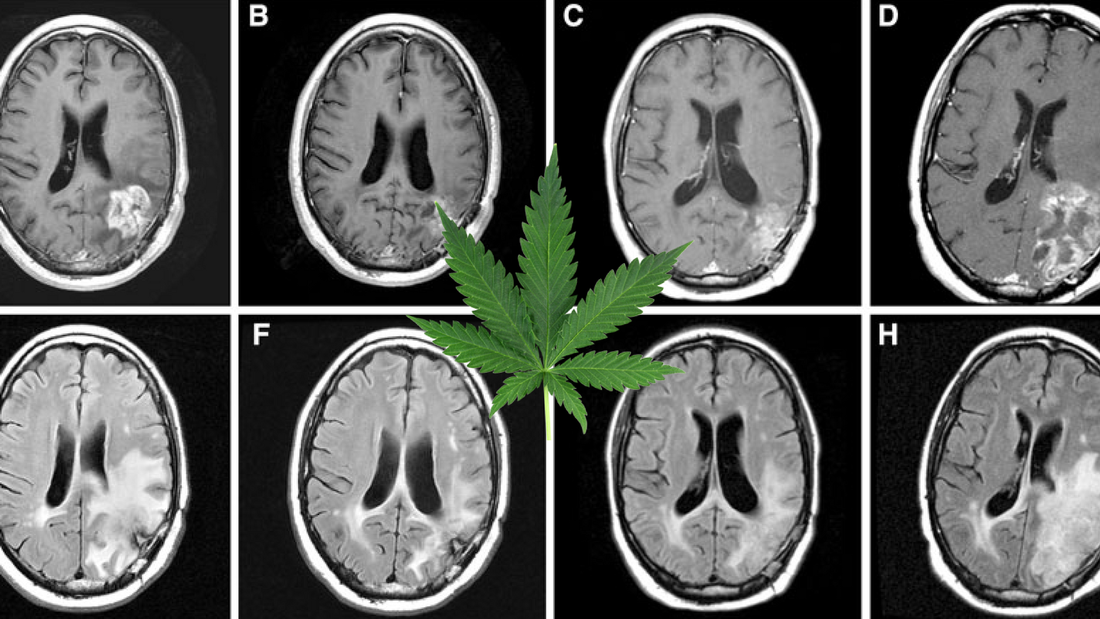
Grades 1 and 2 are considered low-grade, are well-differentiated and usually associated with a better outcome. Grade 3 and 4 gliomas are considered high-grade gliomas, are undifferentiated or anaplastic and have a worse prognosis. GBM is the most common and most aggressive type of primary brain tumour.
What is a glioma?
The cells have irregular shapes with fingers that can spread into the brain. Glioma is a type of tumor that occurs in the brain and spinal cord. Gliomas begin in the gluey supportive cells (glial cells) that surround nerve cells and help them function.
What is malignant or high-grade glioma?
The term malignant or high-grade glioma refers to tumors that are classified as: 1 ● Grade III (anaplastic astrocytoma, anaplastic oligodendroglioma, anaplastic ependymoma) 2 ● Grade IV (glioblastoma) More ...
How is a high-grade glioma diagnosed?
But, to definitely diagnose a high-grade glioma, a biopsy is required. In a biopsy, doctors examine a small sample of the tumor tissue. This helps determine the specific type of tumor, and can help detect the presence of certain biological “markers” in the tumor. These markers may be used to help determine treatment.
What is the prognosis of high-grade gliomas?
High-grade gliomas are classified by their location and by the appearance of the tumor under microscopic examination. This classification helps to assign a prognosis for the patient, but overall prognosis is poor for all types of high-grade gliomas. We need your help to find the best treatments for kids with cancer.
How long can you live with high grade glioma?
Malignant glioma (high-grade glioma) is one of the most malignant tumors in adults (Goodenberger & Jenkins, 2012). The patients' outcome is unlikely to be good, and the average duration of survival is less than 12 months.
Are high grade gliomas curable?
In most people with high-grade glioma, the disease cannot be cured. Involvement of a palliative care physician early in the treatment course can be helpful and has proven beneficial in other types of cancer.
How serious is high grade glioma?
High-grade gliomas (HGGs) are a heterogeneous disease group, with variable prognosis, inevitably causing deterioration of the quality of life. The estimated 2-year overall survival is 20%, despite the best trimodality treatment consisting of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy.
What stage is high grade glioma?
There are four grades of brain tumors; however, gliomas are most often referred to as "low grade" (grades I or II) or "high grade" (grades III or IV), based on the tumor's growth potential and aggressiveness.
