
Low flow delivery devices. These are oxygen devices that supply you with supplemental oxygen. But, the flow is not high enough to prevent you from inhaling room air. So, low flow basically means you will be inhaling a mixture of supplemental oxygen plus room air.
Which oxygen delivery system most reliably?
The smaller the V T or lower the respiratory rate, the higher the F IO2. Low-flow O 2 devices are the most commonly employed O 2 delivery systems because of simplicity, ease of use, familiarity, economics, availability, and acceptance by patients.
What are the different types of oxygen delivery systems?
What are 5 non-invasive ways to deliver oxygen to a patient?
- Takeaways:
- Low-flow.
- Nasal cannulas. Nasal cannulas are the most common type of low-flow oxygen delivery system. …
- Face masks. …
- NRB masks. …
- Moderate-flow.
- High-flow.
- Venturi masks.
What are the methods of oxygen delivery?
Part IV: Oxygen Delivery Methods
- First-Line Options. ...
- Second-Line Options. ...
- Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) NIPPV refers to a method of delivering oxygen without the use of a breathing tube and mechanical ventilator.
What is high flow oxygen delivery?
High flow oxygen therapy is a form of respiratory support used in the hospital where oxygen, often in conjunction with compressed air and humidification, is delivered to a patient at rates of flow higher than that delivered traditionally in oxygen therapy.
What is the difference between high and low flow oxygen delivery devices?
Low-flow systems often are more comfortable, but the ability to deliver a precise oxygen concentration in various respiratory breathing patterns is limited. A high-flow system can deliver very accurate oxygen concentrations, but is often uncomfortable and obtrusive.
What are the three types of oxygen delivery devices?
Oxygen delivery devices have historically been categorized into three basic types based on their design: low-flow, reservoir, and high-flow.
How many liters is low flow oxygen?
Low flow nasal cannulas can only deliver a nasal cannula flow rate of 4-6 liters of oxygen per minute. They don't provide humidified or heated oxygen. So, they often dry out the nasal passages.
Which is the device used for low oxygen therapy?
Nasal cannula Nasal cannulae are widely used in domiciliary oxygen devices.
Which oxygen level system would you use for the lowest flow of oxygen?
Low-flow systems include: Simple face mask. Non re-breather face mask (mask with oxygen reservoir bag and one-way valves which aims to prevent/reduce room air entrainment) Nasal prongs (low flow)
What is the most common oxygen delivery device?
A nasal cannula is the most common oxygen delivery system, used for mild hypoxia (figure 4a).
When is low flow oxygen used?
Low-flow oxygen is a standard treatment option for anyone of these cardiopulmonary diseases: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Pulmonary fibrosis. Emphysema.
Is being on 4 liters of oxygen a lot?
Rates of 4 liters/minute or greater are considered higher oxygen flow. As more scarring develops in the lungs, they become less efficient in delivering the necessary oxygen the body needs.
What is the normal flow rate of oxygen?
The normal flow rate of oxygen is usually six to 10 litres per minute and provides a concentration of oxygen between 40-60%. This is why they are often referred to as MC (medium concentration) masks, as 40%-60% is considered to be a medium concentration of oxygen.
What is dangerously low oxygen level?
If you're using an oximeter at home and your oxygen saturation level is 92% or lower, call your healthcare provider. If it's at 88% or lower, get to the nearest emergency room as soon as possible.
Is liquid oxygen better than a concentrator?
In conclusion, liquid-oxygen treatment was more expensive compared to concentrator treatment. However, treatment effects showed that liquid oxygen had a better impact on quality of life.
How long can you survive with low oxygen levels?
Most people will die within 10 minutes of total oxygen deprivation. Those in poor health often die much sooner. Some people may suffer other medical catastrophes, such as a heart attack, in response to oxygen deprivation.
What are the different types of oxygen therapy?
