What is a probe in a multimeter?
A test probe is a physical device used to connect electronic test equipment to a device under test (DUT). Test probes range from very simple, robust devices to complex probes that are sophisticated, expensive, and fragile.
How do you use a probe on a multimeter?
Test Your Probes or LeadsSet your multimeter to the ohm meter on the selector knob.Plug the black probe into the common port.Insert the red probe into the jack marked for ohms.Gently tap the red and black tips together. ... Your reading should be 0.5 ohms or less.If your reading is higher than that, replace the probes.
Where do you put a probe on a multimeter?
Plug your probes into the appropriate sockets. On most multimeters, the black probe should go into the socket labeled "COM," and the red probe should go into the same socket you would use to measure voltage or resistance (not current), labeled with a V and/or an Ω.
How do you use a test probe?
A brief order of using a logic probe could be:Connect the black clip or line to ground or to a common line of the circuit to be tested. ... Secondly connect the red clip or leave to the positive supply of the circuit.Select the logic family CMOS or TTL. ... Use the probe to connect to the required monitoring points.More items...
How do you test if a wire is live with a multimeter?
0:261:15How to Identify Hot, Neutral and Ground Wires using ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd finally touch the red probe to each exposed wire. If you don't get a voltage reading the wire isMoreAnd finally touch the red probe to each exposed wire. If you don't get a voltage reading the wire is neutral. If you get a reading the wire is hot you can also use color coding to identify.
Is multimeter same as voltmeter?
Multimeters include the same features as voltmeters but also test current, resistance, and continuity. Sometimes, with the right probes and sensors, multimeters also capture additional information like temperature.
Can I use my multimeter to test an outlet?
Set a multimeter to measure voltage. Insert a probe into each slot and read the line voltage measurement. A properly working outlet gives a reading of 110 to 120 volts. If there is no reading, check the wiring and the outlet.
How do you check for a short circuit with a multimeter?
How to Find a Short Circuit with a MultimeterPreparation and Safety.Turn on the Multimeter and Set it to Continuity or Resistance.Test the Function of the Multimeter.Identify and Locate the Circuit Component.Apply the Probe Tips to the Circuit.Check the Display of the Multimeter.
How do you measure 12V with a multimeter?
You have to set the multimeter to a range that it can measure. For example, 2V measures voltages up to 2 volts, and 20V measures voltages up to 20 volts. So if you've measuring a 12V battery, use the 20V setting.
What is the function of the probe?
A probe is a single-stranded sequence of DNA or RNA used to search for its complementary sequence in a sample genome. The probe is placed into contact with the sample under conditions that allow the probe sequence to hybridize with its complementary sequence.
What is electrical probe used for?
Electrical test probes are used to create a temporary connection between an electrical circuit under test and a measuring instrument, often a digital Multimeter.
How do you use a voltage probe?
0:549:58#142: Basics of High Voltage Probes and how to use them - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou just hook up the ground lead to ground and you'd touch the point here to high voltage. And youMoreYou just hook up the ground lead to ground and you'd touch the point here to high voltage. And you can read directly up to 40 kilovolts.
What is the purpose of a standard probe?
Standard probes. When using probes, always keep your fingers behind the finger guard. A standard probe, here from a Amprobe multimeter. It has removable tip cover, this is a safety feature for high energy usage, but can also be useful at lower voltage.
Why is the probe moving around the cable?
Because the probe is moved around the cable will always moving/bending there, anything to prevent sharp bends will improve cable life. Accessories for probe tips. As long as you probe has a simple and long tip, it can use some accessories.
How long is a multimeter shroud?
The shroud is usual about 21-22mm long. There are probes with shorter shroud, they are very common on the cheaper multimeters and will often have 17-18mm shroud. The full size shroud will usual work, but the plug cannot be fully seated.
What is a piercing probe?
Piercing probes (This is also a accessory) The idea is that a tin needle can cut through the isolation and contact the conductor inside. When the probe is removed the hole will basically close itself. This makes it possible to measure on wires without stripping or cutting it and without locating the ends of the wire.
What does it mean when a probe is low voltage?
When working with low voltage you will often want very good connection to probes, this means sharp point on the tip and a tip that generally give good connection (Gold coating can help with that).
How long is a Keysight probe?