What is glioma caused by?
Gliomas are caused by the accumulation of genetic mutations in glial stem or progenitor cells, leading to their uncontrolled growth. Mutated genes are typically involved in functions such as tumor suppression, DNA repair, and regulation of cell growth.
How do you get glioma?
Like most primary brain tumors, the exact cause of gliomas is not known. But there are some factors that may increase your risk of a brain tumor....Risk factors include:Your age. Your risk of a brain tumor increases as you age. ... Exposure to radiation. ... Family history of glioma.
How do you get high grade glioma?
Causes. Sometimes, high doses of radiation therapy can cause high-grade gliomas, but the reason for most high-grade gliomas in children is not known. Although doctors continue their research to understand what causes the tumors to occur, so far there have been few reliable findings.
Is glioma always fatal?
Glioblastoma incidence is very low among all cancer types, i.e., 1 per 10 000 cases. However, with an incidence of 16% of all primary brain tumors it is the most common brain malignancy and is almost always lethal [5,6].
Are high grade gliomas terminal?
Patients with high-grade glioma (HGG), the most frequently occurring primary malignant brain tumor, have a poor prognosis and cannot be cured.
How quickly can glioma spread?
The growth is happening on a microscopic level, but a glioblastoma tumor can double in size within seven weeks (median time). The fastest growing lung cancers, by comparison, have a median doubling time of 14 weeks.
How long can you have glioma before symptoms?
Conclusion: In conclusion, we postulate that glioblastoma might originate median 330 days before the diagnosis, assuming the same growth pattern and biology from day one.
Can a high grade glioma be benign?
Grade 1 tumors are usually benign (non-cancerous), slow-growing and can often be removed through surgery, and grade 4 gliomas are malignant (cancerous), fast growing, very aggressive, and difficult to treat.
Are high grade gliomas terminal?
Patients with high-grade glioma (HGG), the most frequently occurring primary malignant brain tumor, have a poor prognosis and cannot be cured.
Can you survive grade 4 glioma?
Glioblastoma has an incidence of 3.21 per 100,000 population. Median age of diagnosis is 64 years and it is more common in men as compared to women. Survival is poor with approximately 40% survival in the first year post diagnosis and 17% in the second year.
What is the survival rate for glioma?
It is estimated that more than 10,000 individuals in the United States will succumb to glioblastoma every year. The five-year survival rate for glioblastoma patients is only 6.8 percent, and the average length of survival for glioblastoma patients is estimated to be only 8 months.
Can a high grade glioma be benign?
Grade 1 tumors are usually benign (non-cancerous), slow-growing and can often be removed through surgery, and grade 4 gliomas are malignant (cancerous), fast growing, very aggressive, and difficult to treat.
Why are gliomas called high grade?
They are called “high-grade” because the tumors are fast-growing and they spread quickly through brain tissue, which makes them hard to treat. The tumors occur in children of all ages, from infants to adults.
How rare are high grade gliomas?
High-grade gliomas are rare and account for 8-12% of all childhood brain tumors. They occur equally in boys and girls.
How do you know if you have a brain tumor?
One of the most common signs of high-grade gliomas is headaches, particularly headaches that wake children up in the morning and are associated with vomiting. High-grade gliomas can also cause seizures, or cause young children to miss developmental milestones. Sometimes, tumors can cause problems with vision, hearing, or speech, or troubles with balance.
How to diagnose glioma?
The first step in diagnosing a brain tumor is usually to take an image of the brain and/or spine using an MRI or CT scan. These tests can help show that a tumor is present. But, to definitely diagnose a high-grade glioma, a biopsy is required. In a biopsy, doctors examine a small sample of the tumor tissue. This helps determine the specific type of tumor, and can help detect the presence of certain biological “markers” in the tumor. These markers may be used to help determine treatment.
Can radiation cause gliomas?
Sometimes, high doses of radiation therapy can cause high-grade gliomas, but the reason for most high-grade gliomas in children is not known. Although doctors continue their research to understand what causes the tumors to occur, so far there have been few reliable findings. Genetic causes are rare, and the tumor is not believed to be linked to anything in the environment.
What is a high grade glioma?
High-grade gliomas are a diverse group of tumors of the brain and spinal cord that occur in children of all ages . This type of childhood cancer grows rapidly and has the ability to spread through brain tissue aggressively, making it very difficult to treat. High-grade gliomas are classified by their location and by the appearance ...
How are high grade gliomas classified?
High-grade gliomas are classified by their location and by the appearance of the tumor under microscopic examination. This classification helps to assign a prognosis for the patient, but overall prognosis is poor for all types of high-grade gliomas. We need your help to find the best treatments for kids with cancer.
