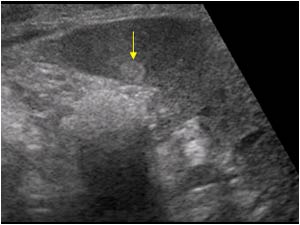
Isodense is an adjective that means possessing a similar radio-density to that of another or adjacent tissue. Formed from the amalgamation of the Greek word 'isos' which means 'equal' and the Latin word 'densus' which means 'thick'. Mass in a medial sense and in this instance means a lump or collection of cohering particles.
What is the mass on a CT scan?
What is a hemangioma mass?
Is isodensepolyp visible on CT?
Does metastatic disease show up on water material density images?
Does Aspergillus mycetoma show isodenseor?
Can cysts be hyperdense?
See 3 more
About this website

What does it mean when a mammogram shows a mass?
Masses can be many things, including cysts (non-cancerous, fluid-filled sacs) and non-cancerous solid tumors (such as fibroadenomas), but they may also be a sign of cancer. Cysts are fluid-filled sacs. Simple cysts (fluid-filled sacs with thin walls) are not cancer and typically don't need to be checked with a biopsy.
Can a radiologist tell if a mass is cancerous?
While even the most advanced imaging technology doesn't allow radiologists to identify cancer with certainty, it does give them some strong clues about what deserves a closer look.
What is a non palpable mass mean?
A nonpalpable breast mass is 1 that cannot be found during clinical examination of the breast, but can be identified by ultrasound, mammography, and MRI; a mass diagnosed as cancer is termed nonpalpable BC. In 20% to 30% of patients with nonpalpable breast masses, breast nodules develop into cancer.
Can a Microlobulated mass be benign?
Circumscribed oval and round masses are usually benign. An irregular shape suggests a greater likelihood of malignancy. The margins can be described as circumscribed, microlobulated, obscured (partially hidden by adjacent tissue), indistinct (ill-defined), or spiculated (characterized by lines radiating from the mass).
Can an MRI tell the difference between a cyst and tumor?
To eliminate any uncertainty, more physicians use diagnostic imaging, such as ultrasounds, mammograms, CT scans and even MRI scans. These tests can help a physician determine whether a growth is a cyst or tumor, and additional testing may be necessary to determine whether it is benign, premalignant or malignant.
Can an ultrasound tell the difference between a cyst and a tumor?
Ultrasound imaging can help determine the composition of lump, distinguishing between a cyst and a tumour. Also known as sonography, it involves the use of high-frequency, real-time sound waves to create an image.
How do you know if a mass is cancerous?
Bumps that are cancerous are typically large, hard, painless to the touch and appear spontaneously. The mass will grow in size steadily over the weeks and months. Cancerous lumps that can be felt from the outside of your body can appear in the breast, testicle, or neck, but also in the arms and legs.
What does non-palpable mean in medical terms?
A nonpalpable breast mass is 1 that cannot be found during clinical examination of the breast, but can be identified by ultrasound, mammography, and MRI; a mass diagnosed as cancer is termed nonpalpable BC.
What is a palpable mass?
Most palpable breast lumps are benign, but a new palpable breast mass is a common presenting sign of breast cancer. These masses may be detected by patient self-examination or during a physical examination carried out by a health professional.
Can an MRI tell if a tumor is benign?
Imaging is used not only for local staging but also to differentiate between benign and malignant lesions. MRI is the preferred imaging modality for the evaluation of soft-tissue masses in clinical practice.
What is a Microlobulated mass?
Ultrasound masses are classified according to their shape and margin. Round or oval masses are benign when their margins are circumscribed (fibroadenoma, intramammary lymph node); on the other hand, with non-circumscribed margins (microlobulated or irregular), masses that are round or oval may be cancers.
Why would an ultrasound be needed after a mammogram?
A breast ultrasound is most often done to find out if a problem found by a mammogram or physical exam of the breast may be a cyst filled with fluid or a solid tumor. Breast ultrasound is not usually done to screen for breast cancer. This is because it may miss some early signs of cancer.
