A chord is a music term that refers to a group of notes played at the same time on a musical instrument. A chord forms a harmonic collection of pitches and frequencies to create a harmonious sound. Chords are made up of two or more musical notes.
Full Answer
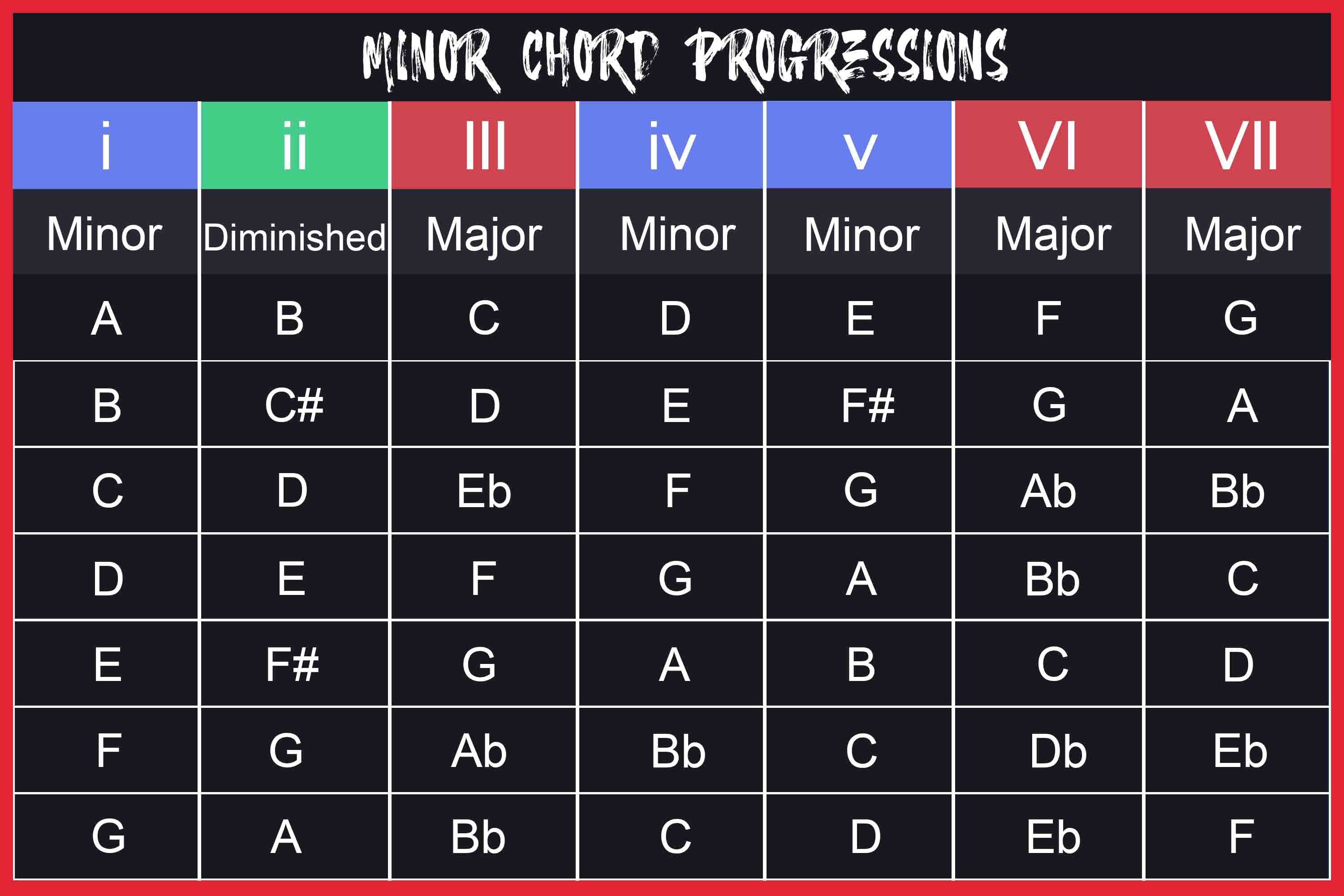
What are the chords for G major scale?
- Chord I, G major consists of the notes, G – B – D, while G major seventh consists of the notes, G – B – D – F#.
- Chord ii, A minor consists of the notes, A – C – E. ...
- Chord iii, B minor contains the notes, B – D – F#. ...
- Chord IV, C major contains the notes, C – E – G. ...
- Chord V, D major contains the notes, D – F# – A. ...
What is a harmonic chord progression?
