
Leasehold estate
A leasehold estate is an ownership of a temporary right to hold land or property in which a lessee or a tenant holds rights of real property by some form of title from a lessor or landlord. Although a tenant does hold rights to real property, a leasehold estate is typically considered personal property.
Full Answer
What do you need to know about a leasehold Covenant?
A leasehold covenant is an agreement operating between landlords and tenants. They are now mostly dealt with under the Landlord and Tenant Act 1995 (see below) Leasehold covenants Landlord and Tenant (Covenants) Act 1995 ss 2, 3, 5-8, 16, 23, 25, 28: S.2 This act concerns landlord/tenancy covenants.
What happens if a leasehold Covenant is breached?
Enforcement of Lease Covenants The lease between a landlord and a leaseholder (i.e. a tenant) will contain a number of covenants relating to the leaseholder’s use and occupation of the land. If these leasehold covenants are breached, the landlord may be able to take action to protect their interests.
What can a landlord do to enforce a lease covenant?
Enforcement of Lease Covenants. Property Litigation. The lease between a landlord and a leaseholder (i.e. a tenant) will contain a number of covenants relating to the leaseholder’s use and occupation of the land. If these leasehold covenants are breached, the landlord may be able to take action to protect their interests.
Can a sub-lessee operate under a leasehold Covenant?
Between these people the covenants may operate. However the reversion holder in the head lease and a sub-lessee are not in privity of estate A leasehold covenant is an agreement operating between landlords and tenants. They are now mostly dealt with under the Landlord and Tenant Act 1995 (see below)
What's a covenant between a lessor and lessee?
The Lessor covenants with the Lessee that the Lessee duly paying the Rent and other money payable under this Lease and observing and performing all other of the Lessee's Covenants may peaceably and quietly hold and enjoy the Premises during the Term without any interruption by the Lessor.
What is a leasehold clause?
A lease clause is a specific part of a contract or rental agreement between the landlord and tenant. These clauses need to be compliant with local state laws and other agreements between the two parties.
What is a deed of covenant leasehold UK?
Largely affecting leasehold properties, a Deed of Covenant is a legal document which states that the leaseholder agrees to undertake an obligation or series of obligations laid out by the freeholder (or landlord).
What's a covenant between a lessor and lessee quizlet?
liability of lessor and lessee are normally found. in the express covenants contained in the deed of lease or in the covenant implied by statute of by the common law. A covenant is a promise made by one party; covenantor. for the benefit of another party; the concenantee which is contained in a contract.
Why would anyone buy a leasehold property?
Owning a leasehold gives you the right to live in a property for a set period of time, which can be years, decades or centuries.
What are the disadvantages of buying a leasehold property?
What are the disadvantages of a leasehold property?You pay service charges and ground rent to the freeholder, which can increase.You need written permission from the freeholder to change the property, and there may be large fees involved.You may not be allowed pets.You might not be able to run a business from home.More items...•
Who pays for deed of covenant leasehold?
5. Who pays for a Deed of Covenant? If the landlord has a standard version for a deed of covenant that it requires you to use, then usually the current owner of the flat will pay the fee (if there is one) to the landlord for the draft deed of covenant.
What does a covenant on a property mean?
A covenant is a rule which states what can and cannot be done on the land. They are usually created in a deed between two parties, with one party agreeing to restrict the use of its land in a certain way for the benefit of another's land.
Why do I need a deed of covenant?
This principle provides that a contract cannot confer rights or impose obligations upon any person who is not a party to the contract. The deed of covenant is therefore used to create a direct contract between the landlord/managing agents and the new leaseholder.
Is it OK to buy leasehold property?
In summary, it is acceptable to purchase a leasehold home, as long as you are careful with what you are buying. In most cases, the long length of the lease, combined with your legal right to renew your lease, will mean that your interest in the property is satisfactory.
What does leasehold mean in Hawaii?
What does leasehold mean in Hawai'i? A leasehold estate is a property where an owner, or lessor, leases real estate to a buyer, or lessee, for a specific period of time. The lessee can live in the property for the lease period and pay the specified rent on the lease.
How does leasehold work in Hawaii?
How Leasehold Works. Basically, you pay the landowner rent for the land your property is on for a fixed term. When the term expires the land reverts to the lessor and all ownership rights are canceled (your property reverts to the landowner).
What is the difference between lease and leasehold?
The lease document sets out the rules which govern your use of a property that is being leased. Leasehold is a form of long-term tenancy where the purchaser buys the right to live in the property for a stated time. This is usually 99 or 125 years. The person who owns the lease on the property is called the leaseholder.
What is the relationship between a leaseholder and a freeholder?
The relationship between the freeholder and the leaseholder is governed by the lease, with rights and obligations for each party . In the most basic terms, ‘rights’ are the things you are entitled to receive, whereas ‘obligations’ are the things you are required to do.
What is the job of a leaseholder?
Importantly, if a leaseholder sublets their property it is the leaseholder’s job to ensure that tenants fully understand – and comply with – the terms of the lease. The lease is the contract between freeholder and leaseholder and so the responsibility for any breaches by the tenant rests firmly with the leaseholder.
What happens if a freehooder fails to meet its obligations?
A freehooder who fails to meet their obligations risks leaseholders taking action against them, whether through issuing Court proceedings or simply withholding service charge payments in protest.
What is a positive covenant?
A positive covenant can be described as an obligation to take action, such as structural repair and maintenance matters. These positive covenants typically fall on the freeholder.
How often do you have to paint a building to be a positive covenant?
An example of a freeholder’s positive covenant in a lease could be the requirement to paint the exterior of the building at least every five years.
