
What does missense mutation mean and how is it caused?
The missense mutation which causes all of this is the difference of one nucleotide. It is first translated into mRNA, then into a protein. The missense mutation causes a valine to be placed where a glutamic acid normally goes. This non-conservative missense mutation causes the shape of the protein, hemoglobin, to change.
What are examples of nonsense mutations?
Examples of nonsense mutation. Beta thalassemias are a group of blood disorders that occur as a result of point nonsense mutation on the gene coding for the beta chains of hemoglobin. The result of the mutation can range from severe anemia to clinically asymptomatic cases depending on the position of the mutation.
Why is it called a nonsense mutation?
Why is it called a nonsense mutation? Stop codons are also called nonsense codons because they do not code for an amino acid and instead signal the end of protein synthesis. Thus, nonsense mutations occur when a premature nonsense or stop codon is introduced in the DNA sequence.
What does a missense mutation look like?
Nonsense Mutation A nonsense mutation is the substitution of a single base pair that leads to the appearance of a stop codon where previously there was a codon specifying an amino acid. The presence of this premature stop codon results in the production of a shortened, and likely nonfunctional, protein.
What is a nonsense mutation?
Listen to pronunciation. (NON-sens myoo-TAY-shun) A genetic alteration that causes the premature termination of a protein. The altered protein may be partially or completely inactivated, resulting in a change or loss of protein function.
Is nonsense mutation same as missense?
A nonsense mutation differs from a missense mutation, which is a point mutation where a single nucleotide is changed to cause substitution of a different amino acid. A nonsense mutation also differs from a nonstop mutation, which is a point mutation that removes a stop codon.
What is nonsense mutation example?
Nonsense Mutation Example This called for an mRNA with the codon “AAG”, which then produced a lysine in the amino acid chain. A nonsense mutation would change the first “T” to an “A”. This makes the first codon “ATC”. The corresponding mRNA segment, “UAG”, is a signal to the ribosome to stop the chain.
How do you remember missense and nonsense mutations?
0:292:53MCAT Mnemonic: Missense and Nonsense Mutations (Ep. 19)YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd codes for alanine. And ACU encodes for any in the second row we have an example of a nonsenseMoreAnd codes for alanine. And ACU encodes for any in the second row we have an example of a nonsense mutation a nonsense mutation if you look at these two sequences.
What is the difference between a missense mutation and a nonsense mutation quizlet?
missense mutations change the sequence and meaning of an mRNA codon, resulting in a different amino acid. A nonsense mutation changes the codon to a stop codon.
What is missense mutation in biology?
Listen to pronunciation. (MIS-sens myoo-TAY-shun) A genetic alteration in which a single base pair substitution alters the genetic code in a way that produces an amino acid that is different from the usual amino acid at that position.
Why is it called nonsense mutation?
Stop codons are also called nonsense codons because they do not code for an amino acid and instead signal the end of protein synthesis. Thus, nonsense mutations occur when a premature nonsense or stop codon is introduced in the DNA sequence.
What is a nonsense mutation quizlet?
A mutation that changes a single nucleotide, but does not change the amino acid created. nonsense mutation. A mutation that changes an amino acid codon to one of the three stop codons, resulting in a shorter and usually nonfunctional protein.
Which is more common missense or nonsense?
