
Measurement in Chemistry
- Error = experimental value – accepted value. Error can also be calculated as a percentage as the relative error, or percent error.
- Percent Error = (|error|/accepted value)*100%. Scientists typically use units from the International System of Measurement (SI). ...
- 1 J = 0.2390 cal and 1 cal = 4.184 J. Temperature is measured in Celsius (C) or Kelvin (K). ...
What are the measurements of Chemistry?
To make each of those types of volatile measurements, we use an instrument called a Fourier Transform Infrared spectrometer, or FTIR. FTIR instruments detect incoming infrared (IR) radiation—the ...
What is the importance of measurement in chemistry?
Measurements provide quantitative information that is critical in studying and practicing chemistry. Each measurement has an amount, a unit for comparison, and an uncertainty. We use base SI units such as meters, seconds, and kilograms, as well as derived units, such as liters (for volume) and g/cm3 (for density).
What is a measurement in chemistry?
Sections:
- 4.184 J = 1 cal. ...
- Example 1:
- Round 26.65 to three significant figures. ...
- Example 2:
- Round 26.652 to three significant figures. ...
- Round 26.7500 to three significant figures.
- Solution: When you look at the 4th digit, it is a 5 with only zeros following it. ...
What are the units of measurement in chemistry?
Units of Measurement
- Standard Units (SI Units) The International System of Units (abbreviated SI) is the metric system used in science, industry, and medicine.
- SI Unit Prefixes. The basic SI units can be expressed as fractions and multiples of basic units by using a set of simple prefixes.
- Volume and Density. ...
- Temperature. ...
What is a measurement easy definition?
1 : the act of determining size, capacity, or quantity The instruments provide accurate measurement. 2 : the extent, size, capacity, or amount of something as has been determined The room's measurements are 20 feet by 14 feet. measurement.
What is measurement and explain?
Measurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events. In other words, measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared to a basic reference quantity of the same kind.
Why is measurement in chemistry important?
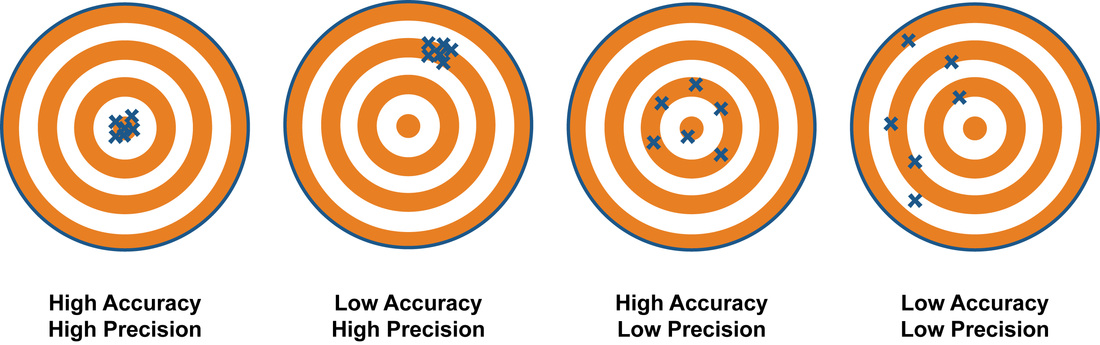
When taking scientific measurements, it is important to be both accurate and precise. Accuracy represents how close a measurement comes to its true value. This is important because bad equipment, poor data processing or human error can lead to inaccurate results that are not very close to the truth.
What is measurement with example?
Measurement is defined as the act of measuring or the size of something. An example of measurement means the use of a ruler to determine the length of a piece of paper. An example of measurement is 15" by 25". The bust, waistline, and hip dimensions of a woman.
How do we make measurements in chemistry?
Measurements can be represented in either decimal or scientific notation. Scientists primarily use the SI (International System) or metric systems. We use base SI units such as meters, seconds, and kilograms, as well as derived units, such as liters (for volume) and g/cm3 (for density).
What are the 3 types of measurement?
The three standard systems of measurements are the International System of Units (SI) units, the British Imperial System, and the US Customary System. Of these, the International System of Units(SI) units are prominently used.
What is the purpose of measurement?
The purposes of measurement can be categorized as measurement being in the service of quality, monitoring, safety, making something fit (design, assembly), and problem solving.
