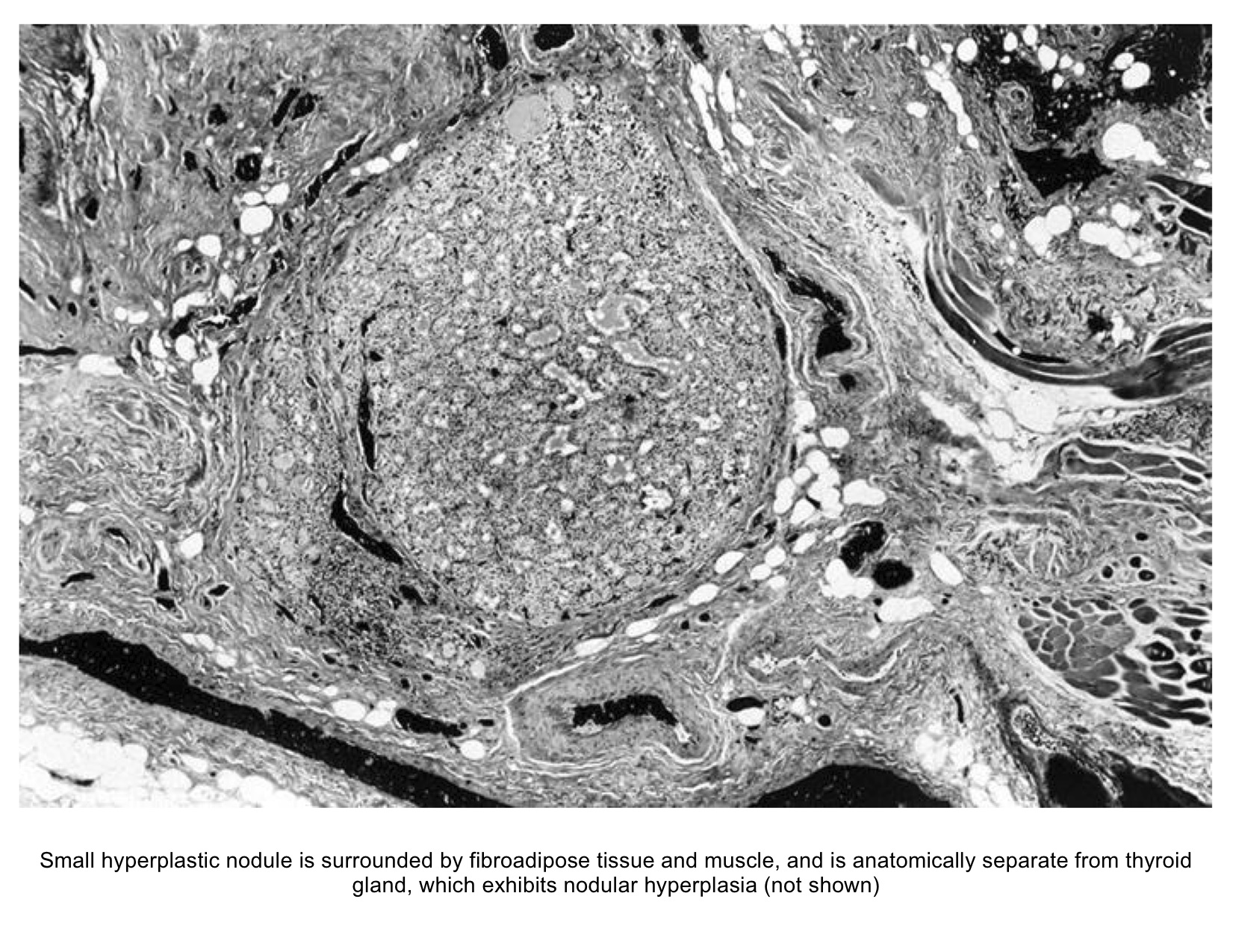
Hyperplastic Nodule. It is not intended to be and should not be interpreted as medical advice or a diagnosis of any health or fitness problem, condition or disease; or a recommendation for a specific test, doctor, care provider, procedure, treatment plan, product, or course of action. MedHelp is not a medical or healthcare provider and your use...
What does hyperplastic mean?
n. An abnormal increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ, with consequent enlargement of the part or organ. American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.
Are thyroid nodules usually benign?