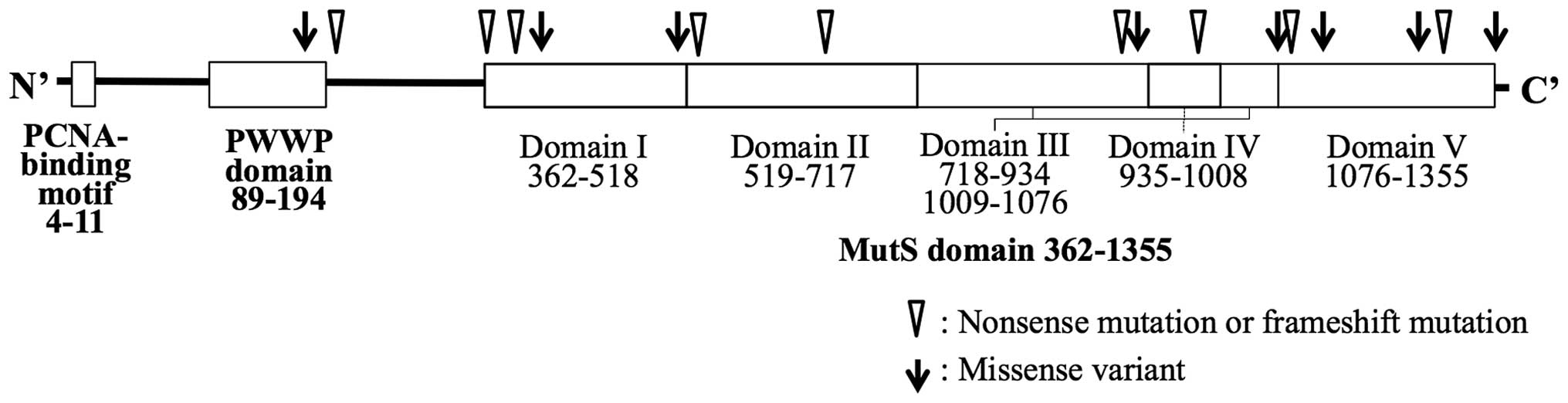
Gene characteristics explain 88% of the variation in the number of missense, 40% of nonsense, and 23% of frameshift mutations. Comparisons of the observed and expected numbers of mutations identified genes with a higher than expected number of mutations– positive outliers.
How do you know if it's a missense mutation?
During this process, a change in the structure of DNA, or a mutation, can change the sequence of amino acids which creates a protein. If it does not change the structure or function of the protein, it may be considered a silent mutation. If it does change the protein, it is considered a missense mutation.
What are the 4 types of mutations?
What Are The 4 Types Of Mutations?Duplication.Deletion.Inversion.Translocation.
What is the effect of a nonsense mutation in a gene?
Nonsense: A nonsense variant is another type of substitution. Instead of causing a change in one amino acid, however, the altered DNA sequence results in a stop signal that prematurely signals the cell to stop building a protein.
How is a missense mutation different from a nonsense mutation How are they similar?
A non-sense mutation is any genetic mutation that leads to the RNA sequence becoming a stop codon instead. Now, missense mutations are a little different, and they're any genetic mutation that changes an amino acid from one to another.
Is nonsense mutation worse than missense?
Both are basic amino acids that play an important role in forming electrostatic interactions in membrane proteins. Thus, the nonsense mutation is potentially worse than silent and missense mutations because nonsense mutation has a higher chance of producing non-functional protein.
What are the 3 types of substitution mutations?
Substitution mutations can be good, bad, or have no effect. They cause three specific types of point mutation: silent, missense, and nonsense mutations.
What is a missense mutation?
A missense mutation occurs when there is a mistake in the DNA code and one of the DNA base pairs is changed, for example, A is swapped for C.
What is a nonsense mutation?
Like a missense mutation, a nonsense mutation also involves a single alteration to the DNA base pair. However, in the case of a nonsense mutation,...
What is an insertion mutation?
An insertion mutation involves the addition of one (or more) nucleotide base pairs into the DNA sequence. Insertion mutations can vary in size, ran...
What is a deletion mutation?
As the title may suggest, a deletion mutation occurs when there a piece of DNA is removed from the sequence. The size of the DNA that is removed ca...
What is a frameshift mutation?
A frameshift mutation occurs when the aforementioned "addition" or "deletion" mutations result in a change to the gene's reading frame, which inclu...
What is a duplication mutation?
In the case of a duplication mutation, a piece of DNA is (abnormally) copied. This might happen once or several times, and can therefore impact the...
What is a missense mutation?
A missense mutation occurs when there is a mistake in the DNA code and oneof the DNA base pairs is changed, for example, A is swapped for C.
What is the result of a deletion mutation?
Addition or deletion mutation results in a change to a gene's reading frame
What is frameshift mutation?
A frameshift mutationoccurs when the aforementioned "addition" or "deletion" mutations result in a change to the gene's reading frame, which includes groups of three bases that encode for an amino acid. The change in the reading frame alters the grouping of the bases and subsequently changes the amino acids that are encoded. Often, the encoded protein is non-functional.
What happens when DNA is removed from a sequence?
As the title may suggest, a deletion mutation occurs when there a piece of DNA is removed from the sequence. The size of the DNA that is removed can vary in length, from a single base pair to an entire gene or several consecutive genes. The removal of the DNA can, again, compromise the function of the encoded protein.
What is genetic mutation?