Will a radiologist tell you if something is wrong?
“They aren't doctors, and while they do know how to get around your anatomy, they aren't qualified to diagnose you.” That is true even though the tech likely knows the answer to your question. Imaging techs administer thousands of scans a year.
What imaging shows tumors?
A CT scan (also known as a computed tomography scan, CAT scan, and spiral or helical CT) can help doctors find cancer and show things like a tumor's shape and size. CT scans are most often an outpatient procedure. The scan is painless and takes about 10 to 30 minutes.
Do tumors show up on ultrasound?
An ultrasound (also known as ultrasonography, sonography, or sonogram) helps doctors look for tumors in certain areas of the body that don't show up well on x-rays. Doctors often use this procedure to guide a needle during a biopsy.
Which test is performed by a radiologist?
Radiologists are medical doctors that specialize in diagnosing and treating injuries and diseases using medical imaging (radiology) procedures (exams/tests) such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear medicine, positron emission tomography (PET) and ultrasound.
Isodense Definitions | What does isodense mean? | Best 1 Definitions of ...
Define isodense. Isodense as a adjective means (sciences, especially biochemistry) Evenly or uniformly dense ; of the same density (as an adjacent object, tissue....
Low breast density in mammography worsens breast cancer prognosis
Very low mammographic breast density worsens the prognosis of breast cancer, according to a recent study. Disease free survivals, as well as overall life expectancies, were significantly shorter ...
Isodense nodular | Answers from Doctors | HealthTap
Created for people with ongoing healthcare needs but benefits everyone.
Isodense Definition & Meaning | Dictionary.com
Isodense definition at Dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation. Look it up now!
What is the definition of isointense? - Answers
Having the same intensity as another object. Used to describe the results of imaging tests, such as x-rays, MRIs, or CT scans. Isoinetnse to muscle means having the same intensity as muscle on a scan.
What are the masses on the skin?
SKIN MASSES. Masses on the skin include moles, seborrheic keratosis, accessory nipples, skin tags, sebaceous cysts (epidermoid inclusion cysts), and neurofibromas ( 9 ). Keloids may also be noted projecting on the breast parenchyma.
What is a lipoma mass?
Patients with a lipoma can be asymptomatic or present with a soft or hard, mobile mass. A radiolucent mass with an expansile circumscribed margin and a thin fibrous capsule are detected in the breast ( Fig. 7.18A ), or less commonly in the pectoral muscle ( Fig. 7.18B ), on the mammogram. Although the diagnosis is reliably made on mammographic findings, a mass with circumscribed margins and a homogeneously hypo-, iso-, or hyperechoic echotexture is imaged on ultrasound (see Fig. 4.40A) ( 10 ); in some patients, short, curvilinear hyperechoic internal septations may be apparent ( Fig. 7.19A ). Gentle mass effect can be seen on surrounding structures ( Fig. 7.19B ). Uncommonly, hemorrhage may occur in preexisting lipomas so that on the mammogram a mixed-density mass ( Fig. 7.20A, B) is seen at the site of a preexisting lucent mass. As the hemorrhage resolves, the lucent nature of the mass becomes more apparent on follow-up mammograms; the mass is complex on ultrasound and fluid–fluid levels may be seen ( Fig. 7.20C ). A mass with the signal characteristics of fat (high T1 and T2 signal, suppressed on fat-suppression images) and no enhancement is incidentally noted on MRIs performed as screening studies in high-risk women or those being evaluated for other breast-related issues ( Fig. 7.21 ). Histologically, these lesions are characterized by the presence of mature lipocytes surrounded by a thin capsule ( 11, 12 ). If otherwise asymptomatic, no intervention or short-term follow-up is indicated. Rarely, liposarcomatous lesions can present in the breast typically as a rapidly growing mass. The size, age of the patient, and growth pattern should suggest a malignant process. On the mammogram, internal septations may be seen in an otherwise lucent mass and the typically homogenous echotexture on ultrasound may be more heterogeneous (see Fig. 8.50 ).