The vast majority — more than 95% — of thyroid nodules are benign (noncancerous). If concern arises about the possibility of cancer, the doctor may simply recommend monitoring the nodule over time to see if it grows. Ultrasound can help evaluate a thyroid nodule and determine the need for biopsy.
What are dysplastic nodules?
The term dysplastic nodule replaces older terms like adenomatous hyperplasia and macroregenerative nodule and refers to a nodular region of hepatocytes with dysplasia but without definite malignancy, which represent an intermediate step in the pathway of hepatocarcinogenesis in cirrhosis. Dysplastic nodules are considered neoplastic, premalignant nodules.
What causes thyroid nodules to grow?
There are different types of thyroid nodules:
- Colloid nodules: These are one or more overgrowths of normal thyroid tissue. ...
- Thyroid cysts: These are growths that are filled with fluid or partly solid and partly filled with fluid.
- Inflammatory nodules: These nodules develop as a result of chronic (long-term) inflammation (swelling) of the thyroid gland. ...

Is hyperplastic nodule cancerous?
Some types of solid nodules, such as hyperplastic nodules and adenomas, have too many cells, but the cells are not cancer cells.
Is hyperplastic thyroid nodule benign?
Most thyroid nodules are benign hyperplastic lesions, but 5-20% of thyroid nodules are true neoplasms. (A retrospective study by Keh et al of 61 patients found 75.4% of solitary thyroid nodules to have a neoplastic pathology and 34.4% to be malignant. )
What are hyperplastic nodules thyroid?
Hyperplastic nodules are highly cellular on fine needle aspiration, made up of: (1) numerous sheets of follicular cells sometimes monolayered but more often showing some microfollicular arrangements or even some papillary features; nuclear overlapping is common but usually the nuclei are regular; (2) more or less ...
What causes thyroid nodular hyperplasia?
Its development is influenced by environmental factors, the most important of which is iodine deficiency, and by genetic factors. In the form traditionally known asendemic goiter, the disease is due to low iodine content of the water and soil, and it can be largely prevented by the addition of iodine to common salt.
Should you remove a benign thyroid nodule?
Most noncancerous, or benign, thyroid nodules do not need treatment unless they are a cosmetic concern or cause symptoms including problems with swallowing, breathing, or speaking and neck discomfort.
What are the symptoms of cancerous thyroid nodules?
SymptomsA lump (nodule) that can be felt through the skin on your neck.A feeling that close-fitting shirt collars are becoming too tight.Changes to your voice, including increasing hoarseness.Difficulty swallowing.Swollen lymph nodes in your neck.Pain in your neck and throat.
When should I worry about thyroid nodules?
Most nodules under 1cm are benign. If you first feel a small nodule that quickly grows to exceed the 1cm measurement, it could indicate something serious. Larger nodules and fast growing nodules can indicate malignancy, or thyroid cancer.
Where can nodular hyperplasia be found?
Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) is the second most common benign tumor of the liver, after hemangioma. It is generally found incidentally and is most common in reproductive-aged women, but it also affects males and can be diagnosed at any age.
What size thyroid nodule is worrisome?
Our study found that the highest malignancy risk was observed in nodules <2 cm and no increase in malignancy risk for nodules >2 cm. Thyroid nodules 1.0-1.9 cm in diameter provided baseline cancer risk for comparison (64.8% risk of cancer).
What foods to avoid if you have thyroid nodules?
These foods contain goitrogens or are known irritants if consumed in large amounts:Soy-based foods: tofu, tempeh, edamame beans, soy milk, etc.Certain fruits: peaches, pears, and strawberries.Beverages: coffee, green tea, and alcohol — these beverages may irritate your thyroid gland ( 27 , 28 , 29 )
Can stress cause thyroid nodules?
Stress alone will not cause a thyroid disorder, but it can make the condition worse. The impact of stress on the thyroid occurs by slowing your body's metabolism. This is another way that stress and weight gain are linked.
Can a thyroid nodule cause weight gain?
Most people who have thyroid nodules lead a normal life. You might need to check in with your doctor more often, but there usually are no complications. If you do have complications, they can include problems swallowing or breathing. You may also sustain significant weight gain or weight loss.
How do I know if my thyroid nodule is benign?
