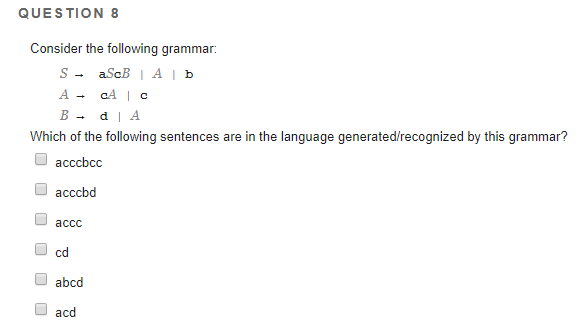
A literal question has a direct answer that is a fact. Examples: Who invites Summer to their Halloween party? What does Summer do when she wants to leave the Halloween party? Interpretive Question: Some suggested question starters: Why? An interpretive question has an answer that can be supported with evidence from the text.
What are inferential and literal questions?
Five essential aspects of reading comprehension include:
- Identifying the main idea of a text and its details
- Chronological sequencing of events from beginning, middle, and end
- Answering the recall questions of who, what, when, and where
- Making predictions
- Learning unfamiliar vocabulary
How to teach literal vs inferential questions?
Literal Vs. Inferential Comprehension Use these 18 half page task cards to help your students understand the difference between literal and inferential questions. Each card includes a high interest passage and 4 questions, which students identify as literal or inferential and then answer. Check out...
What are some examples of logical questions?
- A - The public does not want additional access to beaches.
- B - The government is currently responsible for the maintenance of all public and private beaches.
- C - The public already has some access to many beaches.
- D - Other property has been nationalized in the past, with no complaints from the original owners of the property.
What are good text questions?
Top 5 Conversation Starters
- How would you describe yourself in three words?
- What are your top three favorite things to talk about?
- Let’s play the question game: You ask me a question and then I will ask you a question.
- What four personality traits are the most important to you?
- What topic interests you the most?

What are some examples of literal questions?
Examples of Literal Questions Examples include: "What time does the concert start?" "What size do you wear?" "What references did you use to write your paper?" "Who was the protagonist in the story?" "How many inches are in a foot?" Asking literal questions gives you a deeper, richer understanding of new material.
What is literal question?
Literal questions have responses that are directly stated in the text. Inferential questions have responses that are indirectly stated, induced, or require other information.
What is the example of literal comprehension?
The literal meaning of the story was that Billy built a tower out of blocks. The answers to questions based on literal meaning will always be found in the text. For example: Who was building the tower? The answer is Billy.
What is a non literal question?
What is the difference between literal and inferential questions? Let's rewind just to make sure you are aware! Literal questions are those basic WH questions. Inferential questions require students to use clues from a text (or picture or video) + their background knowledge and make a smart guess.
What is example of literal?
Literal language is used to mean exactly what is written. For example: “It was raining a lot, so I rode the bus.” In this example of literal language, the writer means to explain exactly what is written: that he or she chose to ride the bus because of the heavy rain.
How do you teach inferential or literal questions?
1:002:11How to Teach Literal vs Inferential Questions - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFeel wait a second the text doesn't say how the woman feels. It doesn't literally tell us how sheMoreFeel wait a second the text doesn't say how the woman feels. It doesn't literally tell us how she feels. But we may be able to infer how she feels. How do you think she feels Debbie.
How do you create a literal comprehension?
They need to:decode sounds or scripts to recognise individual words.find the meaning of the word.connect the meaning of words to grammatical knowledge to make literal meaning from longer sections of text.connect literal meaning to cultural conventions to construct social meaning from the text.
What is literal in reading?
Literal comprehension is the understanding of information and facts directly stated in the text. It is recognised as the first and most basic level of comprehension in reading. Students can employ literal comprehension skills (keywords, skim reading and scanning) to better locate information efficiently. Key words.
What are the 4 types of comprehension questions?
8 Types of Comprehension Questions – Latest PSLE formatFactual. Such questions focus on obvious details from the passage. ... Inference. These questions require less obvious details than factual questions. ... Sequencing. ... Vocabulary in context. ... Applied vocabulary.
What is the difference between literal and non literal meaning?
A literal meaning is when a word or phrase is used exactly as it is defined. A non-literal meaning is when the meaning of a word or phrase takes on a special meaning.”
What is a literal and non literal text?
A literal meaning is when a word is the exact textbook definition. Nonliteral meanings are when words have an exaggerated definition, you will find this often used with figurative language. Authors will often use nonliteral language to help reader better understand what they are talking about.
How do you write an inferential question?
Step 1: Identify an Inference Question"According to the passage, we can reasonably infer...""Based on the passage, it could be suggested that...""Which of the following statements is best supported by the passage?""The passage suggests that this primary problem...""The author seems to imply that…"
What is universal question?
universal question asks for change or is a question that people don’t really have a sure answer for. Universal questions are deeper or more difficult questions about life.
What is interpretive question?
An interpretive question has an answer that can be supported with evidence from the text. Sometimes people may answer differently, but the question could still be right as long as evidence supports the question.
What are Literal Equations?
Sometimes, we are given equations in the form of formulas of geometric figures, for example, the perimeter of a square is given by P = 4s, where P is the perimeter of the square and s is the side length of the square. We have two variables P. and s such that P is expressed in terms of s. This is an example of a literal equation.
Literal Equations Formula
There is no one fixed formula to solve literal equations. We can identify a literal equation if it has more than one distinct variable. Literal equations can be linear equations, quadratic equations, cubic equations, etc. Literal equations can be solved by expressing each variable of the equation explicitly in terms of other variables.
Use of Literal Equations
Literal Equations are commonly used in formulas in mathematics and physics. Some common examples of literal equations are:
Solving Literal Equations
Literal Equations can be solved by isolating one variable and expressing it in terms of other variables. Sometimes, we are given the formula to determine the area of a geometric figure and we need to derive the formula to determine the side length of the figure. Steps to solve literal equations are:
FAQs on Literal Equations
Literal equations are defined as the equations consisting of two or more variables (letters or alphabets) such that each variable can be expressed in terms of other variables.
What is a Literal Equation?
The two words, literal and equation, have their own definitions and when grouped together form something unique in math. The word literal, in math, is defined as using variables, or letters, to represent unknown numerical values. The word equation is defined, in math, as having two opposing sides that have the same value.
Rewriting Literal Equations
The rewriting of literal equations involves solving the equation for any variable, in the formula. Solving for any variable means using the rules of equality to be sure the equation remains true. The variable being solved for has to be isolated using inverse operations.