What does a high CO2 level indicate?
High CO2 levels in the blood mean that the body may be experiencing respiratory or metabolic acidosis, conditions in which the blood’s pH level is excessively acidic. High levels of CO2 develop in the blood if the lungs or kidneys are unable remove excess CO2 from the body, states Healthline.
What is the treatment for high CO2 levels?
Treatment For High CO2 Levels. The treatment would depend upon the extent of severity of the condition and level of CO2 saturation in the blood. The treatment comprises of using oxygen mask and ventilators or hyperbaric chambers for the treatment of the condition.
How to lower high CO2 levels in blood quickly?
The health expert taking a sample of your blood will:
- Wrap an elastic band around your upper arm to stop the circulation of blood. ...
- Clean the needle site with alcohol.
- Put the needle into the vein. ...
- Connect a tube to the needle to fill it with blood.
- Eliminate the band from your arm when enough blood is gathered.
- Use a gauze pad or cotton ball over the needle site as the needle is removed.
What causes carbon dioxide levels to be high?
What Are the Causes of High CO2 Levels in the House?
- Buildup in Soil. The soil underneath a house contains carbon dioxide naturally from decaying plants and animals. ...
- Lack of Fresh Air. ...
- Operation of Some Appliances. ...
- Improper HVAC System Operation. ...
- Problems With High CO2 Levels. ...

What is a high PCO2?
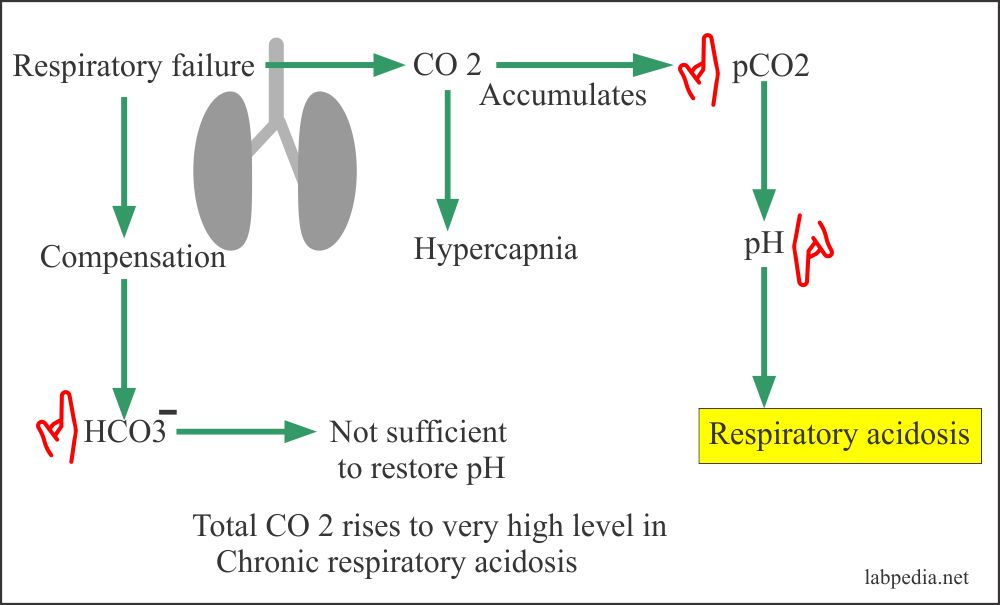
In respiratory acidosis, the ABG will show an elevated PCO2 (>45 mmHg), elevated HCO3- (>30 mmHg), and decreased pH (<7.35). The respiratory acidosis can be further classified as acute or chronic based on the relative increase in HCO3- with respect to PCO2.
Why would PCO2 be elevated?
The most common cause of increased PCO2 is an absolute decrease in ventilation. Increased CO2 production without increased ventilation, such as a patient with sepsis, can also cause respiratory acidosis. Patients who have increased physiological dead space (eg, emphysema) will have decreased effective ventilation.
What are the normal ranges for PCO2?
Generally, under normal physiologic conditions, the value of PCO2 ranges between 35 to 45 mmHg, or 4.7 to 6.0 kPa.
What is normal range of pO2 and PCO2?
ABG (Arterial Blood Gas)pH7.31–7.41pCO241–51 torr5.5–6.8 kPapO230–40 torr4.0–5.3 kPaCO223–30 mmol/LBase excess/deficit± 3 mEq/L± 2 mmol/L1 more row
How do you fix high pco2?
