
Why do high concentrations of blood smell like ammonia?
Ammonia is highly toxic. Blood ammonia levels are usually less than 50 micromoles per liter (micromol /L), but this can vary depending on age. An increase to only 100 micromol /L can lead to changes in consciousness. A blood ammonia level of 200 micromol /L is associated with coma and convulsions.
What is a dangerous level of ammonia in the blood?
· What is a high level of ammonia in the blood? Ammonia, also known as NH3, is a waste product made by your body during the digestion of protein. High ammonia levels in the blood can lead to serious health problems, including brain damage, coma, and even death. High ammonia levels in the blood are most often caused by liver disease.
Why are my ammonia levels still so high?
· An elevated blood ammonia level, also known as hyperammonemia, is the accumulation of the waste compound ammonia in the bloodstream. This buildup can be fatal. High ammonia levels in the blood can happen due to underlying inborn or acquired diseases and lifestyle factors that impact the function of organs such as the liver and kidneys.
What medications can cause elevated ammonia levels?
· Ammonia is a potent neurotoxin, and elevated levels in the blood can cause neurological signs and symptoms that may be acute or chronic, depending on the underlying abnormality. Hyperammonemia should be recognized early and treated immediately to prevent the development of life-threatening complications such as cerebral edema and brain herniation.
See more
· High ammonia levels in the blood are most often caused by liver disease. Other causes include kidney failure and genetic disorders. Your liver may not be working properly if you have high levels of ammonia in your blood. Ammonia is a chemical made by bacteria in your intestines and your body’s cells while you process protein.
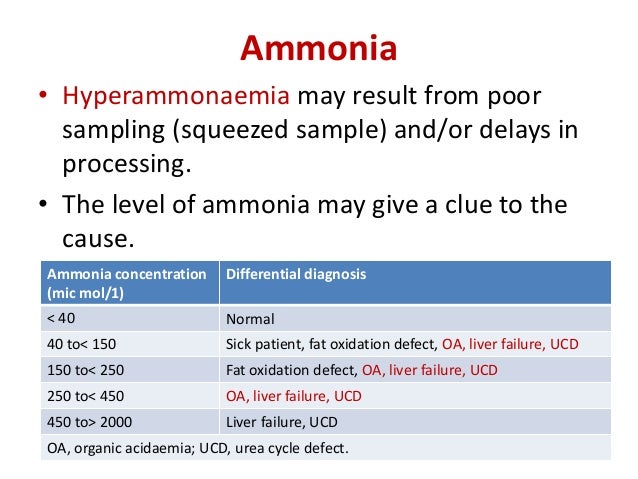
What is the normal ammonia level in blood?
The normal range is 15 to 45 µ/dL (11 to 32 µmol/L). Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or may test different samples.
What is critical ammonia level?
50 to 100 µmol/L: usually asymptomatic. 100 to 200 µmol/L: anorexia, vomiting, ataxia, irritability, hyperactivity. Above 200 µmol/L: Stage II coma, combative state followed by stupor. Above 300 µmol/L: Stage III coma, responsive only to painful stimuli.
How do you get ammonia out of your body?
Your body treats ammonia as a waste product, and gets rid of it through the liver. It can be added to other chemicals to form an amino acid called glutamine. It can also be used to form a chemical compound called urea. Your bloodstream moves the urea to your kidneys, where it's eliminated in your urine.
What causes ammonia levels to rise?
High ammonia levels sometimes point to either liver or kidney disease. But several other things can cause higher ammonia levels, like: Bleeding in your stomach, intestines, esophagus, or other parts of your body. Alcohol and drug use, including narcotics and medicines that take extra fluid out of your body (diuretics)
How high can ammonia levels go before death?
By regression analysis, an arterial ammonia level of ≥124 µmol/l was found to have a sensitivity of 78.6% and specificity of 76.3% as a predictor of death (P <0.001). Ammonia levels above this value had an odds ratio of 10.9 as a predictor of death (95% CI 5.9–284.0).
Can high levels of ammonia be fatal?
If your body can't process or eliminate ammonia, it builds up in the bloodstream. High ammonia levels in the blood can lead to serious health problems, including brain damage, coma, and even death. High ammonia levels in the blood are most often caused by liver disease.
What are the symptoms of too much ammonia in the body?
Symptoms of high ammonia levels in your blood include:Confusion and disorientation.Excessive sleepiness.Changes in consciousness.Mood swings.Hand tremors.Coma.
What medication is given to reduce ammonia levels?
Lactulose is also used to reduce the amount of ammonia in the blood of patients with liver disease. It works by drawing ammonia from the blood into the colon where it is removed from the body. This medication is sometimes prescribed for other uses; ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
What foods are high in ammonia?
These include dairy products, confections, fruits and vegetables, baked goods, breakfast cereals, eggs, fish, beverages such as sports drinks and beer, and meats. Q: If ammonia is safe, why do I think of it as a harmful chemical?