What are the two parts of measurement in chemistry?
A measurement is a quantitative observation that consists of two parts: a number and a unit.
Why is measurement important?
Measurement is important in providing links between strands of mathematics. For example, it provides a rich and meaningful context for the use of number skills and of spatial concepts. Measurement also provides links between mathematics and other school subjects.
What are types of measurement?
You can see there are four different types of measurement scales (nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio).
What are the 2 types of measurement?
The two systems used for specifying units of measure are the English and metric systems.
What is measurement and types of measurement?
Measurement Units Time: Units for expressing time include seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, years, etc. Length: Units for measuring length include millimetres, centimetres, meters, kilometres, etc. Weight: Units for expressing the weight of certain objects include grams, kilograms, tons, etc.
What does in measurement mean?
The inch (symbol: in or ″) is a unit of length in the British imperial and the United States customary systems of measurement. It is equal to 136 yard or 112 of a foot.
What is measurement and why is it important?
Answer: The action of measuring anything, or a certain number of objects, is a measurement. Also measuring certain things correctly is very necessary including distance, time, and accuracy. We can really know the universe around us by measuring such occurrences or, in other words, by taking such measurements.
Why is measurement important?
Measurement is important in providing links between strands of mathematics. For example, it provides a rich and meaningful context for the use of number skills and of spatial concepts. Measurement also provides links between mathematics and other school subjects.
Why is measurement important in chemistry?
For example, a measurement of your height might be 5 ft, which contains a number, 5, and a unit, ft. In chemistry, scientists will often work with very large numbers so, to avoid writing the full length of the number, they will use scientific notation in which a given number is written as the product of a coefficient and 10 raised to a power. For example, 405,000,000,000 is 4.05 x 1011.
What are the units of mass and volume?
The units for mass are grams and the units for volume are lengths of measurement cubed. For example, the units for an object's density may be 10 g/cm3 . This unit shows the relationship between mass and volume when determining density. Density is an intensive property since it relies on the composition of the substance and not its size. It is the mass per unit of volume.
What is the conversion factor?
When converting between equivalent units, the conversion factor will be used. The conversion factor is the number used to change one set of units to another, by multiplying or dividing. In this case, the conversion factor is 1 dollar. It shows the ratio between quarters and dollars. For every dollar, there is an equivalent of 4 quarters.
What is the purpose of measuring in chemistry?
Measurements provide quantitative information that is critical in studying and practicing chemistry. Each measurement has an amount, a unit for comparison, and an uncertainty. Measurements can be represented in either decimal or scientific notation.
What is the purpose of measuring?
Measurements provide the macroscopic information that is the basis of most of the hypotheses, theories, and laws that describe the behavior of matter and energy in both the macroscopic and microscopic domains of chemistry . Every measurement provides three kinds of information: the size or magnitude of the measurement (a number);
How many quarts are in a liter?
One liter is about 1.06 quarts. A cubic centimeter (cm3) is the volume of a cube with an edge length of exactly one centimeter. The abbreviation cc (for c ubic c entimeter) is often used by health professionals. A cubic centimeter is also called a milliliter (mL) and is 1/1000 of a liter.
What units are used to sell ice cream?
Ice cream is sold in quarts (a familiar, non-SI base unit), pints (0.5 quart), or gallons (4 quarts). We also use fractions or multiples of units in the SI system, but these fractions or multiples are always powers of 10.
How long is a meter?
It is now defined as the distance light in a vacuum travels in 1/299,792,458 of a second. A meter is about 3 inches longer than a yard ( Figure 1 ); one meter is about 39.37 inches or 1.094 yards. Longer distances are often reported in kilometers (1 km = 1000 m = 10 3 m), whereas shorter distances can be reported in centimeters (1 cm = 0.01 m = 10 −2 m) or millimeters (1 mm = 0.001 m = 10 −3 m).
What is the prefix for a fractional unit?
Fractional or multiple SI units are named using a prefix and the name of the base unit. For example, a length of 1000 meters is also called a kilometer because the prefix kilo means “one thousand,” which in scientific notation is 10 3 (1 kilometer = 1000 m = 10 3 m).
What is the SI unit?
The standards for these units are fixed by international agreement, and they are called the International System of Units or SI Units (from the French, Le Système International d’Unités ). SI units have been used by the United States National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) since 1964. Property Measured.