HARMONIC PROGRESSION. HARMONIC PROGRESSION (also known as CHORD PROGRESSION) is the logical movement from one chord to another to create the structural foundation and movement of a work in Western Classical Music.In its most basic form, progressions pull chords directly from a single diatonic scale (for instance, a major or minor scale) and each chord in the scale serves a specific harmonic ...
What are diatonic chords?
What are Diatonic Chords? Diatonic chords are the chords that are derived from the notes of a key. You should think of diatonic chords as a family of chords all tied to one another by the notes of a key. They all sort of share the same gene pool.
How to play a D major chord on guitar?
You can also play a version of D Major that's vaguely reminiscent of the open G Major shape:
- Place your 1st finger on the 4th string/4th fret
- Place your 2nd finger on the 5th string/5th fret
- Place your 3rd finger on the 1st string/5th fret
- Mute strings 2, 3, and 6
How do you make a harmonic chord?
0:3310:42Writing Chord Progressions in Harmonic Minor [MUSIC ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo that would be an F sharp diminished triad. So my two chord would be an F sharp diminished. MyMoreSo that would be an F sharp diminished triad. So my two chord would be an F sharp diminished. My three chord you can see would be G B. And D sharp. That's a G augmented triad.
Are harmonics chords?
HARMONIC PROGRESSION (also known as CHORD PROGRESSION) is the logical movement from one chord to another to create the structural foundation and movement of a work in Western Classical Music.
What chords are in the a harmonic scale?
Notes from the Am Natural scale: A, B, C, D, E, F, G. Notes from the Am Harmonic scale: A, B, C, D, E, F, G#
What is harmonic movement in music?
It is the interplay between chords that creates a sense of movement that can be more or less dynamic and/or static. Probably, the most obvious way to achieve harmonic movement is through harmonic rhythm, that is, how fast you change chords – i.e. if it's one chord per measure or one chord per beat.
How do you hit a harmonic on guitar?
4:037:54How to Play Harmonics on Acoustic Guitar in 3 Steps - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOnce you pluck the string remove. Your fretting finger. And you'll get a really nice ringing openMoreOnce you pluck the string remove. Your fretting finger. And you'll get a really nice ringing open sounding harmonic and you can do that for any of the fret positions on the twelfth. Fret.
Why do guitars have harmonics?
The fundamental is the loudest sound produced, but it is accompanied by several harmonics. “Playing harmonics” on guitar is actually playing “artificial harmonics.” Basically, it is a way of eliminating the fundamental and the other overtones. It produces a nice effect that many guitarists like to use.
What is the harmonic scale pattern?
What's The Harmonic Minor Scale? The harmonic minor scale contains seven notes. The interval pattern formula is 1 - 2 - b3 - 4 - 5 - b6 - 7. It is built the same as the natural minor scale (Aeolian mode) but the seventh degree is raised by one semitone.
What chord is harmonic minor?
The Harmonic minor was derived by the need for a Dominant chord on the 5th degree (V) of the minor scale - enabling a Perfect Cadence (a Dominant 7th V chord resolving to a I minor chord). In the Natural minor scale the V (5) chord is a minor chord (Gmin7, G Bb D F, in the key of C).
What is a harmonic key?
The harmonic minor scale (or Aeolian ♯7 scale) has the same notes as the natural minor scale except that the seventh degree is raised by one semitone, creating an augmented second between the sixth and seventh degrees.
What is the basic chord that produces harmony?
The notes E and G provide harmony, and in a G7 (G dominant 7th) chord, the root G with each subsequent note (in this case B, D and F) provide the harmony.
Why is harmonic rhythm important?
Harmonic rhythm is the rate that chords change in a progression. It helps differentiate parts of a song and can create excitement with basic chords.
Does harmony have rhythm?
0:333:24The 3 Basic Elements Of Music: Melody, Rhythm & HarmonyYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou have harmony right or you could have a full chord. And the third element is rhythm. So you haveMoreYou have harmony right or you could have a full chord. And the third element is rhythm. So you have melody every harmony and you have rhythm.
What are harmonics on a guitar?
They involve fretting a note somewhere along the fretboard and then touching or tapping a note one octave above it on the same string. For instance, if you were to fret a note on the third fret, you could create a touch harmonic by touching or tapping that same string on the fifteenth fret.
What notes are harmonics guitar?
Harmonic notes are the same as fretted notes. At the seventh fret, the harmonics are pitched one octave higher than the notes regularly found at the seventh fret. The harmonic at the seventh fret of the high E string, for example, is the B note found at the nineteenth fret of the high E string.
What are natural harmonics?
