What is end-tidal carbon dioxide?
1. What is End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide? End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide refers to the partial pressure or concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) at the end of exhalation, which is normally 35-45 mm Hg. Phase I: Happens suddenly with an inspiration.
What is endend-tidal CO2 monitoring?
End-tidal carbon dioxide (ETco 2) monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance (ventilation). Also called capnometry or capnography, this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.
What is endend-tidal Capnography / EtCO2?
End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) at the end of an exhaled breath. The normal values are 5-6% CO2, which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
What is endend-tidal carbon dioxide?
End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide refers to the partial pressure or concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) at the end of exhalation, which is normally 35-45 mm Hg. Phase I: Happens suddenly with an inspiration.

What is a high end-tidal CO2?
Think respiratory failure when ETCO2 is high The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation, or end-tidal CO2 (ETCO2) is normally 35-45 mm HG. The height of the capnography waveform accompanies this number on the monitor, as well as the respiratory rate.
What is a good end-tidal CO2 during CPR?
Teams should aim for EtCO2 at least >10 mm Hg and ideally >20 mm Hg. Where do these numbers come from? These values are approximately 1/4 the normal EtCO2 (35-45 mm Hg), and ideal CPR will provide at least 1/4 of cardiac output.
What is the normal range of end-tidal CO2?
Normal EtCO2 levels range from 30s and 40s, but this may vary based on the patient's underlying respiratory and metabolic status.
What does ETCO2 greater than 40 mean?
If the values rise to normal (35-45) or above, the patient probably has had a return of pulse so check the rhythm and pulse carefully at the next rhythm check. Keep in mind this monitoring can be accomplished even if no advanced airway is inserted. Here is a great example of ETCO2 monitoring during an arrest.
What is a good end-tidal?
Remember, a normal end-tidal is between 35 and 45.
What is the target range for EtCO2 in a trauma patient?
Standardized ventilation protocols were used by most paramedics; however, one agency instituted ETCO2 monitoring during the second trial year, with paramedics instructed to target ETCO2 values of 30 to 35 mmHg.
What does it mean if end tidal CO2 is low?
In critical care, End Tidal CO2 monitoring is used to assess adequacy of circulation to the lungs, which provides clues about circulation to the rest of the body. Low EtCO2 with other signs of shock indicates poor systemic perfusion, which can be caused by hypovolemia, sepsis or dysrhythmias.
What is the normal range of EtCO2 in MM?
End-tidal CO2 - EtCO2 is a noninvasive technique which represents the partial pressure or maximal concentration of CO2 at the end of exhalation. Normal value is 35-45 mmHg.
How accurate is end tidal CO2?
The 95% level of agreement for PETCO2 and PaCO2 ranged from -0.90 to 9.95 mm Hg (nose) and from -2.39 to 8.82 mm Hg (pharynx).
Is low ETCO2 acidosis?
While EtCO2 values above 24.5-36 mmHg appear to exclude metabolic acidosis status, EtCO2 values less than 24.5-31 mmHg are indicative of acidotic status.
Which is higher ETCO2 vs paco2?
In their study ETCO2 (39.9 ± 12.7 mmHg) was lower than the PaCO2 (45.5 ± 14.1 mmHg). In the current study the values of ETCO2 and PaCO2 overall in the patients were 39.2 ± 13.9 mmHg versus 42.2 ± 14.1 mmHg.
What indicates hypercapnia?
The exact history and physical findings are highly variable depending on the source of hypercapnia. Patients may present with a complaint of flushed skin, lethargy, inability to focus, mild headaches, disorientation, dizziness, shortness of breath, dyspnea on exertion, nausea, vomiting, and/or fatigue.
Which of the following will cause a rise in ETCO2 levels?
Hypoventilation causes an increase in ETCO2. Altered patients whose ETCO2 is high (above 45 mm HG), are not breathing fast or deep enough. Often the decrease in respiratory rate can be seen with the waveform as the ETCO2 climbs and quickly corrected after the patient is stimulated.
How do you lower ETCO2 on a ventilator?
Raising the rate or the tidal volume, as well as increasing T low, will increase ventilation and decrease CO2. Consideration has to be made while increasing the rate, as this will also increase the amount of dead space and might not be as effective as tidal volume.
Does capnography assess perfusion status?
Pulse oximetry and capnography are two tools available for assessing ventilation and perfusion status, especially in the prehospital and emergency department arenas.
What is ETCO 2?
ETco 2 monitoring yields significant information about a patient’s ventilation status when combined with thorough physical assessment. It can be used in a wide range of settings, from prehospital settings to emergency departments and procedural areas.
What is the purpose of a microstream monitor?