The probe is 13cm long and the finger guard is 3.5cm from the tip. Another standard probe, this time from Keysight. The tip is made differently, but the safety ratings are the same. This probe is 15cm long and the finger guard is 4.3cm from the tip. A cheap probe, there is no CAT rating, but it says 1000V on it.
What is the difference between a red and white probe?
The strands are very thin to make the cable flexible. The red one is a typical good quality probe with two layers of isolation (If the white isolation is visible, it is time to replace the lead), again with very thin strands. The white is a normal wire with thick strands and not nearly as flexible as the other two.
What is a multimeter used for?
A multimeter, also known as a volt-ohm meter, is a handheld tester used to measure electrical voltage, current (amperage), resistance, and other values. Multimeters come in analog and digital versions and are useful for everything from simple tests, like measuring battery voltage, to detecting faults and complex diagnostics.
What is digital multimeter?
Digital multimeters are the most commonly available type and include simple versions as well as advanced designs for electronics engineers. In place of the moving needle and scale found on analog meters, digital meters provide readings on an LCD screen.
Why use an analog multimeter?
However, analog multimeters are great for detecting slow voltage changes because you can watch the needle moving over the scale. Analog testers are exceptional when set as ammeters, due to their low resistance and high sensitivity, with scales down to 50µA (50 microamperes).
How many ports does a multimeter have?
The basic functions and operations of a multimeter are similar for both digital and analog testers. The tester has two leads—red and black—and three ports. The black lead plugs into the "common" port. The red lead plugs into either of the other ports, depending on the desired function.
Which is better, a voltmeter or a digital multimeter?
Digital multimeters typically are better than analog in the voltmeter function, due to the higher resistance of digital. But for most users, the primary advantage of digital testers is the easy-to-read and highly accurate digital readout.
Can a multimeter be used on a circuit?
Multimeters are safe to use on energized circuits and equipment, provided the voltage or current does not exceed the maximum rating of the tester. Also, you must be careful never to touch the bare metal ends of the tester leads during an energized test because you can receive an electrical shock.
What type of probe is used for a multimeter?
A multimeter can use many different test probes to connect to the circuit or device under test. Crocodile clips, retractable hook clips, and pointed probes are the three most common types. Tweezer probes are used for closely spaced test points, as for instance surface-mount devices. The connectors are attached to flexible, well insulated leads terminated with connectors appropriate for the meter. Probes are connected to portable meters typically by shrouded or recessed banana jacks, while benchtop meters may use banana jacks or BNC connectors. 2 mm plugs and binding posts have also been used at times, but are less commonly used today. Indeed, safety ratings now require shrouded banana jacks.
What is a multimeter?
A multimeter is the combination of a DC voltmeter, AC voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter. An un-amplified analog multimeter combines a meter movement, range resistors and switches; VTVMs are amplified analog meters and contain active circuitry.
How many digits does a multimeter read?
For example, a multimeter which can read up to 19999 (plus an embedded decimal point) is said to read 4. 1⁄2 digits. By convention, if the most significant digit can be either 0 or 1, it is termed a half-digit; if it can take higher values without reaching 9 (often 3 or 5), it may be called three-quarters of a digit.
What is the voltage drop on a multimeter?
The voltage drop is known as the burden voltage, specified in volts per ampere. The value can change depending on the range the meter sets, since different ranges usually use different shunt resistors.
How much does a multimeter cost?
Multimeters vary in size, features, and price. They can be portable handheld devices or highly-precise bench instruments. Cheap multimeters can cost under US$ 10, while laboratory-grade models with certified calibration can cost over US$ 5,000.
What is the sensitivity of an analog multimeter?
The sensitivity of an analog multimeter is given in units of ohms per volt.
How to measure resistance?
To measure resistance, switches arrange for a small battery within the instrument to pass a current through the device under test and the meter coil. Since the current available depends on the state of charge of the battery which changes over time, a multimeter usually has an adjustment for the ohm scale to zero it.
What is a multimeter?
A Multimeter is a digital device used to test multiple electric values in a circuit, including electric current, resistance, and voltages. Multimeters are standard analog diagnostic tools used by technicians and electricians for troubleshooting problems in all types of electric appliances, power circuits, motors, and HVACs.
What is a multimeter circuit?
The multimeter consists of a circuit present inside the outer safety box with a coordinator circuit and an analog converter to convert 1 and 0 into the digits. This is why it is called a digital multimeter.
Why do logical probes depend on power supply?
