
What is a And ha in chemistry?
In this chemical equation, the molecule HA is the general formula for an acid. "A" is just a placeholder—it could be a picture of a banana for all we care. An example of an acid written in shorthand is HCl (hydrochloric acid), where a chlorine atom gets plopped where the "A" (or the banana) used to be.
What is A -/ ha?
So as long as [A-]/[HA] is between 1/10 and 10, the pH is within 1 unit of pKa. The addition of a strong acid or base to a buffer changes the ratio [A-]/[HA]. When a buffer absorbs an acid (H+), the acid converts A- to HA (A- + H+ → HA) and so the ratio [A-]/[HA] decreases.
How do you calculate the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
One way to determine the pH of a buffer is by using the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation, which is pH = pKₐ + log([A⁻]/[HA]). In this equation, [HA] and [A⁻] refer to the equilibrium concentrations of the conjugate acid–base pair used to create the buffer solution.
What is Ka in Chem?
What is the Ka value? The acid dissociation constant (Ka) is used to distinguish strong acids from weak acids. Strong acids have exceptionally high Ka values. The Ka value is found by looking at the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the acid. The higher the Ka, the more the acid dissociates.
Where is the group A-Ha from?
Oslo, NorwayA-ha / Origin
What happened to the group A-ha?
After 25 years of pouting and posing, A-ha are calling it quits. The Norwegian pop trio have announced that they will go their separate ways at the end of 2010. "Change is always difficult and it is easy to get set in one's ways," the group said.
What are the units for Ka?
This is a quantitative value for the strength of an acid in solution. The acid dissociation constant has no units. Ka is equal to the products over the reactants.
How do you find the Ka value?
To find out the Ka of the solution, firstly, we will determine the pKa of the solution. At the equivalence point, the pH of the solution is equivalent to the pKa of the solution. Thus using Ka = – log pKa equation, we can quickly determine the value of Ka using a titration curve.
What is meant by pKa value?
pKa is a number that describes the acidity of a particular molecule. It measures the strength of an acid by how tightly a proton is held by a Bronsted acid. The lower the value of pKa, the stronger the acid and the greater its ability to donate its protons.
Is Ka the same as pH?
Both Ka and pH are associated with each other. More the Ka, more would be its dissociation and thus stronger would be the acid. A strong acid has less pH value. Therefore, a larger Ka corresponds to a lesser pH value.
What is ka number?
Ka = [H3O+][A−][HA(aq)] Ka is thus simply a number that must be measured for different acids at different temperatures; there is wide disparity in Ka values. For strong acids, Ka values are large (typically greater than 10); for weaker acids, Ka are much smaller, and the equilibrium equation lies to the left.
Is pKa the same as pH?
Difference Between pKa and pH pKa is the negative value of the logarithm of Ka. pH is the logarithmic value of the inverse of H+ concentration. pKa indicates whether an acid is a strong acid or a weak acid. pH indicates whether a system is acidic or alkaline.
What does HA stand for in nursing?
List of medical abbreviations: HAbbreviationMeaningHAhypertonia arterialis headache calcium hydroxyapatiteH/AheadacheHAAhepatitis-associated antigen or #History As AboveHAARThighly active antiretroviral therapy137 more rows
What does HA stand for in texting?
If I make a mild observation, a “ha” is just great. The feel-good standard in chat laughter is the simple, classic “haha”: a respectful laugh. “Haha” means you're genuinely amused, and that maybe you laughed a little in real life.
What type of word is HA?
A representation of laughter.
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation?from byjus.com
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation provides a relationship between the pH of acids (in aqueous solutions) and their pK a (acid dissociation constant). The pH of a buffer solution can be estimated with the help of this equation when the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base, or the base and the corresponding conjugate acid, are known.
Why does Henderson-Hasselbalch fail to predict accurate values for the strong acids and strong bases?from byjus.com
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation fails to predict accurate values for the strong acids and strong bases because it assumes that the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base at chemical equilibrium will remain the same as the formal concentration (the binding of protons to the base is neglected).
