
- Berglund, Kris Arvid. 2004. Artisan Distilling: A Guide for Small Distillers. Michigan State University and Lulea University of Technology.
- Bisson, Linda F. 2013. Overview of the Biology of Brettanomyces: A New Look at an Old Problem. Lecture Series. University of California.