
What are the main features of a fungus cell?
What are three unique features of fungal cells?
- Fungi are eukaryotic organisms means they have true nucleus which are enclosed in membranes.
- They are non-vascular organisms. …
- Fungi have cell walls (plants also have cell walls, but animals have no cell walls).
- There is no embryonic stage for fungi.
- They reproduce by means of spores.
What are fungi cells called?
Single-celled fungi are called yeast. Some fungi alternate between single-celled yeast and multicellular forms depending on what stage of the life cycle they are in. Fungi cells have a nucleus and organelles, like plant and animal cells do.
What type of cell does fungi have?
Types of Eukaryotic Cells
- Animal Cells. Animal cells are the basic building blocks that make up all animals, including birds, fish, reptiles, mammals, and amphibians.
- Plant Cells. Plants are made up of plant cells. ...
- Fungi Cells. The fungi kingdom consists of yeasts, mildews, molds, and mushrooms. ...
- Protist Cells. ...
What is the number of cell do fungus have?
Serratos laceration, valley fever, and fungi are some of these conditions caused by fungi. Humans and fungi share many similarities that distinguish them: yeast and algae have eukaryotes, and cell-forming fungi can make up to 100 cells each. Animals and fungi each form the best structure of one of these pathogens.
What is a fungus simple definition?
(FUN-gus) A plant-like organism that does not make chlorophyll. Mushrooms, yeasts, and molds are examples. The plural is fungi.
What are fungi cells called?
They are characterized by filamentous, vegetative cells called hyphae. A mass of hyphae forms the thallus (vegetative body) of the fungus, composed of mycelium.
What is an example of a fungal cell?
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker's yeast) and Candida species (the agents of thrush, a common fungal infection) are examples of unicellular fungi. Figure 24.1B. 1: Example of a unicellular fungus: Candida albicans is a yeast cell and the agent of candidiasis and thrush.
What makes fungal cells?
The cell wall is a characteristic structure of fungi and is composed mainly of glucans, chitin and glycoproteins. As the components of the fungal cell wall are not present in humans, this structure is an excellent target for antifungal therapy.
Why is fungal cells important?
Together with bacteria, fungi are responsible for breaking down organic matter and releasing carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus into the soil and the atmosphere. Fungi are essential to many household and industrial processes, notably the making of bread, wine, beer, and certain cheeses.
What is fungus made of?
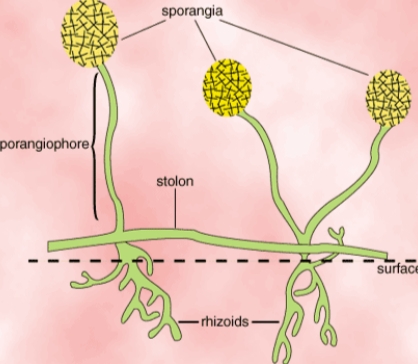
A typical fungus consists of a mass of branched, tubular filaments enclosed by a rigid cell wall. The filaments, called hyphae (singular hypha), branch repeatedly into a complicated, radially expanding network called the mycelium, which makes up the thallus, or undifferentiated body, of the typical fungus.
What is unique about fungi cells?
Unlike plant cells, fungal cells do not have chloroplasts or chlorophyll. Many fungi display bright colors arising from other cellular pigments, ranging from red to green to black.
What are the 4 types of fungi?
Fungi are usually classified in four divisions: the Chytridiomycota (chytrids), Zygomycota (bread molds), Ascomycota (yeasts and sac fungi), and the Basidiomycota (club fungi). Placement into a division is based on the way in which the fungus reproduces sexually.
How big are fungi cells?
Most fungi grow as hyphae, which are cylindrical, thread-like structures 2–10 µm in diameter and up to several centimeters in length.
How does fungus grow?
Fungi grow from the tips of filaments (hyphae) that make up the bodies of the organisms (mycelia), and they digest organic matter externally before absorbing it into their mycelia.
What do fungi need to survive?
