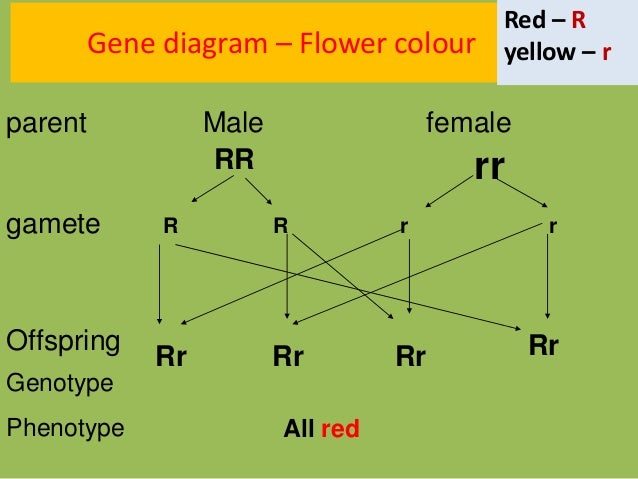
Phenotype refers to the physical expression while genotype refers to the genetic constitution. After a cross between two individuals, the pattern of expressing a visible characteristic among the offspring population is the phenotype ratio. On the other hand, the pattern of genetic makeup among the offspring population is the genotype ratio.
How do you write genotypic and phenotypic ratios?
- XD - Healthy X chromosome;
- Xd - X chromosome with Hemophilia gene; and
- Y - Y chromosome.
How do you calculate genotype ratio?
http://www.ehow.com/how_8288509_calculate-probabilities-likelihood-offspring.html
- 1. Make a Punnet, for one trait, by drawing a two-by-two block of squares. ...
- 4. ...
- Punnet Square Ratio 5b. ...
- http://www.ehow.com/how_8182896_calculate-phenotypic-ratio.html
- Calculating Phenotype Probabilities 1. ...
- Calculating Genotype Ratios
- 1. ...
- http://www.ehow.com/how_10005181_calculate-number-genotypes.html Calculating Genotype Probabilities
- 1. ...
- 2. ...
What are genotypic and phenotypic ratios?
Genotypic Ratio and Phenotypic Ratio. The genotypic ratio describes the number of times a genotype from a parent will be seen in an offspring after a test cross. On the other hand, The phenotypic ratio describes the relative number of offspring manifesting a singular or particular character or combination of traits after doing a test cross that ...
How do you find the phenotype ratio?
Using a Punnett square requires the following steps:
- Start by drawing a square. ...
- Write the genotypic information from either parent on the top of the square, with a letter representing each allele on top of each box.
- Repeat that process by adding the other parent's genetic information on the left side of the square.

What is genotype genotypic ratio?
The genotypic ratio is the ratio depicting the different genotypes of the offspring from a test cross. It represents the pattern of offspring distribution according to genotype, which is the genetic constitution determining the phenotype of an organism.
What is genotype ratio and phenotype ratio 10?
Phenotypic ratio is the ratio of offspring manifesting a particular trait. Genotypic ratio is the ratio of number of times a genotype (combination of alleles) has appeared in the offspring.
What type of cross produces a 1 1 1 1 phenotypic ratio?
dihybrid crossWith the dihybrid cross, you should expect a 1:1:1:1 ratio!
What is the ratio for phenotype?
A phenotypic ratio is a quantitative relation between phenotypes showing the number of times the frequency of one phenotype correlates with another. When a researcher would like to obtain the gene expression for generations of an organism, they use the phenotypic ratio obtained from a test cross.
How do you find the phenotypic ratio of Class 10?
There are some steps to find the phenotypic ratio as Write the amount of homozygous (AA) and heterozygous (Aa) squares as one phenotypic group. In the next step Count the amount of homozygous recessive (aa) squares as another group. Write the result as a ratio of the two groups.
What is the phenotypic ratio of dihybrid cross in f2 generation 10?
1:2:1.
What does a 1 2 1 phenotypic ratio mean?
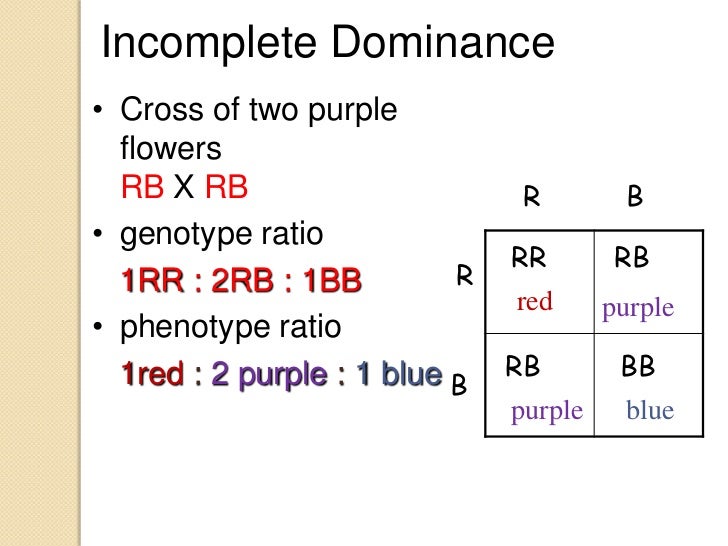
incomplete dominance6. Three phenotypes among the progeny in a 1:2:1 ratio suggest one gene is involved in determining the phenotype, with incomplete dominance as the mode of inheritance (the heterozygote has a different phenotype than either homozygote). In this case the phenotypic ratio is the same as the genotypic ratio. (
What does the 9 3 3 1 ratio mean?