Why are oil cysts mixed density?
In some women, oil cysts may be more appropriately characterized as mixed-density masses ( Fig. 7.26) because of thickened, ill-defined, or spiculated margins, or the presence of a round or oval intracystic mass. With a history of trauma or surgery, and if fat (radiolucency) is associated with these masses in orthogonal projections, no intervention or short-term follow-up is warranted regardless of the spiculated margins or associated nodules (see below, fat necrosis).
Is a lobular carcinoma a mass?
We place much emphasis on detecting microcalcifications and anguish over their characterization and management, but it is important to recognize that most invasive ductal carcinomas, and virtually all invasive lobular carcinomas, present as a mass. In contrast, when associated with malignancy, microcalcifications usually reflect intraductal, noninvasive breast cancer. Our primary goal with screening mammography is the recognition or perception of a possible mass or distortion related to an underlying mass. Our characterization of masses and management recommendations for patients are predicated on physical examination, spot compression, spot rolled, spot tangential, or spot compression magnification views and breast ultrasound. In some women, what appears to be a mass on screening images is shown to be superimposition of normal glandular tissue and what appears as an innocuous asymmetry is identified as likely malignant with further workup. By integrating patient history, clinical, mammographic, and ultrasound findings, and an understanding of breast histopathology, it is possible to approximate a diagnosis and have significant confidence in the appropriate management recommendations.
Is a mass in breast a fatty mass?
Fat-containing masses in the breast are almost always benign ( 1 – 3, 5 ). These masses can be completely fatty ( Table 7.5) or mixed in density ( Table 7.6 ). Although ultrasound findings are described for completeness, the diagnosis is established reliably when lucent or mixed-density masses are seen on the mammogram (with some of these lesions, the features on ultrasound may raise concerns inappropriately). It is important to note that, although many of the entities described are commonly fatty or mixed in density, they may also present as water density masses. So you will find an overlap in the differentials provided for each. For example, lymph nodes and fat necrosis are typically considered mixed-density masses, but each may present as a water density mass. Rarely, entities typically presenting as water density masses (including malignancy) may be noted to have lucent areas.
When is a breast ‘lesion’ called a ‘mass’?
A mass is usually something a little more substantial and clear than a ‘ lesion ‘ per se. A breast mass has volume and it occupies space. It may be in any shape but usually has convex outside borders. A breast mass tends to be denser in the middle than towards the edges.
Is a breast mass suspicious?
If the mass appears more like a ‘ lobule ‘ than a purely round or oval shape, then it is somewhat more suspicious for breast cancer. A breast mass appearing with a very irregular or ‘ random ‘ shape is highly suspicious for breast cancer .
Is breast mass denser in the middle or edges?
A breast mass tends to be denser in the middle than towards the edges. The tissues within a breast mass do not contain fat cells to the same degree as normal tissue. A mass that specialists discover on during a mammogram will typically be described according to the:-. margin (characteristics of it’s ‘ edge ‘).
Is density a sign of breast cancer?
The ‘ density ‘ of a mass, in terms of the relative amounts of fatty elements present, becomes highly suspicious for breast cancer when the density is high. In other words, when there is little evidence on mammogram of fatty tissue within the mass, this tends to suggest that the mass may be primarily malignant cancer cells.
What is spiculated breast mass?
A spiculated breast mass, which has spikes extending out from the main mass, is often highly suggestive of cancer.
What does a benign breast mass feel like?
Palpation of Benign Breast Masses. In contrast to breast cancer tumors, benign lumps are often squishy or feel like a soft rubber ball with well-defined margins. They're often easy to move around (mobile) and may be tender. 4 . Breast infections can cause redness and swelling.
Where do breast tumors grow?
