What is a meson in physics?
Meson, any member of a family of subatomic particles composed of a quark and an antiquark. Mesons are sensitive to the strong force, the fundamental interaction that binds the components of the nucleus by governing the behaviour of their constituent quarks. Predicted theoretically in 1935 by the Japanese physicist Yukawa Hideki,...
What is a meson made up of?
Meson is a fundamental particle categorized under the hadrons. Mesons are the hadronic particles made up of a quark and an antiquark, specifically a meson its own antiparticle. Mesons are the interaction agents between nucleons (protons and electrons).
What are mesons and antiparticles?
Each type of meson has a corresponding antiparticle (antimeson) in which quarks are replaced by their corresponding antiquarks and vice versa. For example, a positive pion (. π +. ) is made of one up quark and one down antiquark; and its corresponding antiparticle, the negative pion (. π −. ), is made of one up antiquark and one down quark.
What is a heavy meson?
However, such heavy mesons are regularly created in particle accelerator experiments, in order to understand the nature of the heavier types of quark that compose the heavier mesons. Mesons are part of the hadron particle family, and are defined simply as particles composed of an even number of quarks.
See more

What are examples of mesons?
Examples of mesons are the p, h, r and w mesons. Mesons do not last long because they have no net baryon or net lepton number and can decay. For instance a p0 meson can decay into two photons. An object made of a red, a green and a blue quark is also colorless.
What is a meson simple definition?
Definition of meson : any of a group of fundamental particles (such as the pion and kaon) made up of a quark and an antiquark that are subject to the strong force and have zero or an integer number of quantum units of spin.
Is a meson a proton?
Hadrons come in two further groups, Baryons and Mesons. Baryons are hadrons that can decay into or are protons. These include: protons, neutrons, antiprotons and antineutrons. Mesons are hadrons that do not decay into protons, such as: pions and kaons.
What are the three types of mesons?
The most common type of mesons are the pions (pi mesons), kaons (K mesons) and the eta meson (η-meson). These are also the only types of meson that are long-lived enough to be seen directly by their tracks in a detector.
What is the purpose of mesons?
Mesons serve as a useful tool for studying the properties and interactions of quarks. Despite their instability, many mesons last long enough (a few billionths of a second) to be observed with particle detectors, making it possible for researchers to reconstruct the motions of quarks.
Where are mesons found?
nucleusMesons are particles found in nucleus. They are responsible for stability of nucleus. They were discovered by Japanese scientist Yukawa.