Oxygen can be delivered in three basic ways: via concentrator, compressed oxygen gas, and liquid oxygen. The least expensive and most efficient method to deliver oxygen therapy at home is via an oxygen concentrator. This device uses electricity to extract nitrogen from room air and delivers oxygen that is 95%-96% pure.
How many types of oxygen masks are there?
Regulations. Three main kinds of oxygen masks are used by pilots and crews who fly at high altitudes: continuous flow, diluter demand, and pressure demand.
Which is the most commonly used type of oxygen delivery system quizlet?
A nasal cannula is the device most often used to administer oxygen therapy.
What is the difference between high flow oxygen and non-rebreather?
HFNC delivers flow, not pressure like CPAP or BiPAP, but the flow can generate an estimated 2-5 cm H2O of PEEP. HFNC is a better oxygen delivery and respiratory support device than the standard non-rebreather oxygen mask, venturi-mask, and simple low flow nasal cannula in a hypoxic patient.
What is low flow oxygen delivery system?
Oxygen delivery systems are generally classified as low-flow or variable-performance devices and high-flow or fixed-performance devices. 2 Low-flow systems provide oxygen at flow rates that are lower than patients’ inspiratory demands; thus, ...
What is high flow oxygen?
An oxygen delivery system is a device used to administer, regulate, and supplement oxygen to a subject to increase the arterial oxygenation. In general, the system entrains oxygen ...
Is a ventilatory system a high flow system?
Thus, if the ventilatory demand of the patient is met completely by the system, then it is a high-flow system. In contrast, if the system fails to meet the ventilatory demand of the patient, then it is classified as a low-flow system.
What is oxygen delivery device?
Oxygen Delivery Devices and Flow Rates are important concepts to understand as a nurse. Oxygen is a life-saving therapy that nurses and respiratory therapists administer every day in the hospital.
How much FIO2 does a nasal cannula deliver?
Nasal Cannula is typically started at 2L/min and then titrated upwards to as high as 6L/min, although 2-4L/min is ideal. This delivers 25-40% FIO2, depending upon their respiratory rate, tidal volume, and amount of mouth breathing.
How much FIO2 is HFNC?
HFNC can be delivered from 8-60L/min ( 30-60 L/min in adults ), and an FIO2 of 100%.
How much FIO2 is needed for a room?
Less than 30% FIO2 can be provided with this, which is not much greater than room air of 21%.
What does it mean when oxygen blows by?
Blow-by oxygen is just that – it’s oxygen that blows by. This does not not apply oxygen directly, but rather indirectly by “blowing” on the patient’s face.
What is the concentration of oxygen in the atmosphere?
Oxygen occurs naturally in our atmosphere, at a concentration of 21%. Another term for oxygen concentration is FIO2, or fraction of inspired oxygen.
How often is oxygen used in the hospital?
Oxygen is used every day in and out of the hospital. In order to understand oxygen delivery devices and flow rates, we need to first understand a few basic principles and definitions.
What is low flow delivery?
Low flow delivery devices. These are oxygen devices that supply you with supplemental oxygen. But, the flow is not high enough to prevent you from inhaling room air. So, low flow basically means you will be inhaling a mixture of supplemental oxygen plus room air.
How much oxygen does a COPD device need?
These are low flow oxygen devices. Depending on the flow, they deliver anywhere from 22-44% FiO2. Most people with COPD only need 2-3 LPM. This delivers FiO2s of 28-32% respectively. This is usually all that's needed to maintain oxygen levels with stable COPD.
How much FiO2 can you inhale?
This allows you to inhale about 75% FiO2. Limitations. The FiO2 may vary depending on leaks in the system, Liter flow set, and your respiratory pattern. If they do not deliver enough oxygen to maintain adequate oxygen levels, a high flow oxygen device (see below) may be indicated.