Like us, fungi can only live and grow if they have food, water and oxygen (O2) from the air – but fungi don't chew food, drink water or breathe air. Instead, fungi grow as masses of narrow branched threads called hyphae.
Where do fungi grow?
Fungi can be single celled or very complex multicellular organisms. They are found in just about any habitat but most live on the land, mainly in soil or on plant material rather than in sea or fresh water.
Are fungi cells prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
eukaryotic organismsThe fungi (Mycota) are eukaryotic organisms that have a mycelial structure formed from slender filaments or hyphae (2–10μm in diameter) that may be unbranched or branched, septate or nonseptate and which are commonly multinucleate.
What are single-celled fungi called?
yeastAnswer and Explanation: A single celled organism in the fungi kingdom is called yeast. Yeast is a naturally occurring organism found both in nature and inside of our bodies.
Is fungi a plant or animal cell?
Fungi are no longer classified as either plants or animals. Fungi have been divided into a different kingdom, Kingdom Fungi, based on key distinguishing characteristics. Fungi are eukaryotic, heterotrophic creatures that thrive in warm, humid environments.
Why are fungi considered eukaryotes?
Fungi are eukaryotes, and as such, have a complex cellular organization. Being eukaryotes, a typical fungal cell contains a true nucleus, mitochondria, and a complex system of internal membranes, including the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus.
What is the fruiting body made of?
The fruiting body is made up of tightly packed hyphae which divide to produce the different parts of the fungal structure, for example the cap and the stem. Gills underneath the cap are covered with spores and a 10 cm diameter cap can produce up to 100 million spores per hour.
How do filamentous fungi grow?
Macroscopic filamentous fungi also grow by producing a mycelium below ground. They differ from moulds because they produce visible fruiting bodies (commonly known as mushrooms or toadstools) that hold the spores. The fruiting body is made up of tightly packed hyphae which divide to produce the different parts of the fungal structure, for example the cap and the stem. Gills underneath the cap are covered with spores and a 10 cm diameter cap can produce up to 100 million spores per hour.
How are fungi subdivided?
Fungi are subdivided on the basis of their life cycles, the presence or structure of their fruiting body and the arrangement of and type of spores (reproductive or distributional cells) they produce.
What are the three groups of fungi?
The three major groups of fungi are: 1 Multicellular filamentous moulds. 2 Macroscopic filamentous fungi that form large fruiting bodies. Sometimes the group is referred to as ‘mushrooms’, but the mushroom is just the part of the fungus we see above ground which is also known as the fruiting body. 3 Single celled microscopic yeasts.
How small are hyphal spores?
They are so small that between 500 – 1000 could fit on a pin head.
What are filamentous moulds made of?
Multicellular filamentous moulds. Moulds are made up of very fine threads (hyphae). Hyphae grow at the tip and divide repeatedly along their length creating long and branching chains. The hyphae keep growing and intertwining until they form a network of threads called a mycelium. Digestive enzymes are secreted from the hyphal tip.
What is a mushroom?
Sometimes the group is referred to as ‘mushrooms’, but the mushroom is just the part of the fungus we see above ground which is also known as the fruiting body. Single celled microscopic yeasts.
What is a fungus?
PreꞒ. an Aspergillus conidiophore. A fungus ( plural: fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, those being Plantae, Animalia, ...
What is the name of the group of fungi?
These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the Eumycota ( true fungi or Eumycetes ), which share a common ancestor (from a monophyletic group ), an interpretation that is also strongly supported by molecular phylogenetics.
How many species of yeast have bioluminescence?
In common with some plant and animal species, more than 70 fungal species display bioluminescence. Unique features: Some species grow as unicellular yeasts that reproduce by budding or fission. Dimorphic fungi can switch between a yeast phase and a hyphal phase in response to environmental conditions.
Why are fungi inconspicuous?
Abundant worldwide, most fungi are inconspicuous because of the small size of their structures, and their cryptic lifestyles in soil or on dead matter. Fungi include symbionts of plants, animals, or other fungi and also parasites. They may become noticeable when fruiting, either as mushrooms or as molds.