Why is the hydrogen ion concentration of solution A lower than that of solution B?from varsitytutors.com
The hydrogen ion concentration of solution A is lower than that of solution B because the pH of solution A is greater. Acidity, or strength, of an acid is determined by the pKa. Since we have the same pKa for both acids, HA and HB will have the same acidity. Acid dissociation constant, Ka, is defined as:
Why is the HH equation so weak?from chem.libretexts.org
The reason the HH equation might produce poor predictions when calculating buffer p H is really because of an oft-made assumption which has nothing to do with the HH equation itself: the weak acid (or weak base is assumed to be so weak that its ionization contributes almost no conjugate base (or conjugate acid) in comparison to the dissolution of the buffer salt </strong>. In other words, we assume the formal concentrations C X of species in the buffer are equal to their actual concentrations [ X]; we replace
What is the difference between solution A and solution B?from varsitytutors.com
A researcher prepares two solutions. Solution A contains an unknown acid, HA, and solution B contains an unknown acid, HB. The researcher performs several tests and collects the following data.
Who created the equation for pH?from byjus.com
An equation that could calculate the pH value of a given buffer solution was first derived by the American chemist Lawrence Joseph Henderson. This equation was then re-expressed in logarithmic terms by the Danish chemist Karl Albert Hasselbalch. The resulting equation was named the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation.
Is the ka constant the same for both acids?from varsitytutors.com
Acid dissociation constant only depends on the pKa; therefore, the Ka for both acids is the same.
What is the Henderson Hasselbalch equation?
The Henderson Hasselbalch equation plays a pivotal role in teaching acid-base equilibrium and therefore receives considerable attention in general, analytical, and biochemistry courses. Titration curves, buffer problems, and a host of related phenomena can be discussed with relative ease using the equation. In 1908, Lawrence Henderson was the first to derive an equation that can calculate the pH of a buffer solution. It led to the extensive use of Henderson’s equation. Subsequently, in 1917, Karl Hasselbalch changed the formula to get it in logarithmic terms. Which eventually led to the formation of the Henderson Hasselbalch equation. We will now be going through the formula and derivation of the Henderson Hasselbalch equation.
Who was the first person to find the pH of a buffer solution?
In 1908, Lawrence Henderson was the first to derive an equation that can calculate the pH of a buffer solution. It led to the extensive use of Henderson’s equation. Subsequently, in 1917, Karl Hasselbalch changed the formula to get it in logarithmic terms.
Does Henderson Hasselbalch work with weak acids?
The Henderson Hasselbalch equation only works with weak acids or weak bases. The reason why it only works for weak acids and bases is that this is a simplified way of defining the acid dissociation constants. Usually, the amount of H2O does not change significantly, and thus can be thought of as constant and omitted.
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation?from byjus.com
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation provides a relationship between the pH of acids (in aqueous solutions) and their pK a (acid dissociation constant). The pH of a buffer solution can be estimated with the help of this equation when the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base, or the base and the corresponding conjugate acid, are known.
Why does Henderson-Hasselbalch fail to predict accurate values for the strong acids and strong bases?from byjus.com
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation fails to predict accurate values for the strong acids and strong bases because it assumes that the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base at chemical equilibrium will remain the same as the formal concentration (the binding of protons to the base is neglected).
Who created the equation for pH?from byjus.com
An equation that could calculate the pH value of a given buffer solution was first derived by the American chemist Lawrence Joseph Henderson. This equation was then re-expressed in logarithmic terms by the Danish chemist Karl Albert Hasselbalch. The resulting equation was named the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation.
Does Henderson-Hasselbalch equation include self dissociation?from byjus.com
Since the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation does not consider the self-dissociation undergone by water, it fails to offer accurate pH values for extremely dilute buffer solutions.
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation used for?
What Is the Henderson Hasselbalch Equation in Chemistry? The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is used to estimate buffer pH. Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels.
Who invented the pH formula?
