
What is the percentage of porosity of a material?
Porosity. Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%.
What is porosity of rock?
Porosity is the percentage of void space in a rock. It is defined as the ratio of the volume of the voids or pore space divided by the total volume. It is written as either a decimal fraction between 0 and 1 or as a percentage.
How do you write porosity as a fraction?
It is written as either a decimal fraction between 0 and 1 or as a percentage. For most rocks, porosity varies from less than 1% to 40%. The porosity of a rock depends on many factors, including the rock type and how the grains of a rock are arranged.
How do you measure porosity?
Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam ). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning .

What is a good soil porosity percentage?
Most textbooks talk about an ideal soil having 50% solids and 50% pore space. Pore space is that portion of the soil not occupied by solid material--the spaces between the particles. These pores may contain air or water.
What is porosity percentage?
Porosity is the percentage of void space in a rock. Porosity is the percentage of void space in a rock. It is defined as the ratio of the volume of the voids or pore space divided by the total volume. It is written as either a decimal fraction between 0 and 1 or as a percentage.
What is the average porosity of soil?
Porosity of soil Aggregation involves particulate adhesion and higher resistance to compaction. Typical bulk density of sandy soil is between 1.5 and 1.7 g/cm3. This calculates to a porosity between 0.43 and 0.36.
What is the maximum value of porosity?
The theoretical maximum porosity for a cubic packed rock, regardless of the value assigned to grain radius, is 47.6%. Porosity values for other packing arrangements (Figure 4) can be calculated.
How do you find porosity percentage?
The first equation uses the total volume and the volume of the void. Porosity = (Volume of Voids / Total Volume) x 100%. The second equation uses the total volume and the volume of the solid. Porosity = ( ( Total Volume - Volume of the Solid ) / Total Volume ) x 100%.
What is high porosity soil?
Porous soils have a low holding capacity for water and become saturated quickly. Large pore spaces allow water to drain through the soil quickly, and porous soil often holds fewer nutrients than other soils. Particles of clay and organic matter help hold nutrients in the soil.
Why is porosity important in soil?
In crop production, soil porosity is important to conduct water, air, and nutrients into the soil (Indoria et al., 2017b). Pore-size distribution provides the ability to soil to store root zone water and air necessary for plant growth (Reynolds et al., 2002).
How do you measure soil porosity?
How is Soil Porosity Calculated? A fairly straightforward formula is used as follows: Soil Porosity = ( 1 - (Bulk Density ÷ Particle Density) ) x 100. This will indicate the percentage of the soil that contains pores.
In which sample the percentage of the porosity will be least?
Metamorphic or igneous rocks have the lowest porosity. It is actually a percentage of void spaces in the rock. Some rocks have high porosity e.g., limestones and some have low porosity for example igneous rock.
What are the 3 factors of porosity?
The principal factors that control porosity are grain size and shape, the degree of sorting (a well-sorted sediment has a narrow range of grain size), the extent to which cement occupies the pore spaces of grains and the amount of fracturing.
What is total porosity?
Total porosity is defined as the fraction of the bulk rock volume V that is not occupied by. solid matter. If the volume of solids is denoted by Vs, and the pore volume as Vp = V - Vs, we.
What is considered high permeability?
1 Permeability. Permeability defines how easily a fluid flows through a porous material. Materials with a high permeability allow easy flow, while materials with a low permeability resist flow.
What is the meaning of porosity?
Definition of porosity 1a : the quality or state of being porous. b : the ratio of the volume of interstices of a material to the volume of its mass.
What is porosity of a material?
What is the porosity of a material? Porosity is the volumetric fraction of pores in the material. These pores can be located on its surface or in its internal structure. Porosity is associated with the density of the material, and with the nature of its compounds and the existence of empty spaces between them.
What is porosity and examples?
Porosity definition The ratio of the volume of all the pores in a material to the volume of the whole. 3. Porosity is defined as being full of tiny holes that water or air can get through. An example of porosity is the quality of a sponge.
What is total porosity?
Total porosity is defined as the fraction of the bulk rock volume V that is not occupied by. solid matter. If the volume of solids is denoted by Vs, and the pore volume as Vp = V - Vs, we.
How much does porosity vary?
For most rocks, porosity varies from less than 1% to 40%. The porosity of a rock depends on many factors, including the rock type and how the grains of a rock are arranged. For example, crystalline rock such as granite has a very low porosity (<1%) since the only pore spaces are the tiny, long, thin cracks between the individual mineral grains.
Which type of rock has the lowest porosity?
The dolomites have the lowest porosities (2–6%), the shales have the widest range of porosities (8–29%, although most are less than 15%), and the sandstones have the highest porosity (11–32%). Figure 1. Distribution of porosities for dolomite, shale, and sandstone.
What is the percentage of void space in a rock?
What is porosity? Porosity is the percentage of void space in a rock. Porosity is the percentage of void space in a rock. It is defined as the ratio of the volume of the voids or pore space divided by the total volume. It is written as either a decimal fraction between 0 and 1 or as a percentage. For most rocks, porosity varies from less ...
What is the density of sandstone?