What does high ammonia levels do to the brain?
Elevated concentrations of ammonia in the brain as a result of hyperammonemia leads to cerebral dysfunction involving a spectrum of neuropsychiatric and neurological symptoms (impaired memory, shortened attention span, sleep-wake inversions, brain edema, intracranial hypertension, seizures, ataxia and coma).
How do you lower ammonia levels naturally?
How to lower ammonia levels naturallyFishless cycle first. You can also do something called Fishless Cycling, where you get the water ready for the fish and mature the tank before any fish are added. ... Lower fish stocking to lower ammonia. ... Feed less to lower ammonia. ... Add plants to lower ammonia.
What is the name of the condition where ammonia is elevated?
Hyperammonemia - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. Hyperammonemia is a metabolic condition characterized by the raised levels of ammonia, a nitrogen-containing compound. Normal levels of ammonia in the body vary according to age. Hyperammonemia can result from various congenital and acquired conditions in which it may be the principal toxin.
What is the term for elevated ammonia levels?
Hyperammonemia is a metabolic condition characterized by raised levels of ammonia, a nitrogen-containing compound. Ammonia is a potent neurotoxin. Hyperammonemia most commonly presents with neurological signs and symptoms that may be acute or chronic, depending on the underlying abnormality.
Is hyperammonemia congenital or acquired?
Etiology. The etiology of hyperammonemia is vast. It is a part of numerous disorders that can be classified as congenital or acquired . The acquired disorders can further be classified as hyperammonemia due to hepatic causes and non-hepatic causes (causes other than a liver disease).
How long does it take for argininosuccinate to cause hyperammonemia?
Defects in carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (CPS) and argininosuccinate synthetase (ASS) result in hyperammonemia that presents in the first 24 to 48 hours of life. Hyperammonemia is mild in arginase deficiency, and the associated neuronal damage is due to elevated levels of arginine.
What is the most common cause of hyperammonemia in children?
An acquired disease-causing hyperammonemia in children is Reye syndrome, a childhood disorder that occurs most commonly after influenza or varicella infection and ingestion of aspirin. Hyperammonemia is coupled with elevated liver enzymes and lactic acidosis. Hepatomegaly is usually seen on examination. Liver Disease.
How many live births are there in the United States with hyperammonemia?
A gross estimate on the incidence of urea cycle disorders is 1 in 250,000 live births in the United States and 1 in 440,000 live births internationally. [11] Pathophysiology.
Is ammonia a toxin?
Normal levels of ammonia in the body var y according to age. Hyperammonemia can result from various congenital and acquired conditions in which it may be the principal toxin. Hyperammonemia may also occur as a part of other disorders that involve various other metabolic abnormalities.
How long does lactulose take to reduce ammonia levels?
It may take 24–48 hours for this drug to work. For portal-systemic encephalopathy: You should have two or three soft stools per day. High ammonia levels caused by the condition are removed from your body through your stool.
Can high ammonia levels cause permanent brain damage?
Elevated concentrations of ammonia in the brain as a result of hyperammonemia leads to cerebral dysfunction involving a spectrum of neuropsychiatric and neurological symptoms (impaired memory, shortened attention span, sleep-wake inversions, brain edema, intracranial hypertension, seizures, ataxia and coma).
Can you check blood ammonia levels at home?
AmBeR and AmBeR Clinical make it easy to test more frequently and can be used in all clinical environments, or in the home for patients who are required to constantly monitor their blood ammonia levels.
What are the final stages of cirrhosis of the liver?
Symptoms of end-stage liver disease may include: Easy bleeding or bruising. Persistent or recurring yellowing of your skin and eyes (jaundice) Intense itching. Loss of appetite. Nausea. Swelling due to fluid buildup in your abdomen and legs. Problems with concentration and memory.
What is the life expectancy of a person with cirrhosis?
The life expectancy for advanced cirrhosis is 6 months to 2 years depending on complications of cirrhosis, and if no donor is available for liver transplantation The life expectancy for people with cirrhosis and acholic hepatitis can be as high as 50%.
What are symptoms of high ammonia levels?
Symptoms of elevated ammonia levels Decreased appetite. Lethargy. Rapid or heavy breathing. Irritability. Altered mental state.
What causes too much ammonia in your system?
High ammonia levels sometimes point to either liver or kidney disease. But several other things can cause higher ammonia levels, like: Bleeding in your stomach, intestines, esophagus, or other parts of your body. Alcohol and drug use, including narcotics and medicines that take extra fluid out of your body (diuretics)
What causes high ammonia levels in blood?
High ammonia levels in the blood are most often caused by liver disease. Other causes include kidney failure and genetic disorders. Other names: NH3 test, blood ammonia test, serum ammonia, ammonia; plasma.
What is the name of the condition where ammonia builds up in the blood and travels to the brain?