An equation to calculate the pH of a buffer solution was derived by Lawrence Joseph Henderson in 1908. Karl Albert Hasselbalch rewrote this formula in logarithmic terms in 1917.
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation?from byjus.com
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation provides a relationship between the pH of acids (in aqueous solutions) and their pK a (acid dissociation constant). The pH of a buffer solution can be estimated with the help of this equation when the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base, or the base and the corresponding conjugate acid, are known.
Why does Henderson-Hasselbalch fail to predict accurate values for the strong acids and strong bases?from byjus.com
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation fails to predict accurate values for the strong acids and strong bases because it assumes that the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base at chemical equilibrium will remain the same as the formal concentration (the binding of protons to the base is neglected).
Who created the equation for pH?from byjus.com
An equation that could calculate the pH value of a given buffer solution was first derived by the American chemist Lawrence Joseph Henderson. This equation was then re-expressed in logarithmic terms by the Danish chemist Karl Albert Hasselbalch. The resulting equation was named the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation.
Does Henderson-Hasselbalch equation include self dissociation?from byjus.com
Since the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation does not consider the self-dissociation undergone by water, it fails to offer accurate pH values for extremely dilute buffer solutions.
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation?from byjus.com
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation provides a relationship between the pH of acids (in aqueous solutions) and their pK a (acid dissociation constant). The pH of a buffer solution can be estimated with the help of this equation when the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base, or the base and the corresponding conjugate acid, are known.
Why does Henderson-Hasselbalch fail to predict accurate values for the strong acids and strong bases?from byjus.com
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation fails to predict accurate values for the strong acids and strong bases because it assumes that the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base at chemical equilibrium will remain the same as the formal concentration (the binding of protons to the base is neglected).
Who created the equation for pH?from byjus.com
An equation that could calculate the pH value of a given buffer solution was first derived by the American chemist Lawrence Joseph Henderson. This equation was then re-expressed in logarithmic terms by the Danish chemist Karl Albert Hasselbalch. The resulting equation was named the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation.
Does Henderson-Hasselbalch equation include self dissociation?from byjus.com
Since the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation does not consider the self-dissociation undergone by water, it fails to offer accurate pH values for extremely dilute buffer solutions.
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation?from byjus.com
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation provides a relationship between the pH of acids (in aqueous solutions) and their pK a (acid dissociation constant). The pH of a buffer solution can be estimated with the help of this equation when the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base, or the base and the corresponding conjugate acid, are known.
Why does Henderson-Hasselbalch fail to predict accurate values for the strong acids and strong bases?from byjus.com
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation fails to predict accurate values for the strong acids and strong bases because it assumes that the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base at chemical equilibrium will remain the same as the formal concentration (the binding of protons to the base is neglected).
Why is the HH equation so weak?from chem.libretexts.org
The reason the HH equation might produce poor predictions when calculating buffer p H is really because of an oft-made assumption which has nothing to do with the HH equation itself: the weak acid (or weak base is assumed to be so weak that its ionization contributes almost no conjugate base (or conjugate acid) in comparison to the dissolution of the buffer salt </strong>. In other words, we assume the formal concentrations C X of species in the buffer are equal to their actual concentrations [ X]; we replace
Who created the equation for pH?from byjus.com
An equation that could calculate the pH value of a given buffer solution was first derived by the American chemist Lawrence Joseph Henderson. This equation was then re-expressed in logarithmic terms by the Danish chemist Karl Albert Hasselbalch. The resulting equation was named the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation.
Does Henderson-Hasselbalch equation include self dissociation?from byjus.com
Since the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation does not consider the self-dissociation undergone by water, it fails to offer accurate pH values for extremely dilute buffer solutions.
What is the principle of Henderson Hasselbalch?
According to the Bronsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases, an acid (HA) can donate a proton (H +) while a base (B) can accept a proton. An acid after losing a proton forms a conjugate base (A – ), and the protonated base exists as conjugate acid (BH + ).
Who developed the pH equation?