Is a meson a boson?
Mesons are intermediate mass particles which are made up of a quark-antiquark pair. Three quark combinations are called baryons. Mesons are bosons, while the baryons are fermions. There was a recent claim of observation of particles with five quarks (pentaquark), but further experimentation has not borne it out.
What is the smallest things in the universe?
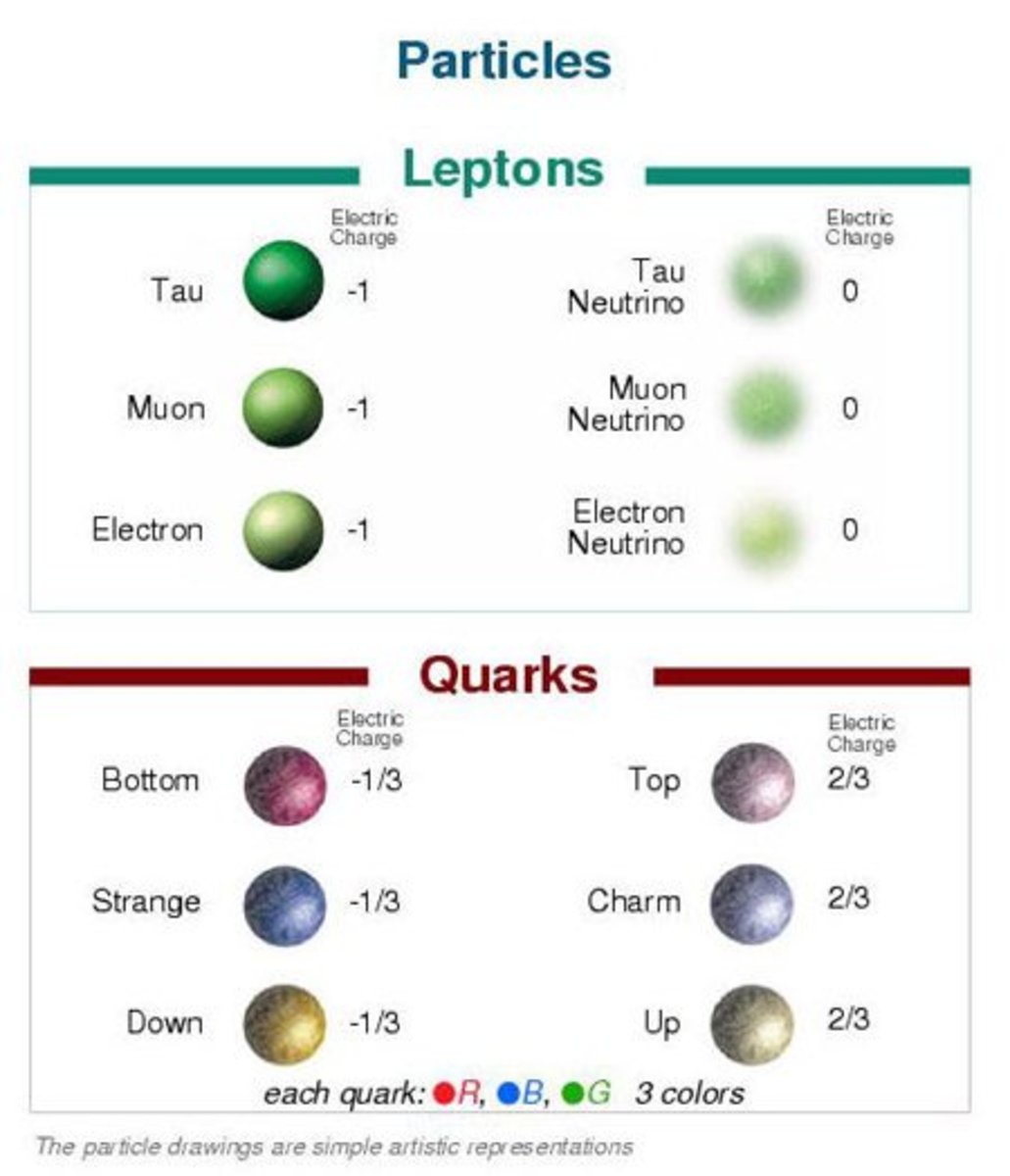
Quarks are among the smallest particles in the universe, and they carry only fractional electric charges. Scientists have a good idea of how quarks make up hadrons, but the properties of individual quarks have been difficult to tease out because they can't be observed outside of their respective hadrons.
How many quarks are in a meson?
one quarkA meson is also a type of hadron, and it contains one quark and one antiquark.
Is a photon a meson?
A Photon is an example of a vector Boson and has a spin s=1 . Phillip E. A meson is a composite particle and a vector boson is a spin 1 force carrier particle.
What is meson theory?
In 1935 Yukawa proposed the meson theory on the dogma that all forces are mediated by fields. Since the electromagnetic interaction is mediated by the electromagnetic field, there must be some other fields mediating the strong and weak interactions.
Which is the heaviest particle?
Neutron is heaviest subatomic particle among the given subatomic particles with mass of 1.008 amu while proton have mass of 1 amu. Was this answer helpful?
What is meson theory?
In 1935 Yukawa proposed the meson theory on the dogma that all forces are mediated by fields. Since the electromagnetic interaction is mediated by the electromagnetic field, there must be some other fields mediating the strong and weak interactions.
What are mesons and baryons?
Baryons are composite particles made of three quarks, as opposed to mesons, which are composite particles made of one quark and one antiquark. Baryons and mesons are both hadrons, which are particles composed solely of quarks or both quarks and antiquarks.
Who is called as Mason?
1 : a skilled worker who builds by laying units of substantial material (such as stone or brick) 2 capitalized : freemason.
What is an antiquark?
An antiquark is a fundamental particle that makes up most of the mass in the antimatter. Each antiquark has an electrical charge, a baryon number, and a strange number. The symbol of an antiquark is q. Antiquarks make antimatter, with some antimatter particles being produced during events called pair creation.
1. What Is a Meson Particle?
Ans: Meson is a fundamental particle categorised under the hadrons. Mesons are the hadronic particles made up of a quark and an antiquark, specific...
2. Give Some Examples of Meson Particles?
Ans: The most common examples of the meson particles are the pions (pi mesons), kaons (K mesons) and the eta meson (η-meson). These are also the on...