What is Baker's yeast?
Baker's yeast or Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a unicellular fungus, is used to make bread and other wheat-based products, such as pizza dough and dumplings. Yeast species of the genus Saccharomyces are also used to produce alcoholic beverages through fermentation. Shoyu koji mold ( Aspergillus oryzae) is an essential ingredient in brewing Shoyu ( soy sauce) and sake, and the preparation of miso, while Rhizopus species are used for making tempeh. Several of these fungi are domesticated species that were bred or selected according to their capacity to ferment food without producing harmful mycotoxins (see below), which are produced by very closely related Aspergilli. Quorn, a meat substitute, is made from Fusarium venenatum.
What are some insects that eat fungi?
Likewise, females of several wood wasp species (genus Sirex) inject their eggs together with spores of the wood-rotting fungus Amylostereum areolatum into the sapwood of pine trees; the growth of the fungus provides ideal nutritional conditions for the development of the wasp larvae. At least one species of stingless bee has a relationship with a fungus in the genus Monascus, where the larvae consume and depend on fungus transferred from old to new nests. Termites on the African savannah are also known to cultivate fungi, and yeasts of the genera Candida and Lachancea inhabit the gut of a wide range of insects, including neuropterans, beetles, and cockroaches; it is not known whether these fungi benefit their hosts. Fungi ingrowing dead wood are essential for xylophagous insects (e.g. woodboring beetles ). They deliver nutrients needed by xylophages to nutritionally scarce dead wood. Thanks to this nutritional enrichment the larvae of woodboring insect is able to grow and develop to adulthood. The larvae of many families of fungicolous flies, particularly those within the superfamily Sciaroidea such as the Mycetophilidae and some Keroplatidae feed on fungal fruiting bodies and sterile mycorrhizae.
What are the surfaces that mycorrhizae can grow on?
They are able to grow on inhospitable surfaces, including bare soil, rocks, tree bark, wood, shells, barnacles and leaves. As in mycorrhizas, the photobiont provides sugars and other carbohydrates via photosynthesis to the fungus, while the fungus provides minerals and water to the photobiont.
What is the cell wall of fungi?
The composition of cell wall is variable among the different groups of fungi or between the different species of the same group. In the majority of fungi, the wall lacks cellulose but contains a form of chitin known as the fungus cellulose which is strictly not identical with insect chitin.
What are the chemical constituents of fungi?
The chief chemical constituents are various polysaccharides, but proteins, lipids besides other substances have also been reported. In the lower fungi, the biflagellate Oomycetes are said to be distinct from all over fungi m the cellulose nature of the cell wall.
What is the cell membrane pressed against?
The cell or plasma membrane is pressed against the cell or hyphal wall except for occasional invaginations in some regions. The Invagination is either in the form of an infolded convoluted pocket or a pouch enclosing granular or vesicular material. Moore and Mc Lear (1961) named it lomasome.
What is the plasma membrane?
Moore and Mc Lear (1961) named it lomasome. Actually the plasma membrane is the surface layer of the protoplast altered to perform special functions. It is differentially permeable and shows a typical tripartite structure under the electron microscope. There is an electron dense layer on either side of the less dense central region.
What is the basic structural constituent of the cell wall in the Zygomycetes and higher fungi?
The basic structural constituent of the cell wall in the Zygomycetes and higher fungi (Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes) is chitin. It is a polysaccharide based on the nitrogen containing sugar (glucosamine). It is probable that more or less closely associated with chitin in the cell wall are pectic materials, protein, lipids, cellulose, ...
How many nuclei are in the cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm in the individual cells contains one, two or more globose or ellipsoid nuclei which in the somatic portion are small and usually range from 1-2 or 3µ in diameter. They cannot be seen without special techniques.
What is the living substance of the cell within the cell wall?
The living substance of the cell within the cell wall is the protoplast. It lacks the chloroplasts but is differentiated into the other usual cell parts such as plasma or cell membrane, vacuolated cytoplasm, cell organelles and one or more nuclei.