Sandstones, ρ = 2.65–2.80 g/cm 3. Nearly half of the sandstones have grain densities close to 2.65 g/cm 3, the density of quartz, suggesting that those sandstones are composed of quartz grains and cement.
How to calculate grain density?
Grain density was calculated by subtracting the pore space volume from the total sample volume and then dividing the difference by the dry mass.
How to determine dry densities?
Dry densities were determined by weighing the samples after drying and dividing the mass by the total sample volume.
What is the density of a rock?
Density is defined as the mass per volume. In rocks, it is a function of the densities of the individual grains, the porosity, and the fluid filling the pores. There are three types of density in rocks: dry density, wet density, and grain density.
Porosity Percentage
The Porosity Percentage calculator computes the porosity of a medium. The porosity represents the relative amounts of space occupied by the "voids" in a volume of material, where the voids can be a combination of liquids or gases.
Notes
In engineering application the porosity is used to indicate a tendency of a material to expand or contract. A high porosity percentage is likely to be seen in loose soils which then will contract under pressure or added loads. A low porosity percentage represents a material that is dense.
What is the porosity of a material?
Porosity is an intrinsic property of every material. It refers to the amount of empty space within a given material. In a soil or rock the porosity (empty space) exists between the grains of minerals. In a material like gravel the grains are large and there is lots of empty space between them since they don’t fit together very well. However, in a material like a gravel, sand and clay mixture the porosity is much less as the smaller grains fill the spaces. The amount of water a material can hold is directly related to the porosity since water will try and fill the empty spaces in a material. We measure porosity by the percentage of empty space that exists within a particular porous media.
What is the property of permeability?
Permeability is another intrinsic property of all materials and is closely related to porosity. Permeability refers to how connected pore spaces are to one another. If the material has high permeability than pore spaces are connected to one another allowing water to flow from one to another, however, if there is low permeability then the pore spaces are isolated and water is trapped within them. For example, in a gravel all of the pores well connected one another allowing water to flow through it, however, in a clay most of the pore spaces are blocked, meaning water cannot flow through it easily.
How to get high porosity hair?
Or, if you don’t have those, put a shower cap over your hair once you’ve added a conditioner. For high porosity hair: Look for ingredients like butters and oils in shampoos and conditioners.
How to test hair porosity?
One of the easiest ways to test your hair porosity is by using a glass of water. Here’s how to do it: Shampoo and rinse your hair to remove any product buildup. Fill a glass with water. Once your hair is clean and dry, drop a single strand of your hair into the glass of water.
What is the meaning of porosity in hair?
Essentially, hair porosity is about your hair’s ability to absorb and retain moisture. The porosity of your hair affects how well oils and moisture pass in and out of the outermost layer of your hair, known as the cuticle. Hair porosity is typically divided into three broad categories:
Why is my hair low porosity?
This makes it harder for moisture to penetrate the hair shaft. You may have low porosity hair if: hair products tend to sit on your hair and don’t absorb easily. it’s hard for water to saturate your hair when washing. it takes a long time for your hair to air dry.
Why does hair porosity change?
Heat damage and other chemical processes can cause normal porosity hair to change over time.
Can you change your hair porosity?
If you have high or low hair porosity due to genetics, you may not be able to change it. However, according to hair care experts, there are things you can do to make your hair healthier, more manageable, and easier to style. For low porosity hair: Use protein-free conditioners.
Does genetics affect porosity?
So, if low porosity hair runs in your family, there’s a good chance you’ll have low porosity hair, too. But while genetics can affect porosity, it isn’t the only contributing factor. Blow drying, bleaching, straightening, overwashing, and using harsh products can all damage your ...
How do pores affect soil biodiversity?
These pores influence soil biodiversity (i.e., soil microorganisms) by facilitating space for their survival. For instance, protozoa, small nematodes, and fungi inhabit the pore space between micro-aggregates while bacteria colonize within the pores of micro-aggregates for their habitat ( Six et al., 2004 ).
What is the role of pore space in soil?
Mainly, pore spaces facilitate the availability and movement of air or water within the so il environment. Four hierarchical pore structures have been characterized as macropores, pore space between macro-aggregates, pores between micro-aggregates but within macro-aggregates, and pores within micro-aggregates in the soil environment. These pores influence soil biodiversity (i.e., soil microorganisms) by facilitating space for their survival. For instance, protozoa, small nematodes, and fungi inhabit the pore space between micro-aggregates while bacteria colonize within the pores of micro-aggregates for their habitat ( Six et al., 2004 ). SOC derived from microorganisms within soils pores is bound and stabilized with aggregates, thereby affecting soil carbon sequestration. Hydrophobic SOC dominated by aromatic and aliphatic compounds (i.e., particulate carbon forms) has been shown to be physically bound in 2–5 μm pore spaces in soils ( Kinyangi et al., 2006 ). In the same study, oxidized carbon fractions clogging pores and coating pore cavities on mineral surfaces have been reported to be in a nanoscale distribution for the organo-mineral assemblage of micro-aggregates in a heavy textured soil.
Does vegetation help with P retention?