A natural harmonic (N.H.) is sounded by picking an open string while lightly touching it with a fret-hand finger directly above a given fret. The natural harmonics that are easiest to produce and are most commonly used are those found directly above the 12th, seventh and fifth frets.
What harmonic is a guitar string?
0:352:34Guitar string harmonics and chords - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd when they pluck. It it makes the string vibrate at the second harmonic this is the firstMoreAnd when they pluck. It it makes the string vibrate at the second harmonic this is the first harmonic of the string when it's plucked by itself.
What is the harmonic minor chord I?
The A harmonic minor chord i is the A minor chord, and contains the notes A, C, and E.
What chords are in the harmonic minor scale?
The Solution below shows the A harmonic minor scale triad chords (i, ii o, III +, iv, V, VI, vii o) on a piano, with mp3 and midi audio.
What does the chord symbol III+ mean?
The chord symbol III+ could be followed by the letter a to indicate that it is C augmented chord in root position (ie not inverted) - A harmonic minor scale chord III+a.
What does the letter iio mean in a harmonic scale?
The chord symbol iio could be followed by the letter a to indicate that it is B diminished chord in root position (ie not inverted) - A harmonic minor scale chord iioa. Instead, iio could be followed by the letter b to indicate that it is B diminished chord in 1st inversion - A harmonic minor scale chord iiob.
What scale is the supertonic triad in?
This step shows the supertonic triad chord of the A harmonic minor scale .
How to identify a triad chord?
To identify the triad chord quality that has these notes, begin by counting the number of half-tones / semitones between the root and each of the notes.
What scale is the root note of a triad chord?
This step shows how to identify the notes and the name of a triad chord whose root note is the 7th scale degree of the A harmonic minor scale.
What is harmonic function?
Harmonic function is the tendency of chords to rest or progress to other chords. It is understood through a categorization of diatonic chords into three functions or families – Tonic (T), Subdominant/Predominant (S), and Dominant (D).
How Do You Harmonize A Scale With Chords?
Do you remember how to find out the chord harmony of any parent scale in a diatonic situation? Just stack diatonic thirds!
Why is harmonic function important?
Harmonic function is a great tool for memorizing tunes simply because you understand chord function at the fundamental level so it’s easy to remember what chords follow other chords.
What is a chord progression?
Chord progressions are formed on a solid foundation of diatonic harmony rather than intuition. Composers build chord progression for a piece of music with a solid understanding of these functions. Good composers select and place chords with a specific intention.
What does a vi do in a chord?
Adding the vi will prolong the tonic function and reinforce the tonal center. You have managed to add a new chord to the progression without changing the harmonic focal point.
Why is it important to learn to harmonize a scale?
It’s important to learn this concept rather than memorize a diatonic series of chords or numerals. It will enable you to harmonize any scale with triads of four-note chords. Plus, understanding how to harmonize a scale is the cornerstone of composition.
Why can you exchange chords within each family?
Now that you know the tonic, subdominant, and dominant families, you can exchange chords within each family because they have the same harmonic functions.
What is Harmonic Function?
The term Harmonic Function (also called Diatonic Function) is used to describe how a specific note or chord relates to the tonal center of a piece of music.
Which chords are tonic?
The two other chords that could potentially function as tonic chords are the III chord (in the key of C Maj this would be an E min chord) and the VI chord (A minor) which is the relative minor key.
What is the German theory of harmonic function?
German Functional Theory. The German Theory of Harmonic Function states that a note or chord can have one of three functions in a piece of music. These are: Tonic function. Dominant function. Subdominant function. There are three chords in any key that can be used to fulfil any of these three functions.
What is the function of a dominant chord?
Dominant Function. The dominant chord has the second most important function – it is used to move back to the tonic from somewhere else. It is usually associated with instability and motion. A lot of pieces of music end with the motion of a dominant chord to a tonic chord.
Which chord primarily functions as a dominant chord?
The chord that primarily functions as a dominant chord is the V chord – G Maj if taken from the C scale above.
How many relative chords are there in a function?
Each function has a primary chord associated with it, and then there are two other relative chords – one a 3rd above and the other a 3rd below – that can also function as such.
What is the main chord of a song?
The tonic, as we first mentioned above, is the main chord of a song – it is the chord built upon the note that the song is in.
What Are Guitar Harmonics?
Guitar harmonics are the result of dampening a note in a way that it produces a high-pitched or bell-like chime. When you play a particular note on the guitar, for example the open A string, you hear the fundamental note, which in this case is A. However, when a string is plucked, it creates vibrations from the guitar’s bridge to the net and thus many other overtones or harmonics, are created as a result of shorter frequencies along the fretboard. Although, when you just regularly pluck a string you only hear the fundamental note. Knowing how to isolate the overtones will help you to uncover the harmonics.