Why are fungal cells different from other cells?
These differences are mainly due to the characteristics of the cells that make them up. Fungal cells have some organelles that are not found in others, such as Wöroning's bodies, in addition to the fact that they can be mutinucleated, binucleated and even anucleated.
What are the structures that make up a filamentous fungus?
Make up hyphae. In filamentous fungi, the cells together make up larger structures called hyphae, which constitute the body of these fungi. In turn, hyphae can have a variable number of nuclei. They are uninucleated (1 nucleus), binucleated (2 nuclei), multinucleated (several nuclei) or anucleate (no nucleus).
What is a fungal cell?
The fungal cell They are the type of cell that make up the tructure of fungi, whether they are unicellular or filamentou. Fungi are a group of organim that, depite having characteritic in common with.
What is the most important structure in a fungal cell?
Cell nucleus. It is one of the most important structures of the fungal cell, since all the genetic material of the fungus is contained in it, delimited by a nuclear membrane. This membrane has small pores through which communication between the cytoplasm and the interior of the nucleus is possible.
What are the enzymes in a fungus?
Some of the enzymes they contain are: catalase, peroxidase, protease and phosphatase, among others. Wöroning bodies: They are organelles of a crystalline nature that are present only in filamentous fungi.
What is the cell nucleus of fungi?
Cell nucleus. References. The fungal cells They are the type of cell that make up the structure of fungi, whether they are unicellular or filamentous. Fungi are a group of organisms that, despite having characteristics in common with plants, belong to a separate kingdom; the Fungi kingdom. This is because they have certain characteristics ...
How many nuclei are there in a yeast?
Finally, depending on the type of fungus, the number of nuclei will vary. In single-celled fungi such as yeast-type, there is only one nucleus. Contrary to this, filamentous fungi, such as basidiomycetes or ascomycetes, have a variable number of nuclei, for each hypha.
What are molds called?
Fungi other than mushrooms are sometimes collectively called molds, although this term is better restricted to fungi of the sort represented by bread mold. (For information about slime molds, which exhibit features of both the animal and the fungal worlds, see protist .) porcini mushroom.
What are the most commonly recognized fungi?
While mushrooms and toadstools (poisonous mushrooms) are by no means the most numerous or economically significant fungi, they are the most easily recognized.
What kingdom are fungi in?
Many of these funguslike organisms are included in the kingdom Chromista. Fungi are among the most widely distributed organisms on Earth and are of great environmental and medical importance. Many fungi are free-living in soil or water; others form parasitic or symbiotic relationships with plants or animals.
What do parasitic fungi eat?
Parasitic fungi feed on living organisms (usually plants), thus causing disease. To feed, both types of fungi secrete digestive enzymes into the nutritive surface on which they are growing. The enzymes break down carbohydrates and proteins, which are then absorbed through the walls of the hyphae.
Why are fungi separate from plants?
Historically, fungi were included in the plant kingdom; however, because fungi lack chlorophyll and are distinguished by unique structural and physiological features (i.e., components of the cell wall and cell membrane), they have been separated from plants . In addition, fungi are clearly distinguished from all other living organisms, ...
How do fungi form spores?
They may be produced either directly by asexual methods or indirectly by sexual reproduction. Spores are commonly formed by the fragmentation of the mycelium or within specialized ...
What is artist's conk?
Artist's conk ( Ganoderma applanatum ), a bracket fungi. Distributed worldwide, the artist's conk is a wood-decaying fungus that primarily grows on dead or dying trees.
What is the role of pigments in fungal cells?
Pigments are associated with the cell wall and vary from black, green and red. They act as a protective layer by protecting fungus from harmful ultraviolet rays. The rigid layers comprise glucans and chitlins. Fungi are a good target for the development of antifungal drugs.
What are the rigid layers of a fungal cell?