3. Is an Electron Considered to be a Meson?
Ans: No. Electron is not a meson, it is a baryon and more specifically electrons are fermions.
What are some examples of meson particles?
Ans: The most common examples of the meson particles are the pions (pi mesons), kaons (K mesons) and the eta meson (η-meson). These are also the only types of meson that are long-lived enough to be seen directly by their tracks in a detector. 3.
What is a meson?
Meson is a fundamental particle categorized under the hadrons. Mesons are the hadronic particles made up of a quark and an antiquark, specifically a meson its own antiparticle. Mesons are the interaction agents between nucleons (protons and electrons). The rest mass of the mesons lies between 250-100mₑ . The most common type of mesons are the pions ...
What is the name of the fundamental particles that carry unit charge?
The mesons are the fundamental particles or the elementary particles carrying unit charge and possessing mass intermediate between the mass of the electron (me) and the mass of the proton (mp).The name meson was proposed by famous nuclear physicist Yukawa in 1935. The mesons are the hadronic subatomic particles composed of a combination ...
What are the different types of mesons?
Pions or The Pi Meson 1 The pi meson is the lightest type of meson. And they are commonly called the pions. 2 Pi mesons are composed of up quarks or down quarks and their antiquark counterparts. 3 Pions are of charge +1, -1, and 0 are denoted π+(+e charge), π-(-e charge), and π0(neutral charge), respectively. 4 The π0 (mass 135 MeV) is composed of either an up or anti up quark pair or a down/anti down quark pair the π+ is an up/anti down pair, and the π- is a down/anti up pair (both have a mass of 140 MeV). All have zero spins. 5 Pi mesons or the pions were predicted theoretically by Hideki Yukawa in the year 1935, and discovered in cosmic ray experiments on the Pic du Midi by researchers from the Bristol University, England, headed by Cecil Powell, in 1947. They are produced copiously in high-energy particle collisions.
What is the heaviest particle?
Mesons are one of the elementary particles classified under baryons and these are considered to be the heaviest particles and the mesons do not include protons in their decay product. In this article, we will go through a detailed explanation of mesons, meson meaning and what is a meson .
How many mesons are there in nature?
We know that there are a total of eight mesons available in nature and these are arranged in an octet for easier understanding and determination of the charge, strangeness and the spin and it is known as the meson octet structure. Such that along the x-axis we will have isospin of the particles and along the y-axis strangeness. The meson octet is as shown in the below figure.
What does "meson" mean?
Meson Meaning. Now, let us understand the meaning of Meson. Basically, a meson is a hadronic particle, which means it is having considerable mass. We can define a meson as a fundamental particle that will never decay into a proton or any particles that could subsequently decay into a proton.
When were mesons discovered?
Predicted theoretically in 1935 by the Japanese physicist Yukawa Hideki, the existence of mesons was confirmed in 1947 by a team led by the English physicist Cecil Frank Powell with the discovery of the pi-meson (pion) in cosmic-ray particle interactions. More than 200 mesons have been produced and characterized in the intervening years, ...
Who discovered the J/Psi particle?
The J/psi particle, discovered independently by teams led by the American physicists Samuel C.C. Ting and Burton Richter in 1974, proved to be a meson made up of a charm quark and its antiquark. (Up to this time, three quark types had been postulated—up, down, and strange.)
What are the two subatomic particles?
subatomic particle: Baryons and mesons. The hadrons, whether stable or resonant, fall into two classes: baryons and mesons. Originally the names referred to the relative masses... Mesons also provide a means of identifying new quarks.
What are the two classes of hadrons?
The hadrons, whether stable or resonant, fall into two classes: baryons and mesons. Originally the names referred to the relative masses of the two groups of particles. The baryons (from the Greek word for “heavy”) included the proton and heavier particles; the mesons (from…
What are mesons made of?
This article contains a list of mesons, unstable subatomic particles composed of one quark and one antiquark. They are part of the hadron particle family – particles made of quarks. The other members of the hadron family are the baryons – subatomic particles composed of three quarks. The main difference between mesons and baryons is that mesons have integer spin (thus are bosons) while baryons are fermions (half-integer spin). Because mesons are bosons, the Pauli exclusion principle does not apply to them. Because of this, they can act as force mediating particles on short distances, and thus play a part in processes such as the nuclear interaction .
Why do mesons play a role in nuclear interactions?
Because of this, they can act as force mediating particles on short distances, and thus play a part in processes such as the nuclear interaction . Since mesons are composed of quarks, they participate in both the weak and strong interactions.
