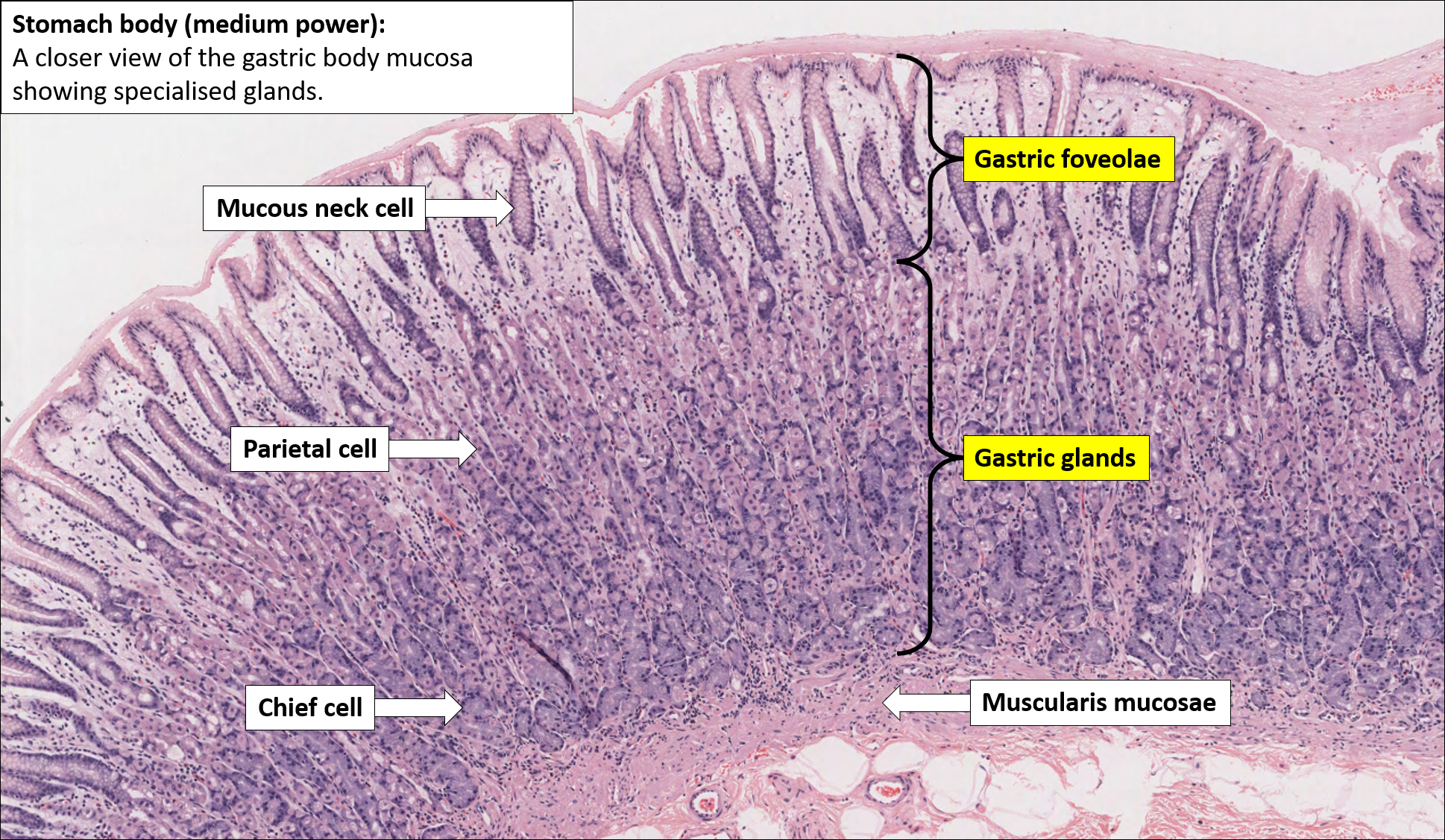
What is a histology slide? Histology is the study of the microanatomy of cells, tissues, and organs as seen through a microscope. Because of the high cost of purchasing (and maintaining) microscopes and preparing (or purchasing) slide collections, histology is often taught today without laboratories. Click to see full answer.
Full Answer
How to prepare histology slides?
The glass slide:
- The first step to prepare the highest quality slide is to choose the best kind of slide glass. ...
- Microscope slides are generally made of optical quality glass. ...
- If you will use fluorescent light to illuminate the specimen, use slides made from fused quartz.
How to examine histology slides?
How to examine histology slides. 1. Inspection: Inspect the slide using just your eyes and a good light source to first determine the shape of the prepared section. Occasionally, a specific section has a characteristic shape and is much easier to identify. e.g on the cross section of tracheal cartilage an annular preparation can be seen. 2.