The rigid layers comprise glucans and chitlins. Fungi are a good target for the development of antifungal drugs. Based on several tests, it has been found that the fungal cell wall has been composed of mannans, glucans, and glycoproteins.
What is the biosynthesis of fungi?
Biosynthesis is a unique feature of the fungal cell wall. They possess a complicated cellular structure. The cells of fungus comprise the membrane-bound nucleus and the DNA that is wrapped around histone proteins. Chlorophyll is absent in fungal cells.
What is the function of the cell wall of fungi?
The cell wall of fungi is a dynamic structure that protects the cell from environmental stress and prevents from various effects that are caused due to changes in osmotic pressure. Biosynthesis is a unique feature of the fungal cell wall. They possess a complicated cellular structure.
How do fungi get nutrients?
It is not possible to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere, hence they have to obtain from the diet. They obtain nutrients from decaying organic matter for which they mainly depend upon plant materials.
Is a fungus a multicellular organism?
Growth of Fungi. Thallus forms the vegetative body of a fungus that is either unicellular or multicellular. The majority of fungi are multicellular organisms. They consist of two different morphological phases, which include the reproductive and vegetative stage. The reproductive stage is more conspicuous.
Is yeast a fungus?
Fungus belongs to a group of eukaryotic organisms that includes unicellular and multicellular fungi. They are categorized into Kingdom ‘Fungi’. They form tangles of filaments. Yeast, on the other hand, is a unicellular organism that reproduces through binary fission or budding.
What types of fungi are there?
The first of the five phyla is chytridiomycosis (Chytrids), the oldest lineage of fungi.
How do fungi reproduce?
Fungi can reproduce by many mechanisms, both sexually and asexually, with the particular mechanisms employed dependant on species. Asexual reproduction usually occurs in fungal mycelium via mycelial fragmentation, allowing large clonal populations adapted to a specific role to rapidly disperse.
What is the hyphae filament made of?
Hyphae filaments are made from tubular cells that connect end on end. Each cell is surrounded by a cell wall composed of a compound called ‘chitin’. The chitin cell wall is a defining feature of the fungi kingdom. When the hyphae of a multicellular fungi creates a complex network of filaments it is called a ‘mycelium’.
How many zygomycetes are there?
Around 1,000 different zygomycetes species have currently been identified. Molds are a group of fast growing fungi that are responsible for the spoiling of many foods such as bread, fruits, vegetables and dairy products. The hyphae of molds spread across a food source and penetrate into the food.
How many species of fungi are there on Earth?
More than 100,000 species of fungi have been identified by biologists. It is estimated that more than 1.5 million species currently exist on Earth. Two groups of multicellular fungi contain over 95% of all species. One of these two groups is called ‘basidiomycetes’ which includes the mushroom producing fungi.
What would happen if fungi were not recycled?
If nutrients were not recycled, a habitat would become infertile and struggle to support life.
What do fungi do to plants?
Many fungi, known as mycorrhizae, live in close association with the roots of plants and actually help them to absorb more nutrients. The vast majority of plants depend on help from fungi to successfully compete with neighbouring plants for nutrients.
Why are fungi important?
Importance of fungi. Fungi are very important for a number of reasons worldwide. Mushrooms, truffles and yeast have a significant place in the food and alcohol industries as sources of food and in the process of fermentation. They are also used in the production of antibiotics. Fungi are one of the most important decomposers ...
How are fungi different from other living things?
Fungi are different from all other living things by the type of cell wall they have surrounding each of their cells. As opposed to plants, bacteria and some protists which have cell walls made from other compounds (e.g. cellulose), the cell walls of fungi are made from a compound called ‘chitin’.
What is the itch on my buttocks?
Jock itch. Jock itch is also known as tinea cruris. It’s a fungal infection that can affect the skin on your gro in area, as well as your inner thighs and buttocks. Like athlete’s foot, it’s caused by dermatophytes, a group of fungi that thrive in warm and humid areas.
What is jock itch?
jock itch. ringworm. yeast infection. onychomycosis, or a fungal infection of the nail. Some types of fungi don’t normally cause infections in humans but can cause sickness in people with weakened immune systems. These are called opportunistic infections.