Fine-needle biopsy: With this test, your provider uses a very thin needle to take a sample of cells from one or more thyroid nodules. They then send the samples to a laboratory for evaluation. Most nodules are noncancerous. However, if the test results are inconclusive, your provider may repeat this test.
What percentage of benign thyroid nodules become malignant?
Only ~8% of thyroid nodules are cancerous, so the vast majority are non-cancerous (benign). When the nodule is benign, guidelines recommend repeat ultrasound evaluation and repeat biopsy if there is significant growth of the nodule.
Can an ultrasound determine if a thyroid nodule is benign?
The vast majority — more than 95% — of thyroid nodules are benign (noncancerous). If concern arises about the possibility of cancer, the doctor may simply recommend monitoring the nodule over time to see if it grows. Ultrasound can help evaluate a thyroid nodule and determine the need for biopsy.
Can non cancerous thyroid nodules grow?
The natural course of benign thyroid nodules has been studied by Durante et al. [8]. In this paper, approximately 15% of such nodules showed continuous growth of more than 20% in a mean follow-up period of 60 months. Similar findings for the growth of benign thyroid nodules have been reported by Erdogan et al.
Where do hyperplastic polyps occur?
They occur in areas where your body has repaired damaged tissue, especially along your digestive tract. Hyperplastic colorectal polyps happen in your colon, the lining of your large intestine. Hyperplastic gastric or stomach polyps appear in ...
What is it called when you have multiple polyps in your colon?
Having multiple hyperplastic polyps in your colon is known as hyperplastic polyposis. This condition puts you at a 50 percent higher risk for developing colorectal cancer. One study found. Trusted Source. that over half of the participants with hyperplastic polyposis eventually developed colorectal cancer.
Can you get cancer from a polyp?
Getting polyps removed before they become cancerous lowers your risk of developing colorectal or stomach cancer by almost 80 percent. Most hyperplastic polyps in your stomach or colon are harmless and won’t ever become cancerous.
Can a polyp in the colon cause cancer?
A hyper plastic polyp in your colon isn’t necessarily a cause for concern. Hyperplastic polyps rarely. turn into colon cancer. They tend not to cause any other major health problems, either. Your risk of colon cancer is much lower if you only have one or a few of these polyps in your colon.
Is a colonoscopy polyp benign?
Hyperplastic polyps are usually found during a colonoscopy. They’re relatively common and usually benign, meaning they aren’t cancerous.
Can a doctor remove a polyp?
In many cases, your doctor can remove any large polyps that they find during a colonoscopy or stomach endoscopy with a device attached to the scope that enters your colon or stomach. Your doctor might also remove polyps if you have a lot of them.
Can hyperplastic polyposis cause colon cancer?
In addition, research suggests that hyperplastic polyposis is more likely to develop into colon cancer if you have certain risk factors, including:
What is the most common cell in hyperplastic lymph nodes?
1. B cell is the most common cell in hyperplastic lymph nodes. 2. B-cell hyperactivation and advanced maturity. 3. B cells are resistant to tolerance with some antigens. 4. Male bone marrow transferred to female BXSB mice produces accelerated disease; female bone marrow confers late lupus when transferred to males;
What causes lymph nodes to become enlarged?
Enlarged or hyperplastic lymph nodes are frequently the result of viral upper respiratory tract illnesses. Common pathogens include rhinovirus, adenovirus, and enterovirus, but measles, mumps, rubella, varicella, EBV, and cytomegalovirus may also cause lymphadenopathy.
Where are the ectopic glands located?
Normal arrangement: usually 4 glands are found adjacent to the thyroid lobes, thoracic inlet or mediastinum (up to 5mm in long axis)#N#▪#N#Ectopic glands can be found anywhere from behind the angle of the mandible down to the aortic root
Why is hyperplasia of lymph nodes considered a cause of hyperplasia?
To date, the causes of hyperplasia of lymph nodes are considered as the reasons for their increase, which is the immune response to any pathological process that makes changes both in the dynamics of tissue metabolism of the lymph node, and in the ratio of certain cells.
What is hyperplasia in biology?
In fact, hyperplasia (Greek - over education) is a pathological process associated with an increase in the intensity of reproduction (proliferation) of tissue cells of any kind and localization. This process can begin anywhere, and its result is an increase in the volume of tissues. And, in fact, such hypertrophic cell division leads to the formation of tumors.