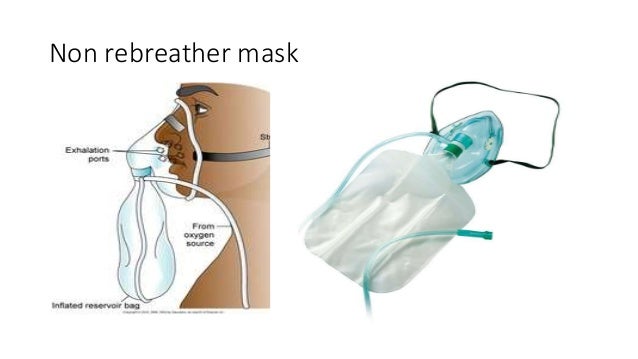
What is the bag called when you exhale?
Supplemental oxygen comes up the tubing. While you are exhaling, this oxygen is stored in the bag. So, this bag is called a reservoir bag . It's a reservoir for oxygen. When you exhale, oxygen is stored in it.
What is a high flow nasal cannula?
High flow nasal cannula. These are fancy, and often weird looking, nasal cannulas. They allow us to deliver flows higher than 6LPM. They can deliver very high flows to you. What we set it at depends on what you can tolerate. It also depends on what your oxygen demands are. With these, we can deliver all the way up to 100% Fio2.
Does 6LPM decrease FiO2?
This may cause the FiO2 you are inhaling to decrease. Also, 6LPM is the maximum effective liter flow. So, if this is not enough to maintain an adequate SpO2, some other oxygen delivery device may be indicated.
Can you inhale room air with a rubber flap?
One of these holes is covered by a rubber flap. This flap acts as a one-way valve. This makes it so you can exhale through it, but you cannot inhale room air. Supplemental oxygen comes up the tubing.
What is Low-Flow Oxygen?
Low-flow delivery systems are specific devices that generally deliver oxygen at flow rates lower than patient’s ventilatory requirements. These are the devices that are used when consistency in fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO 2) delivery is not crucial. It is based on the patient’s anatomic reservoir and minute ventilation.
What is a High-Flow Oxygen?
High-flow oxygen delivery is a non-invasive respiratory support for critically ill patients to deliver very accurate oxygen concentration at flow rates that exceed patient’s respiratory requirements. It is usually defined as the administration of gas flow above 6-15 liters per minute.
Summary
Both high-flow and low-flow oxygen delivery systems are capable of administering a wide range of FiO 2. However, the terms high and low do not reflect the delivered FiO 2; in fact, it refers to the flow of gas delivered to the system.
What is the aim of the oxygen guideline?
The aim of this guideline is to describe the indications and procedure for the use of oxygen therapy, and its modes of delivery.
How much flow is needed for a 12kg slurry?
Flow of 2 L/kg/min up to 12kg, plus 0.5 L/kg/min for each kg above 12kg (to a maximum of 50 LPM)
How to reduce hypothermia?
Ensure adequate clearance of secretions and limit the adverse events of hypothermia and insensible water loss by use of optimal humidification (dependent on mode of oxygen delivery). Maintain efficient and economical use of oxygen.