This equation was developed independently by the American biological chemist L. J. Henderson and the Swedish physiologist K. A. Hasselbalch to determine the pH of the bicarbonate buffer system in blood.
What is neglected in hydrolysis?
The significance of hydrolysis of water and its effect on the pH of the overall solution is neglected. Similarly, the hydrolysis of the base and dissociation of acid is also neglected. The assumption made in the equation might fail while dealing with strong acids or bases.
Why is Henderson-Hasselbalch an approximation?
The reason the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is an approximation is because it takes water chemistry out of the equation. This works when water is the solvent and is present in a very large proportion to the [H+] and acid/conjugate base. You shouldn't try to apply the approximation for concentrated solutions.
How to determine pH of a solution?
Once you have pH or pKa values, you know certain things about a solution and how it compares with other solutions: 1 The lower the pH, the higher the concentration of hydrogen ions [H + ]. 2 The lower the pKa, the stronger the acid and the greater its ability to donate protons. 3 pH depends on the concentration of the solution. This is important because it means a weak acid could actually have a lower pH than a diluted strong acid. For example, concentrated vinegar (acetic acid, which is a weak acid) could have a lower pH than a dilute solution of hydrochloric acid (a strong acid). 4 On the other hand, the pKa value is constant for each type of molecule. It is unaffected by concentration. 5 Even a chemical ordinarily considered a base can have a pKa value because the terms "acids" and "bases" simply refer to whether a species will give up protons (acid) or remove them (base). For example, if you have a base Y with a pKa of 13, it will accept protons and form YH, but when the pH exceeds 13, YH will be deprotonated and become Y. Because Y removes protons at a pH greater than the pH of neutral water (7), it is considered a base.
How to find pH of conjugate base?
pH is the sum of the pKa value and the log of the concentration of the conjugate base divided by the concentration of the weak acid. At half the equivalence point: pH = pKa. It's worth noting sometimes this equation is written for the K a value rather than pKa, so you should know the relationship: pKa = -logK a.
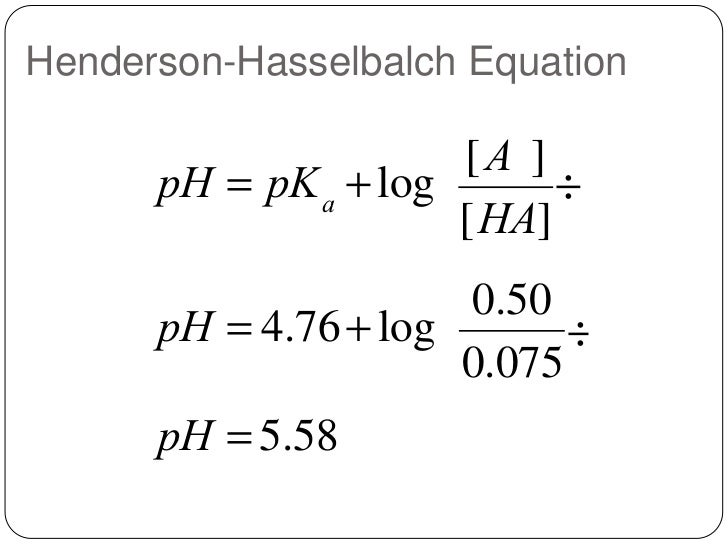
Table of Contents
Equation of Henderson-Hasselbalch
- The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be written as: pH = pKa + log10 ([A–]/[HA]) Where [A–] denotes the molar concentration of the conjugate base (of the acid) and [HA] denotes the molar concentration of the weak acid. Therefore, the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can also be written as: An equation that could calculate the pH value of a given buffer solution was first deri…
Derivation of The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- The ionization constants of strong acids and strong bases can be easily calculated with the help of direct methods. However, the same methods cannot be used with weak acids and bases since the extent of ionization of these acids and basesis very low (weak acids and bases hardly ionize). Therefore, in order to approximate the pH of these types of solutions, the Henderson-Hasselbalc…
Important Points to Remember
- When exactly half of the acid undergoes dissociation, the value of [A]/[HA] becomes 1, implying that the pKa of the acid is equal to the pH of the solution at this point. (pH = pKa + log10(1) = pKa).