When was the top quark discovered?
The top quark (the last and heaviest quark to be discovered to date) was first observed at Fermilab in 1995. Each meson has a corresponding antiparticle (antimeson) where quarks are replaced by their corresponding antiquarks and vice versa. For example, a positive pion (. π+.
Why are weak eigenstates separate particles?
Note that these issues also exist in principle for other neutral flavored mesons; however, the weak eigenstates are considered separate particles only for kaons because of their dramatically different lifetimes.
Who wrote "From controversy to precision on the Sigma Meson: a review on the status of the non-ordinary?
J.R. Pelaez (2016). "From controversy to precision on the sigma meson: a review on the status of the non-ordinary f0 (500) resonance" (PDF). Physics Reports. 658: 1–111. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2016.09.001. S2CID 118569293.
Is a meson stable?
While no meson is stable, those of lower mass are nonetheless more stable than the most massive mesons, and are easier to observe and study in particle accelerators or in cosmic ray experiments.
How many masses does Charm Meson have?
As a result of this situation, the charm meson exists as two distinct particles with two distinct masses. But the difference between the two is infinitesimally small—0.00000000000000000000000000000000000001 grams to be exact, according to the scientists' research, described in a new paper published last month on the arXiv preprint server (that means the work hasn't been peer-reviewed yet). They've recently submitted the work for publication in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Why are mesons so rare?
Back to mesons: They're almost the size of neutrons or protons, but are extremely unstable. So, they're uncommon in nature itself, but physicists are interested in studying them in artificial environments (like in the LHC) because they want to better understand quarks. That's because, along with leptons, quarks make up all known matter.
What subatomic particle can switch between matter and antimatter?
A quirky type of subatomic particle known as the charm meson has the seemingly magical ability to switch states between matter and antimatter (and back again), according to the team of over 1,000 physicists who were involved in documenting the phenomenon for the first time.
Why was the Charm Meson a holdout for so long?
Why was the charm meson a holdout for so long? The charm meson oscillates incredibly slowly, meaning physicists had to take measurements at an extremely fine degree of detail. In fact, most charm mesons will fully decay before a complete oscillation can even take place, like an aging person with a very slow-growing tumor.
What type of particle has quarks?
Scientists have observed the extraordinarily tiny oscillations of a charm meson, a type of subatomic particle that contains both a quark and an antiquark.
What is the name of the particle accelerator at CERN?
Oxford researchers, using data from the second run of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC)—a particle accelerator at the Switzerland-based European Organization for Nuclear Research (known internationally as CERN)—made the determination by taking extremely precise measurements of the masses of two particles: the charm meson in both its particle and antiparticle states.
What are the components of atomic nuclei?
In case you skipped that lecture in quantum physics, quarks are particles that combine together to form "hadrons," some of which are protons and neutrons —the basic components of atomic nuclei.
What is the difference between meson and baryon?
Historically, the name baryon implied a heavy subatomic particle, while the term meson was given to particles with much lower masses. This can be seen from the words’ Greek etymological roots—”barys” for heavy and “mesos” for intermediate.
Which particle has a quark and an antiquark?
Baryons and mesons are examples of hadrons. Any particle that contains quarks and experiences the strong nuclear force is a hadron. Baryons have three quarks inside them, while mesons have a quark and an antiquark.
What are the particles that carry the charge of the strong force?
That is, it is their quark and gluon constituents that carry the charge of the strong force, not the mesons and baryons that comprise them. In short, hadrons are particles containing quarks. Baryons are hadrons containing three quarks, and mesons are hadrons containing a quark and an antiquark.
What are the three classes of particles?
The three classes of particles are hadrons, mesons and baryons. First off, all three terms identify classes of particles. Hadrons are particles that experience the strong nuclear force. This means that they contain quarks. A baryon is a type of hadron, and it contains three quarks. A meson is also a type of hadron, ...
How many quarks are in a baryon?
A baryon is a type of hadron, and it contains three quarks. A meson is also a type of hadron, and it contains one quark and one antiquark. Making an analogy to the animal kingdom, the term hadron corresponds to the term animal, while the terms meson and baryon might correspond to the classifications mammal and reptile.
Is a hadron a meson?
Thus in the modern world, the quark content is the only thing that identifies a hadron as a baryon or a meson. One thing that mesons and baryons have in common is that, even though their constituent quarks carry color, they themselves do not—they’re color-neutral.
What is the charm meson experiment?