What is the cause of a significant increase in the lymph nodes of the mesenteric part of the small?
In addition, a significant increase in the lymph nodes of the mesenteric part of the small intestine occurs as a result of the lesion of the Gram-negative bacterium Francisella tularensis, which causes tularemia, an acute infectious disease carried by rodents and arthropod s.
What is the name of the hyperplasia of the lymph nodes in the neck?
With nonspecific lymphadenitis - depending on the location - there is hyperplasia of the lymph nodes in the neck, lower jaw or axillary lymph nodes. The increase in axillary lymph nodes was noted in mastitis, inflammation of the joints and muscle tissues of the upper extremities, brucellosis, felinosis, etc.
What is the term for inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and nasopharynx?
For inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and nasopharynx (with actinomycosis, caries, chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, etc.), hyperplasia of the submaxillary lymph nodes, behind-the-ear, pre-percutaneous and zagochlorous is characteristic.
Why do lymph nodes have hyperplasia?
To date, the causes of hyperplasia of lymph nodes are considered as the reasons for their increase, which is the immune response to any pathological process that makes changes both in the dynamics of tissue metabolism of the lymph node, and in the ratio of certain cells. For example, in response to genetically distinct cells (antigens) in the lymph node, the production of lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes (macrophages) increases; when bacteria and microbes get into the lymph nodes, they accumulate the products of their vital activity and neutralized toxins. And in the case of oncology, lymph node hyperplasia can involve any of their cells in the pathological process of proliferation. This causes an increase in the size, a change in the shape and structure of the fibrous capsule of the lymph node. Moreover, the tissues of the lymph nodes can sprout beyond the capsule, and in the case of metastases from other organs, they are replaced by their malignant cells.
Where does follicular hyperplasia occur?
These processes occur in the cortex of the lymph nodes. In this case, the secondary follicles behave quite aggressively, displacing the remaining cells, including lymphocytes.
What is a hyperplastic thyroid nodule?
A hyperplastic nodule of thyroid is characterized by architectural and cytologic heterogeneity, usually with abundant colloid and often with subfollicle formation within larger follicles. and cytology make distinction of hyperplasia from adenoma difficult.
What is the classification of a follicular nodule?
The morphologic classification of cellular follicular nodules in nodular glands can be extremely difficult. Hyperplasia may be extremely difficult to distinguish from neoplasia. Classical guidelines that allow distinction of a hyperplastic nodule from a follicular adenoma include the following: (i) multiple lesions suggest hyperplasia whereas a solitary lesion is likely to be neoplastic, (ii) a poorly encapsulated nodule is likely hyperplastic; a well developed capsule suggests a neoplastic growth, (iii) variable architecture reflects a polyclonal proliferation whereas uniform architecture suggests a monoclonal neoplastic growth, (iv) cytologic heterogeneity suggests hyperplasia; monotonous cytology is characteristic of neoplasia, (v) the presence of multiple lesions in hyperplasia means that areas similar to the lesion in question will be present in the adjacent gland; in contrast, neoplasms have a distinct morphology compared with the surrounding parenchyma, (vi) classically hyperplastic nodules are said not to compress the surrounding gland whereas neoplasms result in compression of the adjacent parenchyma. For the most part, large nodules in multinodular glands tend to be incompletely encapsulated and poorly demarcated from the internodular tissue. However, in some glands, large encapsulated lesions with relatively monotonous architecture
What is an atypical adenomas?
Atypical adenomas are highly cellular tumours with unusual gross and/or histologic appearances that suggest the possibility of malignancy but these tumours lack evidence of invasion. They may have necrosis, infarction, numerous mitoses or unusual cellularity. Many so-called "atypical adenomas" are indeed papillary carcinomas. The distinction of an encapsulated follicular variant papillary carcinoma from follicular adenoma relies on cytologic characteristics. The presence of the cytologic features of papillary carcinoma described below should indicate that diagnosis, despite lack of invasion. Whether some follicular nodules classified histologically as adenomas have the biologic potential to become carcinoma is not clear; aneuploid cell populations
What are the characteristics of follicular cells?
The follicular cells are monotonous with elongated, bland nuclei and micronucleoli. Worrisome features include nuclear crowding, altered polarity, pleo-morphism, macronucleoli and coarse chromatin. The main practical role of cytology is to distinguish a colloid nodule or papillary carcinoma from a follicular neoplasm.
