The mixed-design ANOVA model (also known as Split-plot ANOVA (SPANOVA)) tests for mean differences between two or more independent groups whilst subjecting participants to repeated measures. Thus, there is at least one between-subjects variable and at least one within-subjects variable. Click to see full answer.
Full Answer
What are the models of ANOVA?
Jan 04, 2020 · The mixed-design ANOVA model (also known as Split-plot ANOVA (SPANOVA)) tests for mean differences between two or more independent groups whilst subjecting participants to repeated measures. Thus, there is at least one between-subjects variable and at least one within-subjects variable.
What are the three types of ANOVA?
May 20, 2020 · In a mixed design ANOVA, you’ll need to deal with the assumptions of both a between subjects design and a repeated measures design. Homogeneity of variance: You should take a look at the variances of each level of your between subjects independent variable. If the variances look different, you may have a problem.
What is mixed model with repeated measures?
Mixed ANOVA is used to compare the means of groups cross-classified by two different types of factor variables, including: between-subjects factors, which have independent categories (e.g., gender: male/female) within-subjects factors, which have related categories also known as repeated measures (e.g., time: before/after treatment).
What is N and K in ANOVA?
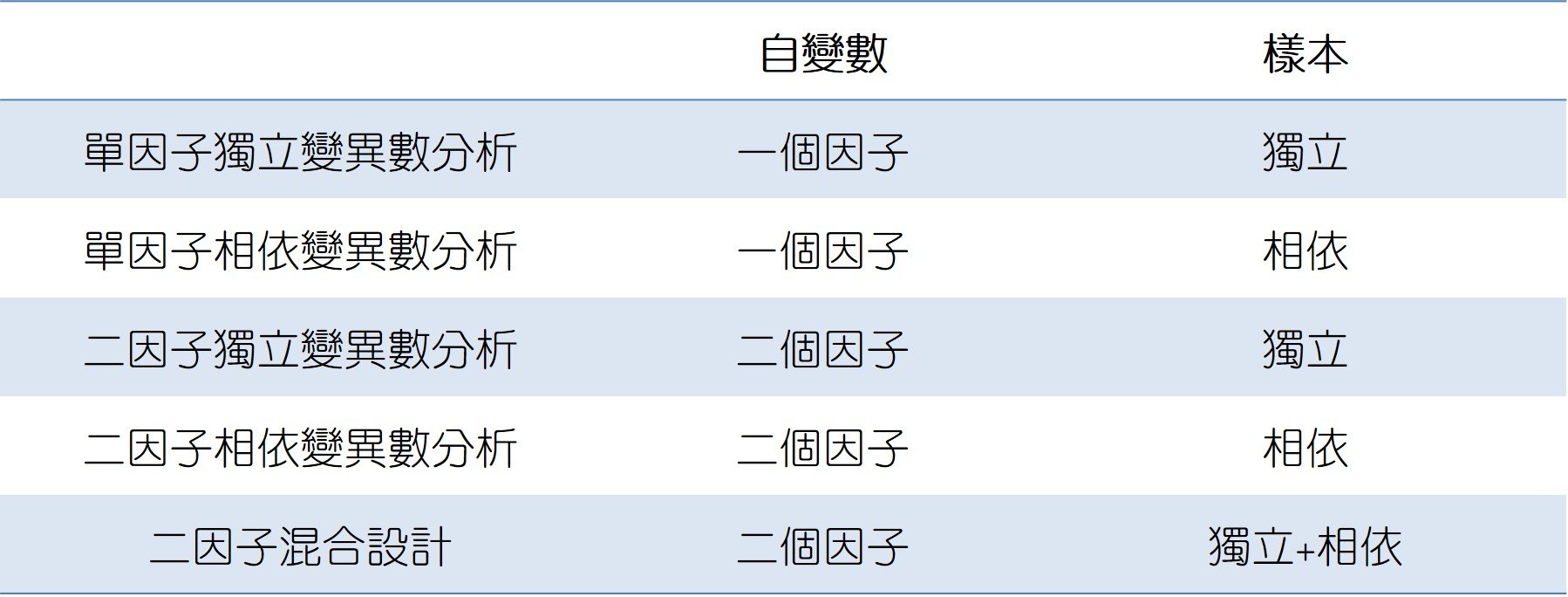
A mixed model ANOVA is a combination of a between-unit ANOVA and a within-unit ANOVA. It requires a minimum of two categorical independent variables, sometimes called factors, and at least one of these variables has to vary between-units and at …
What is a mixed models ANOVA?
A mixed model ANOVA is a combination of a between-unit ANOVA and a within-unit ANOVA. It requires a minimum of two categorical independent variables, sometimes called factors, and at least one of these variables has to vary between-units and at least one of them has to vary within-units.
When would you use mixed-design ANOVA?