How are histology slides prepared?
The Five Steps of Histology Slide Preparation
- Tissue fixation. Slide preparation begins with the fixation of your tissue specimen. ...
- Specimen Transfer to Cassettes. After fixation, specimens are trimmed using a scalpel to enable them to fit into an appropriately labeled tissue cassette.
- Tissue Processing. ...
- Sectioning. ...
- Staining. ...
How to learn histology?
- Dehydration- Water is extracted by using ethanol.
- Clearing- Ethanol is then replaced by a solvent, usually xylene, that helps make tissue transparent.
- Embedding- Tissues are usually embedded in a solid medium to facilitate sectioning because otherwise, it’ll be hard to precisely cut a malleable tissue in micrometers. ...

What is the study of cells and tissues?
Histology. Microanatomy or microscopic anatomy, The study of cells and tissues, from their intracellular components to their organization into organs and organ systems. Cell structure. Cellular membrane, cytoplasm, organelles, nucleus. Tissues.
What is the science of the microscopic structure of cells, tissues and organs?
However, if you take a much closer look, you’ll see that the histology of bones, is a whole other story. Histology is the science of the microscopic structure of cells, tissues and organs.
Where is connective tissue found?
Connective tissue proper is further subdivided into loose connective tissue, mostly found in internal organs as supporting tissue stroma, and dense connective tissue, which can be regular (tendons, ligaments) or irregular (dermis of the skin, organ capsules).
Which epithelium is a convoluted tubule?
Germinal (spermatogenic) epithelium , with spermatogenic cells and nurse (sertoli) cells, forms the convoluted tubules, while small circular interstitial ( Leydig) cells are found in the connective tissue between the tubules. Interstitial cells produce testosterone, a hormone that regulates spermatogenesis.
How to prepare tissue for optic microscopy?
The first step in tissue preparation for optic microscopy is fixation. Here, the tissue of interest is immersed in a fixative solution. This preserves it into the same state that it had when it was in the body, and thus, keeps it from degrading. Next, the tissue is embedded with paraffin wax, which firms the tissue enough permit thin slices. The tissue is sectioned thinly enough so that light can pass through it. These sections are then mounted on a glass slide, using a mounting medium as an adhesive.
How is in situ hybridization used?
This is done by the use of a complementary nucleotide probe, which contains a radioactive or fluorescent label. This method is based on the ability of single stranded DNA or RNA to merge with a complementary strand and build a hybrid which is then detected due to the label. This technique is used for determining the location of specific DNA or RNA sequences in cells or chromosomes, making it useful for various research and diagnostic purposes.
What is a unity of cells with a similar structure that as a whole express a definite and unique
Tissues. A unity of cells with a similar structure that as a whole express a definite and unique function. Epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous. Organs. A unity of tissues with a more complex set of functions, defined by the combination of structure and function of the comprising tissues. Systems of organs.
How long does it take to read histology?
Reading time: 3 minutes. Histology is a beautiful subject that allows us to explore the structure and function of tissues. If we take a little sample of an organ tissue, stain it accordingly and place it under a light microscope, we are able to see the main cells and some other components that build up the tissue.
How to inspect a slide?
1. Inspection: Inspect the slide using just your eyes and a good light source to first determine the shape of the prepared section. Occasionally, a specific section has a characteristic shape and is much easier to identify. e.g on the cross section of tracheal cartilage an annular preparation can be seen. 2.
When are histology slides published?
How Histology Slides are Prepared. Published November 19, 2020. If you’re involved in biological research, chances are at some stage you’ve submitted tissue specimens to a histology lab. Somehow they magically produced beautiful slides for you – each containing thin sections of your specimens, ready for microscopic evaluation.
What are the steps of histology slide preparation?
The Five Steps of Histology Slide Preparation. 1. Tissue fixation. Slide preparation begins with the fixation of your tissue specimen. This is a crucial step in tissue preparation, and its purpose is to prevent tissue autolysis and putrefaction.
Why charge slides?
Charged slides work best for this process – they improve tissue adhesion to the glass, and help to reduce the chance of sections washing off the slide during staining.
Why do we use coverslips in histochemical staining?
Histochemical stains (typically hematoxylin and eosin) are therefore used to provide contrast to tissue sections, making tissue structures more visible and easier to evaluate. Following staining, a coverslip is mounted over the tissue specimen on the slide, using optical grade glue, to help protect the specimen.
What is the process of processing tissue into thin microscopic sections?
3. Tissue Processing. Processing tissues into thin microscopic sections is usually done using a paraffin block, as follows: Dehydration, which involves immersing your specimen in increasing concentrations of alcohol to remove the water and formalin from the tissue.