The circuit of the logical probe requires a supply of power equal to the power supply of the circuit of the device you are going to test with the logical probe. This is because logical probes depend upon the supply of the device it is testing. Technicians should connect the logical probe with the circuit carefully as it is an open ...
What is a low state probe?
Logical low-state probes are used to test circuits that are logically and digitally at a low state . Logic probe displays this with an LED that is commonly colored green. Digital pulses can be detected by logical probes, which are incorporated into the circuitry for pulse detection.
What happens if a logical probe falls on a circuit?
If it falls on the device, it can cause a short circuit in the device and even in the probe itself, damaging both the probe and the device it is testing.
What is a logic probe?
A logic probe is a low-cost probe containing a pen-like tube and three indicator lights to display the state of a line being probed. It allows you to keep a glance at signals of an operating circuit according to the requirement. In a logical probe, technicians do not have to connect wires to LED or signal monitors.
How many LEDs are in a logical probe?
Most advanced logical probe circuits have three LEDs in the body of the circuit. An LED to mark a high logic state (1) An LED to mark a low logic state (0) An LED to show fluctuations in low and high states. A pulse detector is connected to a third LED, which helps display even short pulses on the LED. The circuit of the logical probe requires ...
How many probes does a multimeter have?
Although they come with two probes, many multimeters have more than two places in which to plug the probes, which can cause some confusion. Exactly where you plug the probes in will depend on what you want to measure (voltage, current, resistance, continuity test, or diode test) and the type of multimeter you have.
What is a multimeter?
A multimeter is a handy tool that you use to measure electricity, just like you would use a ruler to measure distance, a stopwatch to measure time, or a scale to measure weight. The neat thing about a multimeter is that unlike a ruler, watch, or scale, it can measure different things — kind of like a multi-tool.
How to measure voltage in a series circuit?
In a series circuit, each circuit element has the same current. So, to measure current in a circuit, you must attach the multimeter in series. In a parallel circuit, each circuit measurement has the same voltage. So, to measure voltage in a circuit, you must attach your multimeter in parallel.
What is the difference between a positive and negative multimeter?
The positive probe of the multimeter (red) is connected to the positive side of a battery while the negative probe of the multimeter (black) is connected to one lead of a lightbulb. The free lightbulb lead is then connected to the negative side of the battery using wire.
What does it mean when a multimeter is not auto ranging?
If your multimeter is not auto-ranging, you might need to adjust the range. If your multimeter's screen just reads "0," then the range you have selected is probably too high. If the screen reads "OVER," "OL," or "1" (these are different ways of saying "overload"), then the range you have selected is too low.
What is the other end of a multimeter called?
The other end is called the probe tip; this is the end you use to test your circuit. Following standard electronics convention, the red probe is used for positive, and the black probe is used for negative. Figure 4. A typical pair of multimeter probes.
What is a diode check?
The diode check feature is useful to determine in which direction electricity flows through a diode. The exact operation of the "diode check" function will vary for different multimeters, and some multimeters do not have a diode check feature at all.
What is the display on a multimeter?
The multimeter itself has a display at the top, which gives you your readout, and there’s a big selection knob that you can spin around to select a specific setting. Each setting may also have different number values, which are there to measure different strengths of voltages, resistances, and amps.
How many volts does a multimeter measure?
So if you have your multimeter set to 20 in the DCV section, the multimeter will measure voltages up to 20 volts. Your multimeter will also have two or three ports for plugging in the probes (pictured above): The COM port stands for “Common”, and the black probe will always plug into this port.
What does it mean when a multimeter shows a 0?
If there is a complete circuit, your multimeter will either beep, show a “0”, or something other than a “1”. If it still shows a “1”, then there’s a problem and your circuit isn’t complete. You can also test that the continuity feature works on your multimeter by touching both probes to each other.