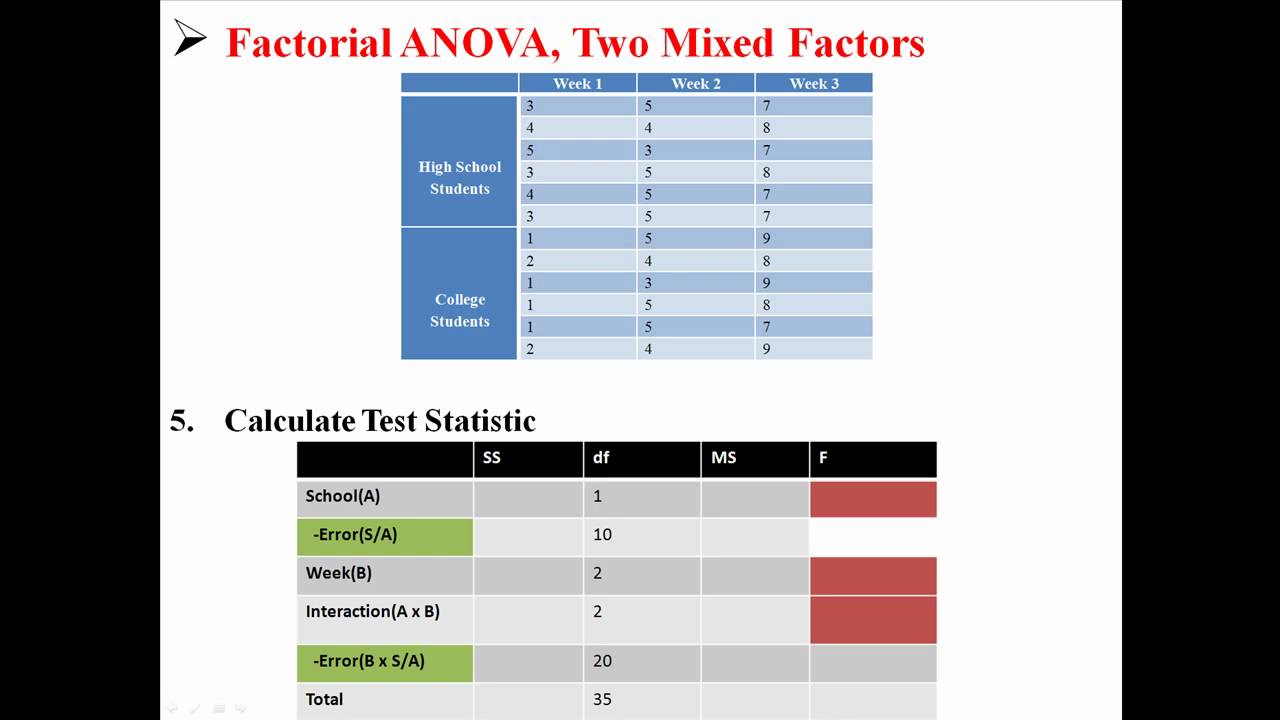
Given that you mix a between-subjects factor (group) with a within-subjects factor (test conditions) in your design, you must use a two-way *mixed-design* ANOVA to analyze the to know whether the test conditions or the group or both lead to significant differences between group and treatment means.Nov 22, 2014
What is the difference between a factorial ANOVA and a mixed ANOVA?
If you have a between subjects factor (like different groups) then you should perform an ANOVA (may be factorial). If you have both, that ANOVA is called mixed.
What is the difference between linear mixed model and ANOVA?
ANOVA models have the feature of at least one continuous outcome variable and one of more categorical covariates. Linear mixed models are a family of models that also have a continous outcome variable, one or more random effects and one or more fixed effects (hence the name mixed effects model or just mixed model).Sep 10, 2016
What does a two way mixed ANOVA do?
It allows to you test whether participants perform differently in different experimental conditions. This tutorial will focus on Two-Way Mixed ANOVA. The term 'Two-Way' gives you an indication of how many Independent Variables you have in your experimental design… in this case: two.
How do you conduct a mixed ANOVA?
3:4417:54mixed ANOVA in SPSS - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt's a few options that we should ask for descriptive statistics of course estimates of effect size.MoreIt's a few options that we should ask for descriptive statistics of course estimates of effect size. We can also ask for homogeneity tests. Because we do have homogeneity of variance in this case.
Is a mixed ANOVA a two-way ANOVA?
Summary. The two-way mixed-design ANOVA is also known as two way split-plot design (SPANOVA). It is ANOVA with one repeated-measures factor and one between-groups factor.
What are the assumptions of a mixed ANOVA?
ANOVA assumptions Normality: scores for each condition should be sampled from a normally distributed population. Homogeneity of variance: each population should have the same error variance. Sphericity of the covariance matrix: ensures the F ratios match the F distribution.
What type of ANOVA should I use?
Use a two way ANOVA when you have one measurement variable (i.e. a quantitative variable) and two nominal variables. In other words, if your experiment has a quantitative outcome and you have two categorical explanatory variables, a two way ANOVA is appropriate.
Why is mixed model better than ANOVA?
Missing Data As implied above, mixed models do a much better job of handling missing data. Repeated measures ANOVA can only use listwise deletion, which can cause bias and reduce power substantially. So use repeated measures only when missing data is minimal.
How do you do a mixed ANOVA in SPSS?
0:002:27Mixed Model ANOVA in SPSS - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo to do this analysis we've got a analyzed. We go to general linear model repeated measures againMoreSo to do this analysis we've got a analyzed. We go to general linear model repeated measures again we might change this to time. There are three time points. We click Add we say define.
What is linear mixed model analysis?
Linear mixed models are an extension of simple linear models to allow both fixed and random effects, and are particularly used when there is non independence in the data, such as arises from a hierarchical structure. For example, students could be sampled from within classrooms, or patients from within doctors.