Medicationbronchodilators, which help your airway muscles work properly.inhaled or oral corticosteroids, which help keep airway inflammation to a minimum.antibiotics for respiratory infections, such as pneumonia or acute bronchitis.
How do you treat high pco2 levels?
TreatmentsVentilation. There are two types of ventilation used for hypercapnia: ... Medication. Certain medications can assist breathing, such as:Oxygen therapy. People who undergo oxygen therapy regularly use a device to deliver oxygen to the lungs. ... Lifestyle changes. ... Surgery.
What causes high CO2 levels in blood test?
It may be caused by many things, including kidney or liver disease, or long-lasting diarrhea. Respiratory alkalosis, a condition in which your blood is not acidic enough because of lung or breathing disorders, including hyperventilation (rapid, deep breathing).
Is CO2 and pCO2 the same thing?
Carbon Dioxide is measured as pCO2 and bicarbonate in a blood gas.
What does a carbon dioxide level of 33 mean?
Normal values in adults are 22 to 29 mmol/L or 22 to 29 mEq/L. Higher levels of carbon dioxide may mean you have: Metabolic alkalosis, or too much bicarbonate in your blood.
What will be the pO2 and pCO2?
In atmospheric air, pO2 is about 159 mm Hg. In alveolar air, it is about 104 mm Hg. In atmospheric air, pCO2 is about 0.3 mm Hg. In alveolar air, it is about 40 mm Hg.
What should pO2 be?
Acute Respiratory Failure - All There Is To KnowMeasureDefinitionNormalpO2Partial pressure of oxygen, or oxygen content, in mmHgpO2 > 80 mmHgpCO2Partial pressure of carbon dioxide, or carbon dioxide content, in mmHg35 – 45 mmHgpHMeasure of the degree of acidity7.35 – 7.454 more rows•Sep 5, 2017
What is the pO2 and pCO2 in the systemic arteries?
c) PO2 – 95mm Hg/ PCO2 – 40mm Hg.
What is PaO2 and PaCO2?
PaO2 = measured the partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood. PaCO2 = measured the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood. HCO3 = calculated concentration of bicarbonate in arterial blood.
What is the value of PCO2?
It often serves as a marker of sufficient alveolar ventilation within the lungs. Generally, under normal physiologic conditions, the value of PCO2 ranges between 35 to 45 mmHg, or 4.7 to 6.0 kPa.
What does higher PACO2 mean?
It is a measurement of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood and is affected by CO2 removal in the lungs. A higher PaCO2 level indicates acidosis while a lower PaCO2 level indicates alkalosis
What is the difference between HCO3 and TCO2?
It is a measurement of the bicarbonate content of the blood and is affected by renal production of bicarbonate. A lower HCO3 – level indicates acidosis while a higher HCO3 – level indicates alkalosis. Total CO2 Contents (TCO2):
What does elevated pO2 mean?
Elevated pO2 levels are associated with: Increased oxygen levels in the inhaled air. Oxygen saturation capacity: In healthy individuals breathing room air at sea level, S aO2 is between 96% and 98%.
What does low pH mean?
Low pH indicates a higher concentration of hydrogen ions (acidosis) while a high pH indicates a lower concentration of hydrogen ions ( alkalosis). The PaCO2 level is the respiratory component of the ABG. It is a measurement of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood and is affected by CO2 removal in the lungs.
What is the most important consideration in pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary embolism (This leads to hyperventilation , a more important consideration than the embolized/infarcted areas of the lung that do not function properly. In cases of massive pulmonary embolism, the infarcted or non-functioning areas of the lung assume greater significance and the pCO2 may increase.)
How much oxygen can a human body carry?
The maximum volume of oxygen which the blood can carry when fully saturated is termed the oxygen carrying capacity, which, with a normal haemoglobin concentration, is approximately 20 mL oxygen per 100 mL blood.
What happens when CO2 levels are high?
Carbon dioxide is in equilibrium with bicarbonate (HCO3) in the blood. When CO2 is elevated, it creates an acidic environment. In people with COPD who have serious breathing problems, the increased CO2 level can result in what is called respiratory acidosis.
What does PaCO2 measure?
