Full Answer
What is a biloma?
In 1979, Gould and Patel 1 originated the term “biloma” and defined it as an encapsulated, extrahepatic collection of bile; however, this definition has evolved over time. A biloma is now more commonly recognized as any well-demarcated collection of bile outside the biliary tree, whether intrahepatic or extrahepatic, encapsulated or not. 2
What is biloma of the abdominal cavity?
Biloma is collection of bile within the abdominal cavity. It happens when there is a bile leak, for example after surgery for removing the gallbladder ( laparoscopic cholecystectomy ), with an incidence of 0.3–2%.
What are extrabiliary bilomas of the liver?
Bilomas refer to extrabiliary collections of bile. They can be either intra- or extrahepatic. There is a slight discrepancy in the reported literature in the use of the term "biloma".
What causes spontaneous biloma of the liver?
Most cases of biloma are caused by liver trauma or surgical intervention. However, spontaneous cases have been reported. We present a patient with spontaneous biloma which may have developed secondary to stenosis of the common bile duct or infarction of the liver. The initial treatment was percutane …

How serious is a biloma?
Biloma can be infected and cause serious and life-threatening complications such as peritonitis, biliopleural fistula which can lead to empyema, bilhemia (the fistula between veins and bile ducts inside liver, resulting in severely elevated bilirubinemia), and hemobilia (the arterial pseudoaneurysm rupture into the ...
What causes a biloma?
A biloma is a rare abnormal accumulation of intrahepatic or extrahepatic bile caused by traumatic or spontaneous rupture of the biliary tree1, 2). It is most commonly caused by surgery, percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC), percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage (PTBD), and abdominal trauma11, 12).
How is a biloma treated?
Large or symptomatic bilomas are treated by percutaneous drainage, in some cases coupled with a biliary drainage procedure to divert bile from the site of injury. External biloma drainage is continued until the biliary output through the drain ceases. Catheter injection often shows the site of leakage.
Is a biloma a bile leak?
A rare etiology of biloma is a spontaneous bile leak (SBL), where a specific cause remains unidentifiable and is usually a diagnosis of exclusion [3].
What are the symptoms of a bile leak?
Symptoms of a bile leak include tummy pain, feeling sick, a fever and a swollen tummy. Sometimes this fluid can be drained off. Occasionally, an operation is required to drain the bile and wash out the inside of your tummy. Bile leakage occurs in around 1% of cases.
Is a biloma an infection?
Infected hepatic fluid collections (bilomas) are a major infectious complication of liver transplantation.
Can you see bile leak on CT?
Although computed tomography (CT) and ultrasonography (US) can suggest bile leaks on the basis of a number of nonspecific imaging findings, hepatobiliary scintigraphy and magnetic resonance (MR) cholangiography with hepatobiliary contrast agents will help identify the site of posttraumatic or postoperative biliary ...
How do you pronounce biloma?
0:240:35Biloma - Medical Meaning and Pronunciation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBe I L Oh M a by Loma.MoreBe I L Oh M a by Loma.
What is a bile duct leak?
A biliary leak occurs when bile leaks out of any of the ducts that transport bile to the small intestine. Bile is made in the liver and secreted to help digest fats. Bile is made in the liver, stored in the gallbladder, and emptied into the small intestine via the common hepatic, cystic, and common bile ducts.
What is Pneumobilia in the liver?
Pneumobilia, or air within the biliary tree of the liver, suggests an abnormal communication between the biliary tract and the intestines, or infection by gas-forming bacteria. Pneumobilia usually can be distinguished from air in the portal venous system by its appearance on computed tomography (CT) scan.
What is biliary fistula?
Biliary fistulas are defined as chronic pipe-like ulcers. They can connect the gallbladder with the biliary tree and rarely involve the gastrointestinal tract (internal fistulas) and the abdominal wall (external fistulas) [1].
What is klatskin tumor?