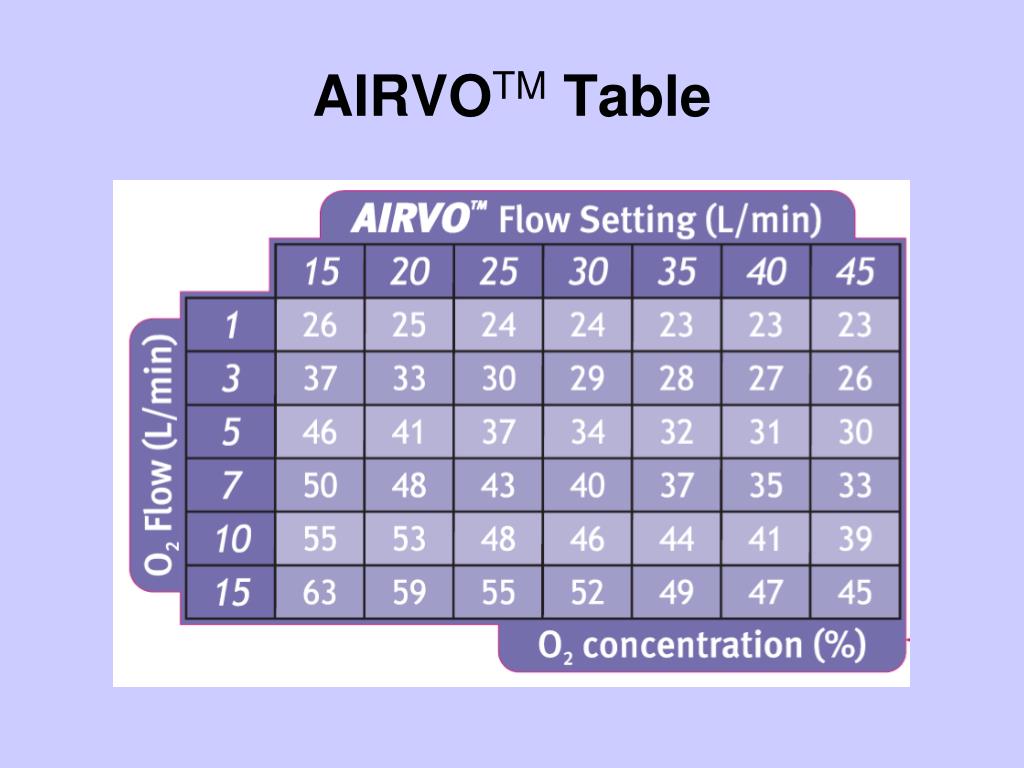
How many modes does the Airvo 2 have?
The AIRVO 2 Humidifier has two modes:
What is a non-rebreather face mask?
Non re-breather face mask (mask with oxygen reservoir bag and one-way valves which aims to prevent/reduce room air entrainment)
What is the name of the condition where the amount of water vapour that a gas can carry increases with temperature?
The amount of water vapour that a gas can carry increases with temperature. Hypercapnea: Increased amounts of carbon dioxide in the blood. Hypoxaemia: Low arterial oxygen tension (in the blood.) Hypoxia: Low oxygen level at the tissues.
How often should you wean off oxygen?
Unless clinically contraindicated, an attempt to wean oxygen therapy should be attempted at least once per shift.
Compressed Oxygen Cylinders
- Oxygen cylinders, or oxygen tanksare the most common delivery system and are widely used. Since they function pneumatically by slowly releasing pressurized oxygen to achieve a steady flow, they do not need electrical power to work. Pros As mentioned above, one of the main benef…
Liquid Oxygen Systems
- Liquid oxygen systems are unique because they use a liquefied form of oxygen that turns into a gas when released. To use this system, you must also have a sizeable liquid oxygen reservoir in your home to refill your portable device before extended use. Pros With liquid oxygen, you can refill your portable tank from your large reservoir at home whenever you need to. With this backu…
Oxygen Concentrators
- Oxygen concentratorsare a unique oxygen delivery system. They function like air filters that remove everything except oxygen from the air. Once this filtration occurs, you can reach almost 100% pure oxygen with the device. And since this filtration occurs inside the unit itself, there is no need to refill tanks. Pros As mentioned above, oxygen concentrators do not need to be refilled. T…
Important Things to Consider
- Your insurance provider plays a role in determining which oxygen delivery system you ultimately qualify for. However, that decision is also determined by your specific oxygen needs and what your daily activities are. If you plan to purchase a device out of pocket, then your insurance coverage will not be a factor. However, if you plan to ask your insurance to cover your device, it i…
Final Thoughts
- These 3 oxygen delivery systems all dispense oxygen sufficiently for medical treatment but with varying levels of maintenance and portability. Before accepting the first option that is given to you, consider the pros and cons of each device. Then, be sure to request a device that will accommodate your lifestyle. Page last updated: October 10, 2018 Sources: 1. University of Flori…