What are the symptoms of brain tumors?
Patients experience different types of brain dysfunction depending on the specific location of the tumor; however, some common problems include: 1 Persistent headaches 2 Nausea and vomiting 3 New onset of seizures
Can gliomas be removed?
Some types of tumors, such as diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas, cannot be removed due to their location and therefore patients have a particularly poor prognosis. Most patients will also receive radiation therapy along with some form of chemotherapy.
Can glioma be long term?
Unfortunately, our current treatments – while life prolonging – do not result in long-term survival for most patients. Research aimed at understanding the genetics and the biology of these tumors is critical if we are to develop effective therapies for high-grade glioma.
How to treat high grade glioma?
Surgery — The initial treatment of high-grade glioma usually involves removing as much of the tumor as safely possible with surgery. The amount of tumor that can be removed is determined by the tumor's size and location, and by how much normal brain will be potentially injured as a result of surgery.
What is a grade I or II glioma?
Grade I or II tumors are termed low-grade gliomas. The term malignant or high-grade glioma refers to tumors that are classified as:
How many grades are there in brain tumors?
Gliomas are classified into four grades (I, II, III, and IV), and the treatment and prognosis depend upon the tumor grade.
What is the genetic classification of glioblastoma?
Astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and glioblastomas are further classified based on whether they have a genetic change in the isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) gene. If there is a mutation, the tumor is designated as IDH mutant, and if there is no mutation, the tumor is designated as IDH wildtype. IDH-wildtype tumors are more aggressive and behave like high-grade glioma.
How do gliomas cause symptoms?
Gliomas cause symptoms by invading (growing) into and/ or creating pressure in nearby normal brain tissue. The most common symptoms include:
What is the primary brain tumor?
Primary brain tumors mainly develop from glial cells. Glial cells provide the structural backbone of the brain and support the function of the neurons (nerve cells), ...
What are the functions of glial cells?
Glial cells provide the structural backbone of the brain and support the function of the neurons (nerve cells), which are responsible for thought, sensation, muscle control, and coordination. This article will discuss the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of high-grade (ie, malignant) gliomas, the largest subset of brain gliomas.
What is malignant glioma?
Close. Malignant glioma cells. Malignant glioma cells. Glioblastoma multiforme (malignant brain tumor) cells. The cells have irregular shapes with fingers that can spread into the brain. Glioma is a type of tumor that occurs in the brain and spinal cord. Gliomas begin in the gluey supportive cells ...
What are the different types of glioma?
Types of glioma include: Astrocytomas, including astrocytoma, anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma. Ependymomas, including anaplastic ependymoma, myxopapillary ependymoma and subependymoma. Oligodendrogliomas, including oligodendroglioma, anaplastic oligodendroglioma and anaplastic oligoastrocytoma. A glioma can affect your brain function and be ...
How are gliomas classified?
Gliomas are classified according to the type of glial cell involved in the tumor, as well as the tumor's genetic features, which can help predict how the tumor will behave over time and the treatments most likely to work. Types of glioma include:
How does glioma affect the brain?
A glioma can affect your brain function and be life-threatening depending on its location and rate of growth. Gliomas are one of the most common types of primary brain tumors. The type of glioma you have helps determine your treatment and your prognosis. In general, glioma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, ...
How do you know if you have gliomas?
Common signs and symptoms of gliomas include: Headache. Nausea or vomiting. Confusion or a decline in brain function. Memory loss. Personality changes or irritability. Difficulty with balance. Urinary incontinence.
What are the risk factors for gliomas?
But there are some factors that may increase your risk of a brain tumor. Risk factors include: Your age. Your risk of a brain tumor increases as you age. Gliomas are most common in adults between ages 45 and 65 years old.
Where does glioma occur?
Glioma is a type of tumor that occurs in the brain and spinal cord. Gliomas begin in the gluey supportive cells (glial cells) that surround nerve cells and help them function. Three types of glial cells can produce tumors. Gliomas are classified according to the type of glial cell involved in the tumor, as well as the tumor's genetic features, ...
What is a glioma?
A glioma is a tumor that forms in the brain or spinal cord. There are several types, including astrocytomas, ependymomas and oligodendrogliomas. Gliomas can affect children or adults. Some grow very quickly. Most people with gliomas need a combination of treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
How many types of glioma are there?
There are three main types of gliomas, grouped by the type of glial cell they start in. Some gliomas contain multiple types of cells. Healthcare providers call these mixed gliomas. They categorize each type of glioma as low-, mid- or high-grade based on how fast they grow and other features.