Hepatic encephalopathy, a condition that happens when the liver is too diseased or damaged to properly process ammonia. In this disorder, ammonia builds up in the blood and travels to the brain. It can cause confusion, disorientation, coma, and even death. Reye syndrome, a serious and sometimes fatal condition that causes damage to ...
What happens if you don't get ammonia?
Urea is passed through the body in urine. If your body can't process or eliminate ammonia, it builds up in the bloodstream. High ammonia levels in the blood can lead to serious health problems, including brain damage, coma, and even death. High ammonia levels in the blood are most often caused by liver disease.
What is the purpose of ammonia test?
An ammonia levels test may be used to diagnose and/or monitor conditions that cause high ammonia levels. These include: Hepatic encephalopathy, a condition that happens when the liver is too diseased or damaged to properly process ammonia. In this disorder, ammonia builds up in the blood and travels to the brain.
What happens during an ammonia test?
What happens during an ammonia levels test? A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out.
Where is ammonia processed?
Normally, ammonia is processed in the liver, where it is changed into another waste product called urea. Urea is passed through the body in urine. If your body can't process or eliminate ammonia, it builds up in the bloodstream. High ammonia levels in the blood can lead to serious health problems, including brain damage, coma, and even death.
What is an Ammonia Level Test?
Ammonia is a by-product of protein breakdown and gas produced by the body during protein metabolism. The liver and kidneys produce ammonia, and an ammonia buffer system in the kidneys helps reduce the body’s ammonia concentration.
Symptoms of high ammonia levels
Having high ammonia levels can cause stinging or burning in the eyes. Additional symptoms may include:
Why You May Need an Ammonia Level Test
A high ammonia level test can serve as a diagnostic and monitoring tool. Among these are:
Causes of high ammonia levels
Different things can cause ammonia levels to rise. Here are a few common ones:
Treatment for high ammonia levels
Blood ammonia levels can rise in some cases, especially in infants, and then go down independently. More severe cases of ammonia buildup can lead to severe problems. The following methods can help remove excess ammonia from the blood:
Summary
You should not substitute medical advice for the information in this article. Keep this in mind. Before dealing with excessive ammonia levels, you should determine what’s causing them.
What causes elevated ammonia levels in the blood?
Gastrointestinal bleeding may cause an elevated blood ammonia level. Red blood cells contain a high concentration of protein. Significant bleeding, especially in the upper part of the digestive system, increases the protein load in the intestine and the production of ammonia. The increased ammonia from the intestine may make it difficult for ...
What happens when ammonia levels are high?
Urea subsequently passes from the body through the urine. High blood ammonia levels can occur with various forms of chronic liver disease, acute liver failure and gastrointestinal bleeding. Elevated blood ammonia levels adversely affect brain ...
Where does ammonia come from?
Blood ammonia comes primarily from the bacterial breakdown of unabsorbed dietary protein in the intestine. Intestinal ammonia passes into the bloodstream and travels to the liver, which converts ammonia into urea. Urea subsequently passes from the body through the urine.
What is the term for the excess ammonia released from the liver?
This condition of excess ammonia bypassing from liver to blood is referred to as Hyperammonemia.
How is ammonia released from the liver?
In general, nitrogenous complexes emitted by the intestinal bacteria are carried to the liver through the portal circulation. There it is metabolized by the urea cycle and it is released in the form of urea through urine. In advanced liver disease, the injured liver causes the excess release of ammonia to the systemic circulation.
What is the effect of ammonia on the brain?
Excess ammonia crosses the blood-brain barrier and metabolized by astrocytes cells to synthesize glutamine. Glutamine increases the osmotic pressure within the astrocyte resulting in morphologic malformations similar to those seen in Alzheimer’s disease Type II.
Does ammonia cause neurotoxicity?
Ammonia-induced Neurotoxicity. The circulating ammonia can increase glutamine, which may have a negative impact on brain cells initiating edema. Brain edema is life-threatening and severe form can lead to death. In acute liver failure, a severe form of edema is observed and in chronic liver failure, mild edema is observed.
Does ammonia cause edema?
The circulating ammonia can increase glutamine, which may have a negative impact on brain cells initiating edema. Brain edema is life-threatening and severe form can lead to death. In acute liver failure, a severe form of edema is observed and in chronic liver failure, mild edema is observed.
Is ammonia a neuroinflammator?
Brain inflammation or neuroinflammation is common in due to ammonia. Microglia and astrocytes were dysregulated, which is responsible for cognitive and motor function impairment. Ammonia blood-brain barrier permeability is increased in type C hepatic encephalopathy condition.
What are the effects of cerebral ammonia?
The effects of increased cerebral ammonia can cause a subsequent increase in brain edema, oxidative stress, osmotic pressure, and astrocyte swelling. Hyperammonemia is the main factor responsible for the brain abnormalities in hepatic encephalopathy. If left untreated it may lead to the development of severe neurological symptoms, seizures, ...