A genetic mutation is a permanentchange to the nucleotide sequence of a gene. More often than not, such genetic mutations are advantageous – they enable evolution and produce new desirable traits in organisms.
What is a mistake in DNA code?
Mistake in the DNA code, one of the DNA base pairs is changed
Can genetic mutations cause disease?
However, genetic mutations can also be problematic if they result in a disease. In humans, genetic disorders are often life-limiting and incredibly tricky to treat.
What are the Similarities Between Missense and Nonsense Mutation?
Missense and nonsense mutations are point mutations caused due to a single nucleotide change.
What is a Missense Mutation?
Missense mutation is a point mutation where a single nucleotide is changed to cause a substitution of a different amino acid. In missense mutation, stop codon is not generated to terminate amino acid sequence synthesis similar to nonsense mutation.
What is a stop codon?
A stop codon is a nucleotide triplet within the mRNA sequence that signals the termination of translation into proteins. In a standard genetic code, there are three different stop codons. They are UAG (‘amber’), UAA (“ochre”) and UGA (“opal”) in RNA. In DNA, these three stop codons occur as TAG (“amber”), TAA (“ochre”) and TGA (“opal”). These stop codons are correctly situated at the end of the genetic code of a gene. Hence, it produces a complete protein without introducing any interruption. Mutations can introduce a premature stop codon to an mRNA sequence. Nonsense mutation is a point mutation which introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA sequence. A single nucleotide change leads to an introduction of a stop codon. When a stop codon is unnecessarily introduced into the mRNA sequence, it terminates the translation without completing the entire translation. Hence, the resultant protein becomes abnormally shortened. Each protein has a unique amino acid sequence. Nucleotide changes in the DNA sequence of the gene result in different proteins which are nonfunctional or incomplete.
What happens when a codon is changed?
The changed codon results in a different amino acid. The resultant amino acid sequence will differ from the unique amino acid sequence due to the substitution of a different amino acid by the mutation.
What are the different types of mutations?
There are different types of mutations such as point mutations, frameshift mutations, missense mutation, silent mutations and nonsense mutations. Missense mutation is a point mutation which results in the substitution of a different amino acid in the amino acid sequence due to the change of a single nucleotide in the mRNA sequence.
What happens when one nucleotide changes in the DNA sequence?
When one nucleotide changes in the DNA sequence, it changes the genetic code of the gene. When it transcribes, the resultant mRNA will have a different codon (nucleotide tripled which results in an amino acid). The changed codon results in a different amino acid. The resultant amino acid sequence will differ from the unique amino acid sequence due ...
What are the changes that occur in DNA?
DNA is constantly subjected to changes due to various factors including internal and environmental origin. DNA damages and mutations are two such changes that occur in DNA. Mutation is defined as a base change in the DNA sequence. Mutations cannot be recognized and repaired by enzymes. Mutated genes result in different amino acid sequences which ...
What is the difference between a nonsense mutation and a missense mutation?
Nonsense mutations replace an amino acid codon with an early stop codon, which prematurely signals the ribosome to stop building a protein. Unlike missense mutations, nonsense mutations almost always have serious consequences.
What causes a missense mutation?
Missense mutations can happen spontaneously or be induced by various kinds of mutagens. Mutagens include physical agents, like UV rays and chemical molecules, as well as bi ological agents, like certain viruses.
What are the most important facts to know about a missense mutation?
A missense mutation is an alteration in the DNA sequence that results in a different amino acid being incorporated into the structure of a protein. Depending on which amino acid it codes for, missense mutations can be conservative (i.e., the resulting protein is functional) or nonconservative (i.e., the resulting protein is non-functional).
What is missense mutation?
A missense mutation is a type of point mutation in which a different amino acid is placed within the produced protein, other than the original. In the process of converting DNA into protein, the language of DNA must be translated into the language of proteins. During this process, a change in the structure of DNA, or a mutation, can change the sequence of amino acids which creates a protein. If it does not change the structure or function of the protein, it may be considered a silent mutation. If it does change the protein, it is considered a missense mutation.
What are some examples of missense mutations?