Where are harmonics located on guitar?
However, the most common and distinct natural harmonics are located on the 12th, 7th, and 5th frets.
What frets are harmonics played on?
Not all natural harmonics result in the same note as their fundamental conterparts. The natural harmonics played at frets 7 and 12 are the same notes as if you played them normally with your finger pressed all the way down on the fret. However, the harmonics played on the 5th fret actually correspond to the same notes found on the 12th fret ...
What frets do you pluck a harmonic on?
For beginners, you may find it easier to actually pluck a string first and then lightly touch the string with the tip of your finger at the 5th, 7th, or 12th fret.
How to make a pinch harmonic?
This is achieved by plucking a string with your guitar pick while almost simultaneous dampening the string with your thumb. Once your thumb dampens the string, it creates that “scream” sound known as a pinch harmonic. To help achieve this, you may find it useful to have less of the pick exposed so that there is less distance between the end of the pick and your thumb. You may also find that plucking the string from a certain angle may help create the pinch harmonic with greater ease.
How are natural harmonics created?
Natural harmonics are created by making the string vibrate in fractions. For example, half of the length fraction results in a 12th fret harmonic, a third of the length fraction results in a 7th fret harmonic, a fourth of the length fraction results in a 5th fret harmonic, etc. You can also play natural harmonics up in the octaves ...
How to play tap harmonics?
Tap harmonics is very similar to touch harmonics in that you use the same technique of moving up 12 frets to play the artificial harmonic. However, in this case, instead of using your thumb or a pick to sound the harmonic, you do so by tapping the string lightly.
What does the Roman numeral mean in a chord?
Roman numerals indicate each chords position relative to the scale. The triad and extended (four voice) chord sequence derived from the harmonic minor scale are as follows. Chord progressions using the harmonic minor scale will often be mixed with chords taken from the other minor scales.
Who is the author of Guitar Chords?
Author: Lee Nichols Creator of www.guitar-chords.or.uk
Why the Term ‘Harmonic Rhythm’?
In music, ‘harmony’ is anything that has to do with chords and chord progressions. ‘Rhythm’ is all about when notes are sounded and for how long.
What bar does the A minor chord occur on?
Since the A minor chord occurs on the strong beat (2nd bar) and is twice as long as the surrounding chords, it feels like an arrival. The arrival is only temporary however and the real conclusion comes on the fifth bar, where the tonic chord occurs on the strong beat. Chord progression with harmonic rhythm in 4/4.
Why is the ending of the 4/4 chord weaker than the previous version?
The ending, moreover, is slightly weaker than the previous version because the final chord is on the third beat of its bar (rather than the strong first beat). Chord progression with harmonic rhythm in 4/4, with upbeat and ending on a weaker beat.
What does the sparse harmonic rhythm give the song?
In this song we get more chord changes but still they are not frequent. As we’ve already seen, the sparse harmonic rhythm gives the music a sense of space. It gives the melody and the lyrics a sense of lightness.
How many times can you rewrite chord progressions?
Also experiment for yourself by rewriting any simple chord progression 3 or 4 times every time with a different harmonic rhythm. How does changing the harmonic rhythm affect the character of the progression?
How many levels of rhythm are there in music?
So in music we often have at least two levels of rhythm happening at the same time: the melodic rhythm and the harmonic rhythm:
Is the melody rhythm the same as the chords?
The melodic rhythm is just the same but instead of the chords, it’s the duration of the notes of the melody.
What is jazz harmony?
Jazz harmony, which of course has undeniable roots in 19th-century European music ( in addition to African rhythm, blues, and spirituals), made great use of 20th-century harmonic concepts. When you consider that Charlie Parker cited Igor Stravinsky as an influence and that Stravinsky was influenced by ragtime and jazz you come to understand the cross-pollination that has occurred between musical genres over the years.
Who introduced harmonic planing?
In my theory class, Professor Thomas Benjamin introduced me to the concept of harmonic planing. Whereas most 19th-century harmony deals with tonic-dominant-tonic motion (and its many alternate paths), 20th-century harmony is a completely different animal altogether.
What is diatonic planing?
Ex. 1 illustrates diatonic planing, i.e., moving voices around according to the scale or key. Note that you can move all kinds of chord shapes around triads, fourths, or whatever you want. With planing, you don’t have to worry about root movement. You only need top be concerned about how one chord sounds after another.