While sidestream and mainstream monitors rely on infrared absorption, the newest type of ETco 2 monitor uses molecular correlation spectrography for greater precision. The Microstream monitor has a rapid response time and may be used with both invasive and noninvasive ventilation. It’s commonly used in procedural areas, such as gastroenterology labs, where moderate sedation is administered. Its main limitations are cost and the need for a monitor separate from the bedside monitor or ventilator.
How does a sidestream monitor work?
Sidestream monitors rely on a separate monitor or analyzer connected to the patient’s airway by tubing. Gas samples are aspirated from exhaled gas flow via the ventilator circuit through a T-adapter and are read at the monitor. Sampling rates usually range from 150 to 200 mL/minute, making these monitors unsuitable for neonates. A slight delay in data retrieval may occur due to the lag time between airway and monitor. Sidestream monitors can be used with noninvasive ventilation and are relatively inexpensive when part of a monitoring package.
What is ETCO 2 monitoring?
A standard of care in the operating room for more than 25 years, ETco 2 monitoring is becoming a common adjunct in the intensive-care and procedural-care settings.
What are the different types of ETCO monitors?
Three primary types of ETco 2 monitors are available: sidestream, mainstream, and Microstream ®. All have evolved to be lighter, more accurate, and easier to calibrate. Each type has certain advantages and limitations.
What is a time based capnogram?
A time-based capnogram can provide useful information based on its morphology and phases; it’s commonly used in the clinical arena. (See Basic time-based capnogram by clicking the PDF icon above.) Volume-based (expiratory) capnography yields a waveform with characteristic phases plotted over a known exhaled volume.
Where is ETCO 2 used?
It’s commonly used in procedural areas, such as gastroenterology labs, where moderate sedation is administered. Its main limitations are cost and the need for a monitor separate from the bedside monitor or ventilator. Interpreting ETco 2 monitoring data.
What is the normal etCO2 for CPR?
Where do these numbers come from? These values are approximately 1/4 the normal EtCO2 (35-45 mm Hg), and ideal CPR will provide at least 1/4 of cardiac output.
What is the best way to verify ETT placement?
ACEP’s policy on verification of ETT placement reminds us that physical examination and fogging in the tube are not reliable to confirm placement. Providers should use EtCO2 detectors (e.g. waveform capnography or colorimetry) to confirm ETT position. Ultrasound in the hands of an experienced provider is also recommended. 3
What is the PQRST mnemonic?
The PQRST mnemonic comes from a team in Norway who in 2014 published on how it can help providers optimize all the ways that EtCO2 can help with managing patients. 1 As a reminder, EtCO2 represents the amount of carbon dioxide at the end of exhalation. Capnography, however, reflects both a number (EtCO2 in mm Hg) and a waveform. Figure 1 reviews the meaning of each phase of the waveform. 2 It’s useful to keep these terms separate in our minds when reviewing the PQRST mnemonic.
What is etco2 monitoring?
End-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) monitoring is a measure of metabolism, perfusion, and ventilation. In the ED, we typically think of a EtCO2 as a marker of perfusion and ventilation. However, EtCO2 is an extremely powerful surrogate for endotracheal tube (ETT) P osition, CPR Q uality, R eturn of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), S trategies for treatment, and T ermination (of CPR). Do these letters look familiar? They should! In this post we take a deep dive into each of these potential uses of EtCO2 in the ED.
How long does it take for EtCO2 to be able to terminate CPR?
EtCO2 may provide an additional data point when deciding whether it is appropriate to terminate CPR. Approximately 20 minutes into a resuscitation, the likelihood of ROSC is significantly higher if EtCO2 >20 mm Hg and much less if EtCO2 <10 mm Hg. 4
What are some examples of waveform morphology during CPR?
The waveform morphology during CPR can help us decide what our next intervention should be. Examples include ETT dislodgment, cuff leak, and bronchospasm.
How specific is an increase in etCO2?
An increase of EtCO2 to normal values (35-45 mm Hg) or an increase by 10 mm Hg is about 97% specific. One caveat is that sodium bicarbonate may transiently raise the EtCO2, but this does not reflect ROSC. 2.
What is the CO2 level of BioPAC?
The impetus for this question-- we're using the BIOPAC system and with a small sample of healthy subjects, we're seeing values of 3.5%-4.5% CO2 which translates to 27-34 mmHg (unless we're calculating it wrong).
What is the best sampling rate for CO2?
Also, I note from the biopac info that the CO2 module is fitted with a variable speed sampling pump; for accurate real time CO2 readings this should be set at the fastest recommended sampling rate (150-200 mL/min for an adult, 50 for an infant).
What should you be taking your values from?
Ideally you should be taking your values from a calibrated paper trace , using an analog signal (sorry, showing my age!).
How many hours a week do you need to be a coauthor?
Please leave your email address if you are interested. 10 hours a week is required as there is a lot of projects to be done!
Does CO2 reach expiratory levels?