The large-scale undertaking that produced the charm meson data is called the Large Hadron Collider beauty experiment. It seeks to examine why we live in a world full of matter, but seemingly no antimatter, according to CERN.
How many masses does Charm Meson have?
As a result of this situation, the charm meson exists as two distinct particles with two distinct masses. But the difference between the two is infinitesimally small0.00000000000000000000000000000000000001 grams to be exact, according to the scientists' research, described in a new paper published last month on the arXiv preprint server (that means the work hasn't been peer-reviewed yet). They've recently submitted the work for publication in the journal Physical Review Letters.
What is the opposite of quarks?
Antiquarks are the opposite of quarks and are considered a type of antimatter. These particles can cancel out normal matterwhich is kind of a problem if you want the universe to, well, exist. The various kinds of antimatter are almost all named using the anti- prefix, like quark versus antiquark. More specifically, a charm meson typically has a charm quark and an up antiquark, and its anti- partner has a charm antiquar k and an up quark.
What are the particles that combine to form a hadrons?
To understand what's going on here, we first have to unpack the meson particle. These are extremely short-lived subatomic particles with a balanced number of quarks and antiquarks. In case you skipped that lecture in quantum physics, quarks are particles that combine together to form "hadrons," some of which are protons and neutronsthe basic components of atomic nuclei.
What is the name of the particle accelerator that is used to measure the mass of two particles?
Oxford researchers, using data from the second run of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC)a particle accelerator at the Switzerland-based European Organization for Nuclear Research (known internationally as CERN)made the determination by taking extremely precise measurements of the masses of two particles: the charm meson in both its particle and antiparticle states.
What subatomic particle can switch between matter and antimatter?
A quirky type of subatomic particle known as the charm meson has the seemingly magical ability to switch states between matter and antimatter (and back again), according to the team of over 1,000 physicists who were involved in documenting the phenomenon for the first time.
Why was the Charm Meson a holdout for so long?
Why was the charm meson a holdout for so long? The charm meson oscillates incredibly slowly, meaning physicists had to take measurements at an extremely fine degree of detail. In fact, most charm mesons will fully decay before a complete oscillation can even take place, like an aging person with a very slow-growing tumor.
What is the name of the phenomenon where the neutral B mesons transform into their own antiparticles and back?
The neutral B mesons,#N#B0#N#and#N#B0#N#s, spontaneously transform into their own antiparticles and back. This phenomenon is called flavor oscillation. The existence of neutral B meson oscillations is a fundamental prediction of the Standard Model of particle physics. It has been measured in the#N#B0#N#–#N#B0#N#system to be about 0.496 / picoseconds, and in the#N#B0#N#s –#N#B0#N#s system to be Δms = 17.77 ± 0.10 (stat) ± 0.07 (syst) / picosecond measured by CDF experiment at Fermilab. A first estimation of the lower and upper limit of the#N#B0#N#s –#N#B0#N#s system value have been made by the DØ experiment also at Fermilab.
Why are B-mesons important?
B-mesons are an important probe for exploring quantum chromodynamics. Various uncommon decay paths of the B mesons are sensitive to physics processes outside the standard model. Measuring these rare branching fractions sets limits on new particles. The LHCb experiment has observed and searched for several of these decays such as Bs → µ+ µ−.
When did Fermilab discover the B-S meson oscillation?
On 25 September 2006, Fermilab announced that they had claimed discovery of previously-only-theorized B s meson oscillation. According to Fermilab's press release:
Can a bottom quark and a top quark be combined?
The combination of a bottom antiquark and a top quark is not thought to be possible because of the top quark's short lifetime. The combination of a bottom antiquark and a bottom quark is not a B meson, but rather bottomonium which is something else entirely. c) antiquark respectively.
What is an ETA meson?
Eta and eta prime mesons. ) are isosinglet mesons made of a mixture of up, down and strange quarks and their antiquarks. The charmed eta meson (. defined, but are made of charm quarks and bottom quarks respectively. The top quark is too heavy to form a similar meson, due to its very fast decay.
What is the pseudo-scalar of a quark?
The#N#η#N#particles belong to the "pseudo-scalar" nonet of mesons which have spin J = 0 and negative parity, and#N#η#N#and#N#η′#N#have zero total isospin, I, and zero strangeness, and hypercharge. Each quark which appears in an#N#η#N#particle is accompanied by its antiquark, hence all the main quantum numbers are zero, and the particle overall is "flavourless" .