The 9:3:3:1 ratio simply means that nine are wild-type meaning they are normal; six exhibit one mutant and one normal character, three are normal for one trait the other three are normal for the opposite trait; one has both mutant phenotypes.
Which of the following crosses will lead to a 9 3 3 1 ratio of phenotypes?
dihybrid crossThis 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio is the classic Mendelian ratio for a dihybrid cross in which the alleles of two different genes assort independently into gametes.
What is a 1 1 ratio?
1:1 ratio is 1 part or 1 unit of a particular quantity. for example, two bottles of water both having 2 liters of water each the ratio will be 22=11=1:1. two boxes both having 50 grams of butter each the ratio will be 5050=11=1:1.
What is a 3 1 ratio in genetics?
With 3:1 ratios there are three progeny with the dominant phenotype for every one (on average) with the recessive phenotype.
What gives a 3 1 ratio in genetics?
The F2 generation always produced a 3:1 ratio where the dominant trait is present three times as often as the recessive trait. Mendel coined two terms to describe the relationship of the two phenotypes based on the F1 and F2 phenotypes.
What is the difference between genotypic and phenotypic ratio?
The genotypic ratio describes the number of times a genotype from a parent will be seen in an offspring after a test cross. On the other hand, The phenotypic ratio describes the relative number of offspring manifesting a singular or particular character or combination of traits after doing a test cross that is based on the genotype of the offspring.
What is genotype in biology?
Genotype Definition. A genotype is an array, assemblage, or combination of genes that are responsible for the many genetic traits of an organism. When genotype is mentioned, it is referring to the organism’s gene, not traits. That is the organism’s raw information in the DNA. Furthermore, it is an expression of an organism’s genetic information ...
What is the genotypic ratio of a homozygous allele?
Thus the genotypic ratio is 1:2:1 meaning 1 homozygous dominant allele (PP), 2 heterozygous alleles (Pp, Pp), and 1 homozygous recessive allele (pp). On the other hand, the phenotypic ratio will be 3:1, meaning 3 out of 4 will be purple in color (PP, Pp, and Pp) and only one will be white in color (pp).
What is the equation for phenotype?
a more advanced equation will be. Phenotype = genotype (G) + environment (E) + genotype and environment (GE) Furthermore, there are two types of phenotypes, the first is called extreme phenotype which happens when both alleles of the parent produce a hybrid characteristic that differs and surpasses that of the parents.
How is genotype determined?
Therefore, genetic information or genotype is determined by the makeup of the alleles. In addition, an allele can be homozygous, that is, having a pair of dominant or recessive genes, or heterozygous, that is having both dominant and recessive genes in its paring.
What is the locus of an allele?
Locus; This is the location or position on a chromosome that an allele can be found. Homozygous Alleles; These are the same copies of alleles, either dominant or recessive. For example, (HH or rr) Heterozygous Alleles; These are different copies of alleles, with one being dominant, and the other recessive.
How is an organism's phenotype determined?
Thus an organisms’ phenotype is determined by its genotype and environment. In addition, phenotype covers a living things’ morphology or physical form and structure.
What is phenotypic ratio?
Definition. Phenotypic ratio helps us to predict gene expression in the future generations of organisms. In phenotypic ratio calculations, we map out specific parental alleles and predict the probability of how they will be expressed in their offspring. Knowledge of allele dominance is required, although it is possible to figure out very simple ...
What is the basic unit of inheritance that is the result of the genes of the parents?
Gene: a basic unit of inheritance that is the result of the genes of the parents. Genes are coded messages that produce specific proteins inside a cell, but only if a cell has been switched on to express it. Allele: a version of a gene that comes from one of the two parents.
What is the dominant allele in a Punnett square?
In a Punnett square, the mother’s alleles are noted at the top and the father’s at the side. The dominant allele is always listed first. Mother in red (LL), father in blue (ll) – offspring (purple) are a mix of both (Ll) As all four offspring are long-haired, a phenotypic ratio calculation is redundant.
Is phenotypic ratio redundant?
As all four offspring are long-haired, a phenotypic ratio calculation is redundant. We only need to measure the phenotypic ratio when more than one phenotype exists. In this example, there are two possible genotypic outcomes – long hair and short hair – but only long hair is expressed (phenotype).
Is there a 100% visibility rate in a single dominant phenotype?
There is a 100% visibility rate in the single dominant phenotype. As there is no second phenotype, there is no phenotypic ratio. If we did put this result as a ratio, it would be 4:0. The genotypic ratio, however, does not look at the observable trait (the phenotype) but at potential allele combinations.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype vs. Phenotype. The genetic makeup of an organism is called its genotype and its observable traits are its phenotype. In other words, what a person looks like is the result of his or her DNA.
What is the color of Mendel's plants?
The phenotype of the plants is their color, yellow and green. When Mendel crossed these two plants, all the offspring (F 1) were yellow. But the green color was not lost as it showed up again in the next generation (F 2 ).
Is a yellow pea homozygous?
Both the green and yellow P 1 pea plants had identical alleles for the gene that controls their color, meaning they were homozygous. When two green or two yellow plants were bred together, all the offspring of the green plants were green, and all the offspring of the yellow plants were yellow.