Also the range of traditional values were taken from arterial levels, and i think there is good reason to believe that even the plateau levels of end-expiratory CO2 don't reach true expiratory levels (check it out yourself by breathing slower (and somewhat deeper) with the sensor on (but make sure you don't start hyperventilating (your minute ventilation volume increases from normal resting pattern of breathing).
Is it necessary to obtain normative physiological data for that goal?
It is not necessary to obtain normative physiological data for that goal.
How to control etco 2?
Control using rate of ventilation. If EtCO 2 is low (i.e., being blown off too fast), begin by assisting the patient to breathe more slowly or by ventilating at 10-12 bpm. If EtCO 2 is high (i.e., accumulating too much between breaths), begin by ventilating at a slightly faster rate.
What is phase 3 of EtCO 2?
P: Ventilation. Patients with emphysema may have so much damage to their lung tissue that the shape of their waveform may “lean in the wrong direction.” In a similar way, patients with a pneumothorax won’ t be able to maintain the plateau of phase 3 of the EtCO 2 wave. The shape will start high and then trail off as air leaks from the lung, producing a similar, high on the left, lower on the right shape. 8,13
What is the shape of a fast ventilation wave?
S: Rounded low rectangle EtCO 2 waveform . Faster ventilation will produce wave shapes that aren’t as wide or as tall since rapid exhalation doesn’t take as long and contains less CO 2. (See Figure 6a, p. 51.) Slower ventilation produces wave shapes that are wider and taller as exhalation takes longer and more CO 2 builds up between breaths. (See Figure 6b, p. 51.)
What is the purpose of capnography?
Capnography is a great way to confirm airway device placement and monitor ventilation , but it can do so much more. Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is a product of metabolism transported via perfusion and expelled through ventilation. End-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO 2) waveform monitoring allows you to measure all three simultaneously, making it the most important vital sign you use. 1
How many BPM should I use for a ventilator?
Children should be ventilated at a rate of 15-30 bpm; 25-50 bpm for infants. Ventilating too quickly won’t let enough CO 2 build up in the alveoli, resulting in lower EtCO 2 readings. Ventilating too slowly will allow extra CO 2 to build up, resulting in higher readings.
What is the pressure of oxygen in the alveoli?
Oxygen is then pushed from the partial pressure of 100 mmHg in the alveoli to the lower partial pressure of 95 mmHg in the capillaries surrounding the alveoli. Oxygen gets carried through the circulatory system, getting absorbed along the way.
What happens if you vent too slowly?
Ventilating too slowly will allow extra CO 2 to build up, resulting in higher readings. Shape of the waveform should normally be a rectangle with rounded corners. Different waveform shapes can indicate different conditions. Trending of the quantity, rate and shape of EtCO 2 should be stable or improving.
What is the ETCO2 waveform?
ETCO2 is a recognized gold standard for confirming the correct location of the endotracheal tube. As long as the continuous ETCO2 waveform shows, it’s confirmed that the tracheal tube is in the trachea. The ETCO2 waveform can help vets make the final judgment when intubating cats, rabbits, and rodents that are difficult to intubate.
What is the ETCO2 of normal animals?
The ETCO2 of normal animals ≈PA CO2 (partial pressure of carbon dioxide in alveolus) ≈Pa CO2 (partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arteries), which is slightly lower than PaCO2. 2.
What is ETCO2 monitoring?
ETCO2 monitoring is continuous and non-invasive, which can be used to guide the temporary suspension of the ventilator. When SpO2 and ETCO2 remain normal during spontaneous breathing, the ventilator can be removed. Attention should be paid to the presence of abnormal ETCO2, and blood gas examination should be applied if necessary.
How is CO2 produced?
CO2 produced by tissue and cell metabolism is transported to the lungs through capillaries and veins, and finally expelled through exhalation. The body’s carbon dioxide output (VCO2) and alveolar ventilation value (VA) determine the end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2). ETCO2 = VCO2 × 0.863 / VA (0.863 is a constant that converts gas volume to pressure). The ETCO2 of normal animals ≈PA CO2 (partial pressure of carbon dioxide in alveolus) ≈Pa CO2 (partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arteries), which is slightly lower than PaCO2.
What are the advantages of a stand alone monitor?
The advantages of stand-alone ETCO2 monitors: 1.The greatest advantage is good compatibility, which means a stand-alone capnography monitor can be matched with other monitors. 2. In addition, they are compact, lightweight, space-saving, easy to move, and applicable for more diverse scenarios.
Why is CO2 monitoring important?
Monitoring the emission of CO2 can assess the metabolic rate of the body and assist in diagnosing malignant hyperthermia, which is characterized by a large increase in CO2 occurs earlier than the increase of body temperature.
What is phase 3 in chemistry?
Phase III: A very rapid increase in ETCO2, which represents exhalation of mixed air.
When is end-tidal capnography recommended?