What is the most aggressive brain tumor?
Astrocytomas, including glioblastomas and diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DIPGs): These tumors start in cells called astrocytes. Glioblastomas are astrocytomas that are very aggressive or grow fast. They are the most common malignant brain tumor in adults. Astrocytomas are common gliomas in children. A rare but very aggressive form of brain cancer in children is DIPG. It forms in the brain stem and mostly affects children.
How long do glioblastomas live?
Certain mutations can also affect the prognosis. The older someone is when they’re diagnosed and treated, the worse the outlook. The five-year survival rate for adults and children is highest for low-grade ependymomas, oligodendrogliomas and astrocytomas. It’s lowest (between 6% and 20%) for glioblastomas.
Where do oligodendrogliomas start?
Oligodendrogliomas: These tumors start in glial cells called oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrogliomas tend to grow more slowly but can become more aggressive over time. Like ependymomas, they rarely spread outside the brain or spine. They’re more common in adults than children. Oligodendrogliomas account for about 1% to 2% of all brain tumors.
Where do ependymomas form?
Ependymomas: These tumors start in ependymocytes, a type of glial cell. Ependymomas usually form in the ventricles of the brain or the spinal cord. They may spread through cerebrospinal fluid (the fluid that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord), but don’t spread outside the brain or spine. Ependymomas make up about 2% of all brain tumors. They’re more common in children than adults.
Where do gliomas grow?
Normally, these cells support nerves and help your central nervous system work. Gliomas usually grow in the brain, but can also form in the spinal cord.
What is a glioma?
Glioma is a common type of tumor originating in the brain. About 33 percent of all brain tumors are gliomas, which originate in the glial cells that surround and support neurons in the brain, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and ependymal cells.
What is the diagnosis of glioma?
Diagnosis of glioma involves: A medical history and physical exam: This includes questions about the patient’s symptoms, personal and family health history. A neurological exam: This exam tests vision, hearing, speech, strength, sensation, balance, coordination, reflexes and the ability to think and remember.
What are the risk factors of glioma?
There is no obvious cause of glioma. They can occur in people of all ages but are more common in adults. Gliomas are slightly more likely to affect men than women, and Caucasian people than African-American people.
What is the most malignant brain tumor?
High-grade astrocytomas, called glioblastoma multiforme, are the most malignant of all brain tumors. Glioblastoma symptoms are often the same as those of other gliomas. Pilocytic astrocytomas are low-grade cerebellum gliomas commonly found in children. In adults, astrocytomas are more common in the cerebrum.
What is a mixed glioma?
Mixed gliomas (also called oligo-astro cytomas) are made up of more than one type of glial cell. Their diagnosis as a distinct tumor type is controversial and may be resolved with genetic screening of tumor tissue. These tumors are often found in the cerebrum and are most common in adult men. Oligodendrogliomas form from oliogodendrocytes, ...
What is the name of the tumor that sends messages from the brain to the eyes?
Optic pathway gliomas are a type of low-grade tumor found in the optic nerve or chiasm, where they often infiltrate the optic nerves, which send messages from the eyes to the brain. People with neurofibromatosis are more likely to develop them. Optic nerve gliomas can cause vision loss and hormone problems, since these tumors are often located at the base of the brain where hormonal control is located. Gliomas affecting hormone function may be known as hypothalamic gliomas.
Why are gliomas called intraaxial tumors?
Gliomas are called intra-axial brain tumors because they grow within the substance of the brain and often mix with normal brain tissue.
What is the difference between a low grade and a high grade glioma?
high-grade glioma. Oncologists often use the terms "low-grade" and "high-grade" to categorize malignant gliomas based on how quickly the tumors spread. Low-grade gliomas grow very slowly, but are still malignant and can progress to high-grade gliomas if left untreated.
How to contact Moffitt for glioma?
If you’d like to learn more about the treatment options Moffitt offers for both malignant and benign glioma, call 1-888-663-3488 or submit a new patient registration form online to request an appointment. No referral is required.
Can glioma be removed?
However, treatment can be very effective for low-grade glioma. Surgeons can often remove an entire tumor with no need for follow-up treatment, and the prognosis is typically favorable. High-grade gliomas spread quickly, and multiple forms of treatment are often necessary to relieve the associated pain and neurological symptoms.
Is glioma malignant or benign?
Are All Gliomas Malignant? Glioma is a type of brain cancer that is often – but not always – malignant. In some cases, the tumor cells do not actively reproduce and invade nearby tissues, which makes them noncancerous. However, in most cases, gliomas are cancerous and likely to spread.