What is measurement in science?
Measurements are observations of a quantitative nature that are taken by some form of equipment. Some equipment, like our five senses, can give us very approximate measurements, while other technology, like a scale, provides more exact measurements.
What are the most common measurements used in chemistry?
Some of the common quantities we measure in chemistry are distance (length), volume, mass, time, velocity, temperature, density, pressure, amount, concentration, energy, and electric charge.
Why are atoms so small?
Because individual atoms are so small, the substances that we can actually see and study, even something as small as a drop of rain, are comprised of an incredibly large number of atoms. There are literally thousands of billions of billions of particles in a drop of water.
What are base units?
Base units are measurements that have their own independent scale and cannot be expressed in terms of other base units. All other measurement quantities, such as volume, force, and energy, can be derived from these seven base units. For instance, volume is calculated by multiplying together three different lengths (height, width, and depth).
Is one set of units more correct than the other?
No one set of units is more correct than the other . However, as we begin measuring, calculating, and sharing measurements, we will want a standard set of values that we and others can use. An international governing body has developed a metric system of units of measurement for scientists called the Système International (SI).
What is measurement in science?
Updated July 02, 2019. In science, a measurement is a collection of quantitative or numerical data that describes a property of an object or event. A measurement is made by comparing a quantity with a standard unit.
What is the study of measurement called?
The study of measurement is called metrology . There are many measurement systems that have been used throughout history and across the world, but progress has been made since the 18th century in setting an international standard.
What is the most common metric system?
There are a few common standard systems you may encounter: International System of Units (SI): SI comes from the French name Système International d'Unités. It is the most commonly used metric system. Metric System: SI is a specific metric system, which is a decimal system of measurement. Examples of two common forms of the metric system are ...
Why are measurements calibrated?
Measurements are calibrated, which is to say they are compared against a set of standards in a system so that the measuring device can deliver a value that matches what another person would obtain if the measurement were repeated. There are a few common standard systems you may encounter:
What are some examples of metric units?
Examples of two common forms of the metric system are the MKS system (meter, kilogram, second as base units) and CGS system (centimeter, gram, and second as base units). There are many units in SI and other forms of the metric system that are built upon combinations of base units. These are called derived units.
What are the criteria used to compare measurements?
Accuracy matters, so there are criteria that scientists use to compare measurements: type, magnitude, unit, and uncertainty. The level or type is the methodology used for taking the measurement. Magnitude is the actual numerical value of a measurement (e.g., 45 or 0.237).
How to measure length of string?
The length of a piece of string can be measured by comparing the string against a meter stick. The volume of a drop of water may be measured using a graduated cylinder. The mass of a sample may be measured using a scale or balance. The temperature of a fire may be measured using a thermocouple.
What is the uncertainty of a chemical measurement?
Chemical measurements. Whenever a measurement is made in chemistry, there is always some uncertainty in the result obtained. There are many causes of uncertainty in chemical measurements. For example it may be difficult to judge: whether a thermometer is showing a temperature of 24.0°C, 24.5°C or 25.0°C. exactly when a chemical reaction has ...
What is the resolution of a measuring instrument?
The resolution of a measuring instrument is the smallest change in a quantity that gives a change in the reading that can be seen. A thermometer with a mark at every 1.0°C has a resolution of 1.0°C. It has a higher resolution than a thermometer with a mark at every 2.0°C.
Introduction
Measurement and Numbers
- Measurement is a fundamental aspect of science and chemistry. Our understanding of the chemical world would not be possible if we did not compare, contrast, categorize, and analyze our observations to obtain the information we have about chemical substances. Let’s consider water as an example. Many of the qualitative (non-numerical) properties of w...
Magnitude and Scale
- When we think about the physical quantities that are measured in chemistry, we must also consider the concepts of magnitude and scale. The following video introduces these concepts: As the video suggests, chemistry is a discipline in which we study things that are very, very small. We measure things like the size of an atom, which is approximately 1/10000000000 of a meter. Bec…
The Relative Size of Things
- We can express the relative size of things with which we are familiar. For instance, the Figurebelow shows the height of a human as measured in meters, or 100 scale. We see a dust mite, measured in micrometers scale; and a virus, measured in nanometers scale. These are examples of length related to relative size and scale. Relative size and scale of things. CC BY-N…