Usually, end-tidal capnography is used by emergency physicians and paramedics to determine the respiration of the patient. End-tidal capnography can also be used in the following settings:
Is capnography really useful?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood are incredibly important for proper oxygenation and metabolism, that’s why capnography is very useful. An irregular amount of CO2 in a patient’s breath and the degree of that irregularity can tell healthcare providers a great deal about the condition and treatment required. It can inform you about the human body ’s functions in an emergency situation, and it can often do so before any other measurement. Because its utility expands beyond just hospitals into pre-hospital emergency settings, its advantages become increasingly clear, and it becomes easier to consider capnography as a valuable tool that it is for emergency medical services. It helps paramedics to help critically ill patient’s condition by giving readings during chest compressions and breathing assessments.
What are the four phases of the capnogram?
Capnogram (measured by the capnometer) is used in airway management to monitor the respiration levels. Below are the four phases of capnography:
What is phase 2 of CO2?
Phase II: In this phase, CO2 from the lungs reaches the upper airway and mixes with dead space air, which causes a rapid increase in CO2. Carbon is detected using capnogram in exhaled air. It is also called an ascending phase or early exhalation.
What is end tidal capnography?
End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) at the end of an exhaled breath.
What is a capnogram?
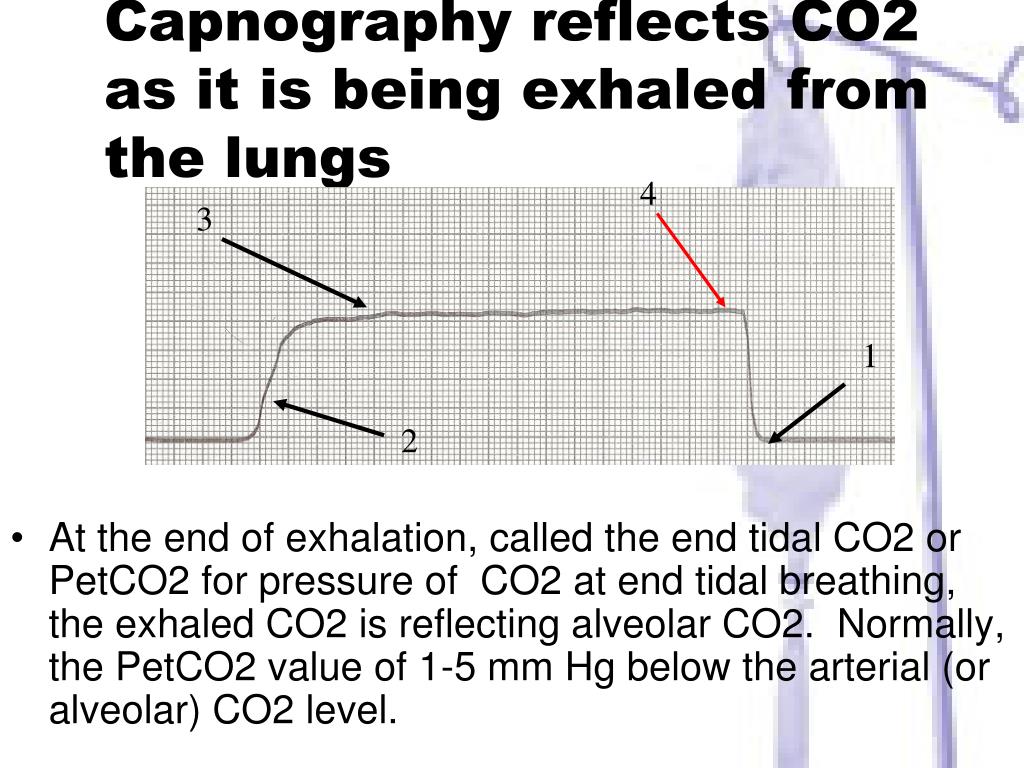
Capnogram (measured by the capnometer) is used in airway management to monitor the respiration levels. Below are the four phases of capnography: 1 Phase I: It is called the beginning of exhalation or baseline, and there is no carbon dioxide (CO2) present. In this phase, no gas exchange occurs; hence, it is usually called a dead space (air in tubing and bronchus). 2 Phase II: In this phase, CO2 from the lungs reaches the upper airway and mixes with dead space air, which causes a rapid increase in CO2. Carbon is detected using capnogram in exhaled air. It is also called an ascending phase or early exhalation. 3 Phase III: In this phase, there is CO2 recorded uniformly in the nose/mouth and lungs. 4 Phase IV: It is called an end-tidal phase. It shows the start of inspiration. Normal end-tidal CO2 values are 35-45 mmHg. This phase is also called a descending phase because oxygen fills when inhalation begins and CO2 concentration decreases.
Where is CO2 recorded in phase 3?
Phase III: In this phase, there is CO2 recorded uniformly in the nose/mouth and lungs.