Breast tumors can grow in the mammary glands, or the milk ducts. They begin as tiny as a seed and may not be felt or detected by a physical exam, mammogram, MRI, or ultrasound until they grow larger.
What is a mass suspicious of breast cancer?
A mass suspicious of breast cancer is a ‘space-occupying’ lesion seen on at least two mammogram projections. Furthermore, cancerous tumors also tend to be more dense in the middle than at the edges. Radiologists tend to describe breast masses according to their shape, margin, and density.
What is a simple cyst?
A screening finding of a simple cyst. If your mammogram shows mass, a simple cyst is the most common pseudo-mass found at screening. Breast cysts tend to affect women in the 30 to 50 age range, and are uncommon in post menopausal women. Cysts often form in the lobule from a distended acini.
Is a clustered microcyst benign?
Complicated cysts and clustered microcysts are considered ‘probably benign’ if they are non palpable. That would correspond to a “ BIRADS category 3, and given short term follow-up. However, if the lesions are palpable a breast cancer surgeon will probably aspirate (drain with a needle), and order a biopsy too.
How to remove a kidney mass?
The contemporary mainstay of surgery for renal masses is laparoscopy, the act of performing abdominal surgery by inflating the abdomen with carbon dioxide, inserting a camera and several instruments that allow for surgery through small incisions with a rapid recovery . Once it is determined that treatment of a kidney mass is necessary, the next step is to review the actual films, usually a contrast CT, to determine if removing only the tumor is feasible. This is always the desired approach, and in Dr. Engel’s hands will always be attempted. In cases however where the tumor is in a central location, invades deeply into the center of the kidney, or if negative margins cannot be assured in the operating room, the entire kidney will be removed. One only needs one healthy kidney, so in such a circumstance the patient is not usually adversely affected.
How to treat renal mass?
Treatment for renal masses is predominately surgical. Radiation and/ or chemotherapy play almost no role in the initial management of a kidney mass unless proof of metastasis exists. In certain cases, a patient may be a candidate for percutaneous management such as freezing the tumor (cryotherapy) or heating the tumor (microwave or ultrasound). Such a patient would be an elderly patient or a patient with co-morbidities precluding surgery, and a tumor location and size that is amenable to such an approach. Cryotherapy is sometimes offered laparascopically by Dr. Engel, but only in cases where laparoscopic partial nephrectomy is precluded due to the location of the tumor.
What is the most common benign renal mass?
The most common benign renal mass is called an oncocytoma. Oncocytomas have a typical appearance when large, but when small look similar to malignancy. Another common benign renal mass, more common in fertile women, is called an Angiomyolipoma.
What is the most common imaging method for finding a mass on the kidney?
Kidney Masses. The incidental discovery of a mass on the kidney has become a commonplace occurrence now that imaging modalities such as ultrasound, MRI and particularly CT scanning is so prevalent. It is of course very scary to be told that by accident a mass or lesion has been found on one’s kidney, and almost always in such a circumstance ...
What is the mass on a CT scan?
On CT scan the mass is usually isodenseto brain tissue.
What is a hemangioma mass?
Hemangiomas are ususally isodensesoft tissue attenuation masses enhancing homogenously and brilliantly on contrast administration helping in delineation of exact extent.
Is isodensepolyp visible on CT?
The isodensepolyp was clearly visible on CT, filling up the nasopharynx and extending downward to the oropharynx; no intracranial communication was noted.
Does metastatic disease show up on water material density images?
Metastatic disease should appear isodenserelative to the adjacent liver parenchyma on the water material-density images and demonstrate iodine uptake on the iodine material-density images (Figure 7).
Does Aspergillus mycetoma show isodenseor?
Zinreich et al reported that MRI in six cases of Aspergillus mycetoma showed isodenseor decreased signal intensities on T1-weighted images, which were similar to the kinds of images that are seen in patients with bacterial sinusitis, polyps, and carcinomas.
Can cysts be hyperdense?
On noncontrast CT imaging, the cysts can be hyperdense, isodense, or hypodense.