- For every unit change in the pH to pKa ratio, a tenfold change occurs in the ratio of the associated acid to the dissociated acid. For example, when the pKa of the acid is 7 and the p…
- When exactly half of the acid undergoes dissociation, the value of [A]/[HA] becomes 1, implying that the pKa of the acid is equal to the pH of the solution at this point. (pH = pKa + log10(1) = pKa).
- For every unit change in the pH to pKa ratio, a tenfold change occurs in the ratio of the associated acid to the dissociated acid. For example, when the pKa of the acid is 7 and the pH of the solut...
- The value of [A–]/[HA] is dependent on the value of the pH and pKa. When pH < pKa; [A–]/[HA] < 1. When pH > pKa; [A–]/[HA] > 1.
Limitations of The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation fails to predict accurate values for the strong acids and strong bases because it assumes that the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base at chemical equilibriumwill remain the same as the formal concentration (the binding of protons to the base is neglected). Since the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation does not consider the self-di…
Solved Example
- A buffer solution is made from 0.4M CH3COOH and 0.6M CH3COO–. If the acid dissociation constant of CH3COOH is 1.8*10-5, what is the pH of the buffer solution? As per the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, pH = pKa + log([CH3COO–]/[CH3COOH]) Here, Ka = 1.8*10-5 ⇒ pKa= -log(1.8*10-5) = 4.7 (approx.). Substituting the values, we get: pH = 4.7 + log(0.6M /0.4M) = 4.7 + …
Theory For The Henderson Hasselbalch Equation
- A simple buffer solution consists of a combination of an acid and a salt of the conjugate base. The most defining property of a buffer solution is its ability of it to resist the changes occurring in a pH, even if a small amount of acid or base is added to it. Let us consider some assumptions Assumptions 1: Let us consider an acid that is monobasic and dissociates itself into H+and A-. …
Applications of The Henderson Hasselbalch Equation
- The major applications of the following equation are: It helps in the estimation of the pHvalue of a solution that contains acid and a base related to it, the solutions are generally called a buffer solution. The general formula for finding the above equation is pH= pKa+ log10 ( [A- ] / HA) pH= acidity of a buffer solution pKa= negative logarithm of Ka Ka = acid dissociation constant [A- ] = …
More About The Henderson Hasselbalch Equation
- The Henderson Hasselbalch equation plays a pivotal role in teaching acid-base equilibrium and therefore receives considerable attention in general, analytical, and biochemistry courses. Titration curves, buffer problems, and a host of related phenomena can be discussed with relative ease using the equation. In 1908, Lawrence Henderson was the first...
Derivation of The Henderson Hasselbalch Equation
- We will be going through two Henderson Hasselbalch derivations, the first one will be the derivation of the Henderson Hasselbalch Equation for base, and the second one will be for acid. Let's consider all the assumptions to be made for the derivation before we start with the derivations. Assumption 1:The acid is monobasic. Assumption 2:We can ignore the self-ionizati…
Solved Problems
- Question 1)Estimate the pHof a buffer with 0.2M acetic acid (CH3COOH) and 0.5M acetate (CH3COO-), the acid dissociation constant is given as 1.8 * 10−5. Solution 1)Given: [A-] = [CH3COO-] = 0.5M HA = [CH3COOH] = 0.2M Ka = 1.8 * 10−5 we need to calculate pKa, pKa = - log Ka -log Ka = - log 1.8 * 10−5 pKa= 4,7 Now we write the Henderson Hasselbalch equation, pH = p…
Analysis
Usage
History
Example
Properties
Clinical significance
Diagnosis
Definition
- The clinical form of the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation allows for the calculation of plasma bicarbonate (HCO3) concentration when pH and PCO2 are known (pK [dissociation constant] is 6.1 and s [solubility coefficient] is 0.0301):
Nomenclature
Function