Although plant demand for P is generally low, the presence of vegetation has been shown to increase P retention in bioretention system studies ( Lucas and Greenway, 2008; Read et al., 2008 ). Plants and microbes may successfully obtain a greater percentage of P relative to that portion sorbed to soils by taking it up more rapidly, especially in low-sorbing bioretention filter media and in the presence of mycorrhizal fungi ( Bolan, 1991; Richardson et al., 2005 ). Although microbes compete more effectively than plants for nutrients in the rhizosphere, in the long term, plant roots are more successful in removing nutrients because of the longer lifespan of their tissues and their ability to store and translocate greater amounts of nutrients ( Kaye and Hart, 1997 ). The longer lifespan of plants gives vegetation the ability to function as a nutrient and heavy metal sink over time and it has been suggested that the harvesting of bioretention system vegetation can be used as a permanent P and heavy metal removal mechanism ( Davis et al., 2006; Hsieh et al., 2007a; Muthanna et al., 2007b ).
Overview
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam).
There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning.
Void fraction in two-phase flow
In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase.
Void fraction usually varies from location to location in the flow channel (depending on the two-phase flow pattern). It fluctuates with time and its value is usually time averaged. In separated (i…
Porosity in earth sciences and construction
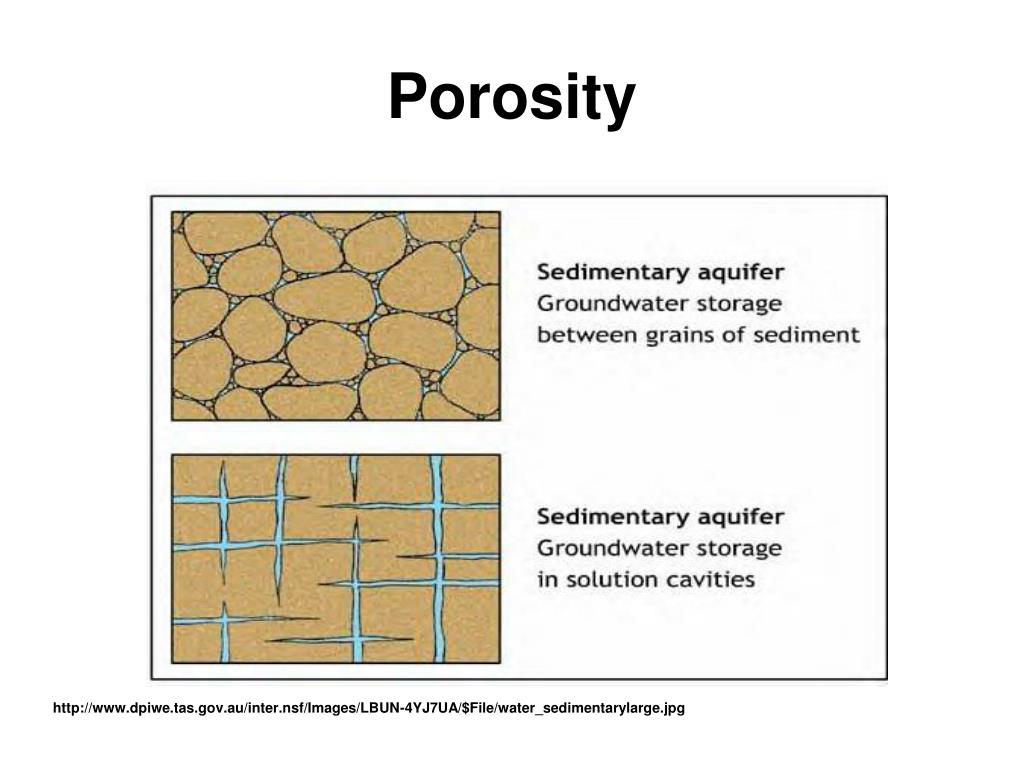
Used in geology, hydrogeology, soil science, and building science, the porosity of a porous medium (such as rock or sediment) describes the fraction of void space in the material, where the void may contain, for example, air or water. It is defined by the ratio:
where VV is the volume of void-space (such as fluids) and VT is the total or bul…
Porosity of fabric or aerodynamic porosity
The ratio of holes to solid that the wind "sees". Aerodynamic porosity is less than visual porosity, by an amount that depends on the constriction of holes.
Die casting porosity
Casting porosity is a consequence of one or more of the following: gasification of contaminants at molten-metal temperatures; shrinkage that takes place as molten metal solidifies; and unexpected or uncontrolled changes in temperature or humidity.
While porosity is inherent in die casting manufacturing, its presence may lead to component failure where pressure integrity is a critical characteristic. Porosity may take on several forms fr…
Measuring porosity
Several methods can be employed to measure porosity:
• Direct methods (determining the bulk volume of the porous sample, and then determining the volume of the skeletal material with no pores (pore volume = total volume − material volume).
• Optical methods (e.g., determining the area of the material versus the area of the pores visible under the microscope). The "a…
See also
• Void ratio
• Petroleum geology
• Poromechanics
• Bulk density
• Particle density (packed density)
External links
• Absolute Porosity & Effective Porosity Calculations
• Geology Buzz: Porosity