What is a follicular lesion?
On aspiration cytology, the diagnosis of "follicular lesion" covers both follicular adenoma and follicular carcinoma, which are difficult if not impossible to distinguish because the diagnostic criteria do not rest on cytologic characteristics.
What is a sporadic nodular goitre?
Sporadic nodular goitre is characterised by numerous follicular nodules with heterogeneous architecture and cytology, features that have suggested a hyperplastic rather than neoplastic pathogenesis (7-10). The gland may be distorted by multiple bilateral nodules and can achieve weights of several hundred to a thousand grams, but this disorder is often identified as a dominant nodule in what clinically appears to be an otherwise normal gland. Histologically, the nodules are irregular; some are poorly circumscribed while others are surrounded by scarring and condensation of thyroid stroma, creating the appearance of complete encapsulation. They are composed of follicles of variable size and shape. Some follicles are large, with abundant colloid surrounded by flattened, cuboidal or columnar epithelial cells, often with cellular areas composed of small follicles lined by crowded epithelium with scant colloid in a small lumen, alone or pushing into large colloid-filled follicles as "Sanderson's polsters" (Figure 1). There may be focal necrosis, haemorrhage with haemosiderin deposition and cholesterol clefts, fibrosis, and granulation tissue; these degenerative changes are usually found in the centre of large nodules, creating stellate scars.
What is thyroid follicular hyperplasia?
Thyroid Follicular Hyperplasia And Neoplasia. Follicular nodules are the most commonly encountered problems in the surgical pathology of the thyroid. These lesions can be classified along the full spectrum of thyroid pathology from hyperplastic nodules to benign follicular adenomas and malignant fol-licular carcinomas.
How to remove cancerous nodules?
Surgery. A common treatment for cancerous nodules is surgical removal. In the past, it was standard to remove a majority of thyroid tissue — a procedure called near-total thyroidectomy. However, today more limited surgery to remove only half of the thyroid may be appropriate for some cancerous nodules. Near-total thyroidectomy may be used depending on the extent of the disease.
How to treat a benign thyroid nodule?
If a biopsy shows that you have a noncancerous thyroid nodule, your doctor may suggest simply watching your condition. This usually means having a physical exam and thyroid function tests at regular intervals.
How long does it take for thyroid nodules to shrink?
This causes the nodules to shrink and signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism to subside, usually within two to three months. Anti-thyroid medications.
What is the best way to determine if a thyroid nodule is solid or cystic?
Doctors may also use it as a guide in performing a fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy.
What to do if you have an overactive thyroid nodule?
Surgery. If treatment with radioactive iodine or anti-thyroid medications isn't an option, you may be a candidate for surgery to remove the overactive thyroid nodule. You'll likely discuss the risks of surgery with your doctor.
What is the best way to check thyroid nodules?
Your doctor may recommend a thyroid scan to help evaluate thyroid nodules. During this test, an isotope of radioactive iodine is injected into a vein in your arm. You then lie on a table while a special camera produces an image of your thyroid on a computer screen.
How long does it take to biopsy a nodule?
The procedure is usually done in your doctor's office, takes about 20 minutes and has few risks.
What is a prostate nodule?
Prostate changes over time. A prostate nodule is a firm, knuckle-like area on the prostate gland. A nodule can develop due to a variety of reasons, including prostatitis and prostate cancer. The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system and is about the size and shape of a walnut. It is located just below the bladder and in front ...
Where are prostate nodules located?
It is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It helps produce semen, which carries the sperm from the testicles through the penis during ejaculation. This article will look at the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of prostate nodules.
What is the name of the inflammation of the prostate gland?
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland. It often results from a bacterial infection.
Can a prostate nodule be cancerous?
A prostate nodule may be cancerous. If a doctor finds a nodule during a health check, they may recommend a biopsy to rule out cancer. During a biopsy, a doctor removes a piece of tissue and sends it to a lab for testing. What are the alternatives to a biopsy for prostate cancer?
Is a prostate nodule the same as a tumor?
A nodule or tumor on the prostate gland is essentially the same thing. They are both abnormal growths. However, people often use the word nodule for a benign growth. They more often think of a tumor as cancer. However, not all tumors are cancerous.