Summary. Klatskin tumors are are a type of cholangiocarcinoma that begins in an area called the hilum, where the left and right bile ducts join and leave the liver. It is the most common type of cholangiocarcinoma, accounting for more than half of all cases.
What is a biloma in medical terms?
The term biloma describes an encapsulated collection of bile within the abdomen, usually secondary to bile duct disruption. The commonest causes reported in the literature are iatrogenic (secondary to hepatobiliary surgery), trauma or complications due to choledocholithiasis.
What bacteria causes cholangitis?
Bacteria that commonly cause cholangitis are Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Enterococcus, Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, and anaerobes. Although most infections are polymicrobial, this situation may not always prevail.
How do you pronounce biloma?
0:240:35Biloma - Medical Meaning and Pronunciation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBe I L Oh M a by Loma.MoreBe I L Oh M a by Loma.
What is a bile duct leak?
A biliary leak occurs when bile leaks out of any of the ducts that transport bile to the small intestine. Bile is made in the liver and secreted to help digest fats. Bile is made in the liver, stored in the gallbladder, and emptied into the small intestine via the common hepatic, cystic, and common bile ducts.
Biloma
Grayscale US shows a biloma after surgical removal of a liver mass. Low-level internal echoes suggest infected bile. Peripheral surgical suture with a ring-down artifact and clip with posterior shadowing are seen.
Bacterial and Miscellaneous Infections of the Liver
Tirdad T. Zangeneh, ... Stephen A. Klotz, in Zakim and Boyer's Hepatology (Seventh Edition), 2018
Ascites
Biliary ascites usually results from a spontaneous perforation of the common bile duct, most commonly at the junction with the cystic duct. 29–33 Rare instances of cystic duct perforation have been reported.
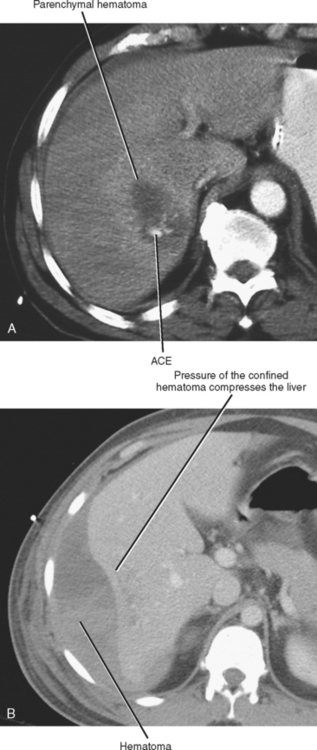
Hepatic and Biliary Trauma
Hunter B. Moore MD, ... Ernest E. Moore MD, FACS, in Abernathy's Surgical Secrets (Seventh Edition), 2018
Physiologic and Inflammatory Abnormalities of the Gastrointestinal Tract
Biliary ascites is caused by spontaneous perforation of the biliary tree. In 68% of the cases, the perforation occurs in the main biliary tree. In the remainder, the perforation is located at the junction of the cystic and common ducts or in an accessory bile duct. Two clinical forms are apparent.
Technical Problems
Treating biloma requires diagnosis and treatment of the underlying leakage and intervention regarding the threat of abscesses and sepsis caused by bacterial superinfection of the biloma. Drainage by an indwelling catheter, which can be placed under sonography or CT guidance, is adequate and sufficient in most cases (see Fig. 76-4 ).
Hypoechoic Liver Mass
Grayscale US shows a biloma after surgical removal of a liver mass. Low-level internal echoes suggest infected bile. Peripheral surgical suture with ring-down artifact and clip with posterior shadowing are seen along the cut liver edge.
Definition: What is Biloma?
This is a collection of bile inside your abdomen, which has become surrounded with epithelial cells. These are groups of tightly compressed cells that layers themselves on the external and internal surfaces of the organs of your body and other surfaces in your body. It is also known as a biliary cyst.