A common and well-known example of a missense mutation is sickle- cell anemia, a blood disease. People with sickle-cell anemia have a missense mutation at a single point in the DNA. This missense mutation calls for a different amino acid, and affects the overall shape of the protein produced. This, in turn, causes the entire shape of blood cells to be different. People with the disease experience symptoms of not being able acquire oxygen efficiently, and experience blood clotting. However, they are partially protected from blood borne parasites which live in blood cells. Malaria is a disease caused by these parasites, and people with sickle-cell anemia have an inherent defense against the parasite. Their sickle-shaped blood cells cannot support the life cycle of the parasite.
What happens when a missense mutation changes an amino acid?
If a missense mutation changes an amino acid, it first changes the primary structure, or the basic sequence of amino acids. The secondary structure of proteins consists of patterns and structures formed by interactions between these amino acids.
How does a missense mutation affect the function of a protein?
This type of missense mutation can greatly change the function of a protein, as it will likely change the shape and structure of the protein. Proteins have various levels of structure, all which depend upon the DNA. If a missense mutation changes an amino acid, it first changes the primary structure, or the basic sequence of amino acids.
What happens when a mutation calls for the same amino acid as before the mutation?
If a mutation calls for the same amino acid as before the mutation, it is considered silent. On the other hand, several other codons also call for signals to stop and process the protein. In this case, instead of adding an amino acid, the sequence is ended and the protein is ejected from the ribosome.
How many amino acids are in a point mutation?
The DNA is read in units of three, called codons. These codons call for one of 21 amino acids, which the ribosome complex will assemble in order by reading the messenger RNA, or mRNA. If there are 3 spots in a codon, and 4 possible nucleotides to go in that spot, the codons can call for 64 different signals. Since there are only 21 amino acids, many of these codons call for the same amino acid. If a mutation calls for the same amino acid as before the mutation, it is considered silent.
What happens when a mutation does not change the structure of a protein?
If it does not change the structure or function of the protein, it may be considered a silent mutation. If it does change the protein, it is considered a missense mutation. Point mutations.
What is the difference between a missense and nonsense mutation?
A missense mutation changes one amino acid codon into another amino acid codon, while a nonsense mutation changes an amino acid codon into a stop codon.
What is missense mutation?
A missense mutation involves a change in one amino acid in a protein, arising from a point mutation, in a single nucleotide.
Can mutations have any effect?
It is not possible to say anything with certainty about the overall effect of a single mutation — all mutations provide non-random natural selection with its needed random variation, but most mutations have no effect whatsoever.
Is mutation beneficial to evolution?
Mutations are not inherently “beneficial” or “not beneficial” “for evolution”.
Is there evolution or mutation?
There is no Evolution, there are Developments, Changes and Adaptations, and the same word for: Mutation, it is simply a biological change, from what it was prior to the change, however the word “Mutation”, sounds so much more scientific, does it not, it was like the names they gave the people, (Who avoid anything Healthy), when the Internet first came out, you are now: “Surfing the net”, wow, all of a sudden, the biggest dork in business made the internet “Cool by reference”, same as Mutation, so then which change was to the greater benefit, and with rational insight, the substance, has no rea
Is a single base change a triplet?
Short answers (links to Wikipedia): They are both point mutations, i.e., a single base change, and both makes a DNA triplet something other than the “original” DNA:
Is a missense mutation constructive?
I’d guess that missense mutations might be constructiv e, whereas nonsense mutations are more likely destruct ive — in mRNA, a premature stop codon probably results in a truncated ( i.e., incomplete) protein, in other RNA transcriptions it most likely results in a non-functional RNA molecule.
Key Difference – Missense vs Nonsense Mutation
What Is A Missense Mutation?
What Is A Nonsense Mutation?
- A stop codon is a nucleotide triplet within the mRNA sequence that signals the termination of translation into proteins. In a standard genetic code, there are three different stop codons. They are UAG (‘amber’), UAA (“ochre”) and UGA (“opal”) in RNA. In DNA, these three stop codons occur as TAG (“amber”), TAA (“ochre”) and TGA (“opal”). These stop codons are correctly situated at th…
What Are The Similarities Between Missense and Nonsense Mutation?
- Missense and nonsense mutations are point mutations caused due to a single nucleotide change.
- Both mutations result in different proteins.
Summary – Missense vs Nonsense Mutation
- Missense and nonsense mutations are two types of point mutations which cause a single nucleotide change in the DNA sequence. Missense mutation leads to a substitution of a different amino acid in the amino acid sequence. Nonsense mutation leads to an introduction of a premature stop codon into the mRNA sequence. This is the difference between misse...