What is the landlord and tenant act?
The Landlord and Tenant Act 1985 imposes a duty on the landlord (where the lease granted is less than 7 years) to keep the external structure in repair and certain items in good working order, such as the supply of utilities and for sanitation .
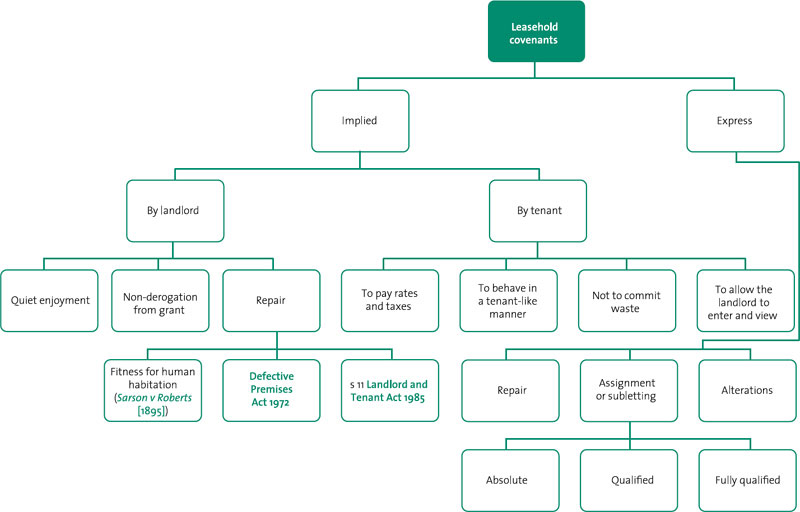
What is leasehold covenant?
Leasehold covenants are the undertakings made in contracts concerning the leasing of property. They may be express (verbal or written) or implied (in common law or by statute). The term ‘ leasehold ’ in property law describes a lease from the freeholder of a property that enables the leaseholder to use the property for a specified period subject to the covenants set out in the lease in return for the payment of rent .
What is covenant in a lease?
A covenant is simply an agreement between the parties, although its breach may also give rise to a cause of action.
What happens if you don't pay rent?
In the case of non- payment of rent, the landlord must issue a formal demand for payment prior to them forfeiting the lease. However, some leases contain a term permitting the forfeiture of the lease for non- payment ‘whether formally demanded or not’.
What is the general legal principle that if A agrees to give a benefit to B, then A should not?
This is the general legal principle that if A agrees to give a benefit to B, then A should not proceed to do something that substantially deprives B of the enjoyment of that benefit. For example, if the landlord does something that makes the property less fit for the purpose for which the lease was granted to the tenant .
What is the meaning of the case of Warren v Keen?
stated that a periodic tenant on a short lease must ‘do the little jobs about the place which a reasonable tenant would do. In addition, he must, of course, not damage the house …But…if the house falls into disrepair through fair wear and tear or lapse of time, or for any reason not caused by him, then the tenant is not liable to repair it.’
What is the O'Brien v Robinson case?
The case of ‘O’Brien v Robinson (1973) established that the landlord’s liability is subject to proper notice being given by the tenant that remedial work is required and that they have had a reasonable opportunity to carry out such works .
What are the two types of covenants?
There are two types of Covenants. Expressed Covenants and Implied Covenants.
Can a landlord terminate a tenancy agreement early?
A landlord must apply to the court to obtain an order for possession of the property, if he wants to end the tenancy agreement early due to a breach of Covenant by a tenant, but a tenant can also apply at a court for relief from the landlord’s application to terminate the tenancy agreement. For this to be successful, the tenant must have paid all arrears of rent, all the landlord’s costs and in the circumstances, it must be fair to allow the tenant to stay.
Does a covenant to repair include work that renews virtually the whole of the property in one go?
The statement of an Expressed Covenant to repair in the lease should not include work that renews virtually the whole of the property in one go, brings completely new improvements to the property or requires the correction of design faults within the property unless such there are faults causing physical damage to the property which falls within a Covenant to repair.
What is a commercial landlord and tenant?
Commercial Landlord & Tenant. Enforcement of Lease Covenants. The lease between a landlord and a leaseholder (i.e. a tenant) will contain a number of covenants relating to the leaseholder’s use and occupation of the land. If these leasehold covenants are breached, the landlord may be able to take action to protect their interests.
What is positive covenant?
Positive covenants require certain action from the party in question, such as requiring a leaseholder to maintain and keep the property in a certain condition. A lease will also contain covenants which the landlord must comply with, and are therefore enforceable by the leaseholder.
What is a lease covenant?
Lease covenants. A lease may contain both restrictive and positive covenants. Restrictive covenants seek to prevent certain conduct or uses, much in the same way as restrictive covenants attached to real property. For example, stopping the construction of additional buildings on the land.
What happens if you breach a lease covenant?
Breaching lease covenants. If a leaseholder has breached a lease covenant, the terms of the lease will often specify the available remedies. Even if a remedy is not specified, the breach may be sufficient to justify action such as forfeiture of the lease or injunction proceedings.
What covenants are in a lease?
A lease may contain both restrictive and positive covenants.
What is alternative dispute resolution?
Alternative Dispute Resolution – Methods used to attempt to resolve disputes outside of court proceedings. Appeal – A party may feel they have the…
Can a leaseholder enforce a covenant against another leaseholder?
Situations may also arise where a leaseholder wishes to enforce a lease covenant against another leaseholder. The terms of the lease may not allow them to do so directly, meaning they have to ask the landlord to take action on their behalf. This will usually involve the leaseholder agreeing to indemnify the landlord for any costs incurred in taking this action.