What is a fungal infection?
What is fungal infection? Fungal infections can affect anyone, and they can appear on several parts of the body. A jock with athlete’s foot, a baby with thrush, and a woman with a vaginal yeast infection are just a few examples. Fungi are microorganisms characterized by a substance in their cell walls called chitin.
What is ringworm?
Ringworm is a fungal infection that can affect your skin and scalp. Similar to athlete’s foot and jock itch, it’s caused by dermatophytes. Ringworm is also part of a group of fungi that grow on skin, particularly in damp and humid parts of your body.
How long does it take for a fungal infection to heal?
Fungal infections can be uncomfortable or even painful. In some cases, they can take weeks or months to effectively treat. If you think you have a fungal infection, see your doctor. They can diagnose the type of infection and recommend an appropriate antifungal medication.
What is athlete's foot?
Athlete’s foot is also known as tinea pedis. It’s a type of fungal infection that can affect the skin on your feet, as well as your hands and nails . The infection is caused by dermatophytes, a group of fungi that can thrive in the warm and humid areas between your toes.
How do fungi reproduce?
Fungi reproduce by releasing spores that can be picked up by direct contact or even inhaled. That’s why fungal infections are most likely to affect your skin, nails, or lungs. Fungi can also penetrate your skin, affect your organs, and cause a body-wide systemic infection. Some common types of fungal infection include:

Overview
A fungus (plural: fungi or funguses ) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista.
Etymology
The English word fungus is directly adopted from the Latin fungus (mushroom), used in the writings of Horace and Pliny. This in turn is derived from the Greek word sphongos (σφόγγος 'sponge'), which refers to the macroscopic structures and morphology of mushrooms and molds; the root is also used in other languages, such as the German Schwamm ('sponge') and Schimmel ('mold').
The word mycology is derived from the Greek mykes (μύκης 'mushroom') and logos (λόγος 'disco…
Characteristics
Before the introduction of molecular methods for phylogenetic analysis, taxonomists considered fungi to be members of the plant kingdom because of similarities in lifestyle: both fungi and plants are mainly immobile, and have similarities in general morphology and growth habitat. Like plants, fungi often grow in soil and, in the case of mushrooms, form conspicuous fruit bodies, whic…
Diversity
Fungi have a worldwide distribution, and grow in a wide range of habitats, including extreme environments such as deserts or areas with high salt concentrations or ionizing radiation, as well as in deep sea sediments. Some can survive the intense UV and cosmic radiation encountered during space travel. Most grow in terrestrial environments, though several species live partly or sol…
Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the systematic study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy, and their use to humans as a source of medicine, food, and psychotropic substances consumed for religious purposes, as well as their dangers, such as poisoning or infection. The field of phytopathology, the study of plant diseases, is closely rel…
Morphology
Most fungi grow as hyphae, which are cylindrical, thread-like structures 2–10 µm in diameter and up to several centimeters in length. Hyphae grow at their tips (apices); new hyphae are typically formed by emergence of new tips along existing hyphae by a process called branching, or occasionally growing hyphal tips fork, giving rise to two parallel-growing hyphae. Hyphae also sometimes fu…
Growth and physiology
The growth of fungi as hyphae on or in solid substrates or as single cells in aquatic environments is adapted for the efficient extraction of nutrients, because these growth forms have high surface area to volume ratios. Hyphae are specifically adapted for growth on solid surfaces, and to invade substrates and tissues. They can exert large penetrative mechanical forces; for example, many plant pathogens, including Magnaporthe grisea, form a structure called an appressorium that evol…
Reproduction
Fungal reproduction is complex, reflecting the differences in lifestyles and genetic makeup within this diverse kingdom of organisms. It is estimated that a third of all fungi reproduce using more than one method of propagation; for example, reproduction may occur in two well-differentiated stages within the life cycle of a species, the teleomorph (sexual reproduction) and the anamorph (asex…