Symptoms
The symptoms that are associated with a biloma vary from person to person. Some may have symptoms of tenderness or abdominal pain while others may experience confusion and have a fever, especially if it becomes infected.
Causes of Biloma
Because they are a collection of bile inside your abdomen, there are two common reasons for you to develop one. It could be from problems with your bile duct or damage to your liver. Bile is a fluid that is produced in your liver and plays a part in your digestive process. The bile duct is what transports the bile.
Diagnosis
To diagnosis a biloma, they will use ultrasound imaging of your abdomen. If there is a deposit of bile, it will show up in the medical imaging. Having an ultrasound done will determine whether any action needs to be done at this point.
Treatment
In some cases of biloma, the problem will resolve on its own by your body reabsorbing the contents, while other times it may need to be drained. This is especially true if it is large and your body cannot clear it by itself or the biloma has become infected.
Introduction
In 1979, Gould and Patel 1 originated the term “biloma” and defined it as an encapsulated, extrahepatic collection of bile; however, this definition has evolved over time. A biloma is now more commonly recognized as any well-demarcated collection of bile outside the biliary tree, whether intrahepatic or extrahepatic, encapsulated or not. 2
Etiology
During the early 1990s, the increasingly widespread application of laparoscopic cholecystectomy was implicated in the increasing rate of disruptions of the biliary tree, which was identified as one of the most common postoperative complications, occurring in up to 7% of cases.
Pathophysiology and Composition
Encapsulation of a biloma is thought to result from 1 of 2 mechanisms depending on the rate of the biliary leak. More commonly, a slow bile leak produces encapsulation by inducing a mild inflammatory response and fibrosis. A rapid bile leak often produces biliary peritonitis, which may result in encapsulation.
Clinical Presentation
The most common presenting symptoms of bilomas are abdominal fullness and dull right upper quadrant abdominal discomfort, as most bilomas are intrahepatic or located in the right subphrenic or subhepatic region. However, migration of bile to the left subphrenic space can result in predominately left-sided pain.
Imaging
US is often the initial imaging modality used in cases of biloma, as patients tend to present with right upper quadrant abdominal discomfort. US imaging most often demonstrates a cystic lesion, but blood clots and other debris can sometimes be identified.
Management
Postoperative biliary fluid collections occur more often than many clinicians realize, especially after cholecystectomies. These fluid collections are typically small and asymptomatic and usually resolve without intervention.
Conclusion
Bilomas may lead to significant morbidity if they are not diagnosed and managed in a timely matter. Imaging modalities, including US, CT, MR imaging, and hepatobiliary cholescintigraphy, are often vital for diagnosis.

Definition: What Is Biloma?
- This is a collection of bile inside your abdomen, which has become surrounded with epithelial cells. These are groups of tightly compressed cells that layers themselves on the external and internal surfaces of the organs of your body and other surfaces in your body. It is also known as a biliary cyst. Although these cysts can happen to anyone the o...
Symptoms
- The symptoms that are associated with a biloma vary from person to person. Some may have symptoms of tenderness or abdominal pain while others may experience confusion and have a fever, especially if it becomes infected.
Causes of Biloma
- Because they are a collection of bile inside your abdomen, there are two common reasons for you to develop one. It could be from problems with your bile duct or damage to your liver. Bile is a fluid that is produced in your liver and plays a part in your digestive process. The bile duct is what transports the bile.
Diagnosis
- To diagnosis a biloma, they will use ultrasound imaging of your abdomen. If there is a deposit of bile, it will show up in the medical imaging. Having an ultrasound done will determine whether any action needs to be done at this point.
Treatment
- In some cases of biloma, the problem will resolve on its own by your body reabsorbing the contents, while other times it may need to be drained. This is especially true if it is large and your body cannot clear it by itself or the biloma has become infected. If it is found to be infected the surgeon will drain it by flushing it to make sure that all the material that was infected has been cl…