PaCO2 specifically evaluates carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood. The ABG test also evaluates the partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2), bicarbonate (HCO3), and the pH level of blood. Verywell/Cindy Chung.
What is the purpose of the PACO2 test?
PaCO2 specifically evaluates carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood.
What is the name of the disorder that causes high blood pressure?
Aldosteronism (a type of hormonal disorder that causes high blood pressure) 1
What is the normal pressure of carbon dioxide?
The normal range of partial pressure of carbon dioxide is between 35 and 45 millimeters of mercury (mmHg). If the value is higher than 45 mmHg, it's indicative that you have too much carbon dioxide in your blood. Under 35 mmHg, and you have too little. 3
What happens if oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood?
If the partial pressure of both oxygen and carbon dioxide are normal, the molecules will move from the alveoli into the blood and back as they should. Changes in that pressure can result in too little oxygen or the accumulation of too much carbon dioxide in the blood. Neither is considered optimal.
How does atmospheric pressure affect the body?
From a broad perspective, changes in atmospheric pressure (such as climbing a mountain, scuba diving, or even sitting in a commercial flight) can exert pressure on the body, which can alter how well or poorly blood moves from the lungs to the capillaries and back .
What is the value of PCO2?
It often serves as a marker of sufficient alveolar ventilation within the lungs. Generally, under normal physiologic conditions, the value of PCO2 ranges between 35 to 45 mmHg, or 4.7 to 6.0 kPa.
What is PCO2 in blood?
The collection of samples and the use of PCO2 is a topic of further discussion below. The partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) is the measure of carbon dioxide within arterial or venous blood. It often serves as a marker of sufficient alveolar ventilation within the lungs. Generally, under normal physiologic conditions, ...
How long does PCO2 last?
In chronic respiratory alkalosis, or alkalosis lasting 3 to 5 days, for every 10mmHg drop in PCO2, it is expected that serum bicarbonate will decrease by 4 to 5 mEq/L.[5][6] . The regulation of PCO2 is also involved in metabolic acidosis and alkalosis, as well.
How does bicarbonate affect respiratory acidosis?
There are differences in the acute and chronic stages of respiratory acidosis or alkalosis. Acute respiratory acidosis from increased PCO2 will result in immediate changes to serum bicarbonate levels due to the bicarbonate buffer system; however, this is limited in its ability to achieve homeostasis. The kidney will gradually increase the serum bicarbonate levels in chronic cases. Chronic respiratory acidosis is when the acidemia exists for 3 to 5 days, which is approximately how long it will take the kidney to buffer the acidemia. In acute respiratory acidosis, normally, the serum bicarbonate will increase by 1 mEq/L for every 10 mmHg increase in PCO2. For chronic respiratory acidosis, the serum bicarbonate will increase by 4 to 5 mEq/L for every 10 mmHg rise in PCO2. [6][5] The result typically causes a mild chronic acidosis or low-normal pH near 7.35.[6] In regards to respiratory alkalosis, the same timeframe applies to acute versus chronic. In acute respiratory alkalosis, for every decrease in PCO2 by 10 mmHg, the serum bicarbonate will also decrease by 2 mEq/L. In chronic respiratory alkalosis, or alkalosis lasting 3 to 5 days, for every 10mmHg drop in PCO2, it is expected that serum bicarbonate will decrease by 4 to 5 mEq/L.[5][6]
How is PCO2 measured?
Typically the measurement of PCO2 is performed via an arterial blood gas ; however, there are other methods such as peripheral venous, central venous, or mixed venous sampling. The collection of samples and the use of PCO2 is a topic of further discussion below. Issues of Concern.
How does PaCO2 regulate minute ventilation?
The method that PaCO2 is involved in the regulation of minute ventilation is by bodily pH. Carbon dioxide is involved in the bicarbonate buffer system . In the presence of an excess of CO2, there will be a shift to carbonic acid, ultimately causing the generation of hydrogen cations and bicarbonate anions.
What blood gas is used to measure PCO2?
Traditionally, the arterial blood gas is the more reliable sample to monitor PCO2; this is facilitated with the placement of an arterial catheter for hemodynamic monitoring, as the collection of arterial blood gases becomes readily available. However, if the patient does have central venous access, then the collection of venous blood gas is acceptable. The central venous blood gas is the most well established correlative blood gas alternative to the arterial blood gas in terms of PCO2 measurement. [1]