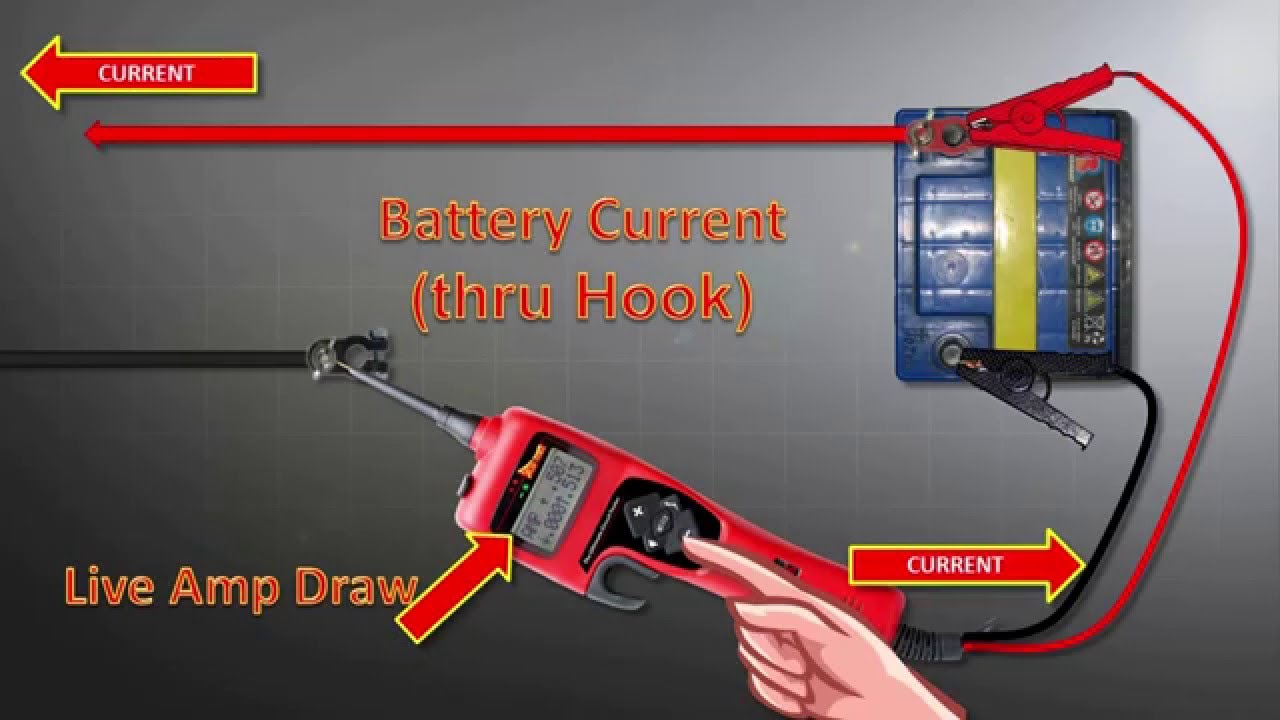
What is an amp test?
Testing Current (Amps) Testing the current draw of something is a bit trickier, as the multimeter needs to be connected in series. This means that the circuit you’re testing needs to be broken first, and then your multimeter is placed in between that break to connect the circuit back up.
What is a VMA port?
The VΩmA port (sometimes denoted as mAVΩ) is simply an acronym for voltage, resistance, and current (in milliamps). This is where the red probe will plug into if you’re measuring voltage, resistance, continuity, and current less than 200mA.
Do multimeters have separate ports?
Your multimeter might have completely separate ports for measuring amps, while the other port is specifically just for voltage, resistance, and continuity, but most cheaper multimeters will share ports. Anyway, let’s get started actually using a multimeter.

Overview
General properties of multimeters
Any meter will load the circuit under test to some extent. For example, a multimeter using a moving coil movement with full-scale deflection current of 50 microamps (μA), the highest sensitivity commonly available, must draw at least 50 μA from the circuit under test for the meter to reach the top end of its scale. This may load a high-impedance circuit so much as to affect the circuit, thereby giving a low reading. The full-scale deflection current may also be expressed in t…
History
The first moving-pointer current-detecting device was the galvanometer in 1820. These were used to measure resistance and voltage by using a Wheatstone bridge, and comparing the unknown quantity to a reference voltage or resistance. While useful in the lab, the devices were very slow and impractical in the field. These galvanometers were bulky and delicate.
Operation
A multimeter is the combination of a DC voltmeter, AC voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter. An un-amplified analog multimeter combines a meter movement, range resistors and switches; VTVMs are amplified analog meters and contain active circuitry.
For an analog meter movement, DC voltage is measured with a series resistor …
Measured values
Contemporary multimeters can measure many values. The most common are:
• Voltage, alternating and direct, in volts.
• Current, alternating and direct, in amperes.
The frequency range for which AC measurements are accurate is important, d…
Resolution
The resolution of a multimeter is the smallest part of the scale which can be shown, which is scale dependent. On some digital multimeters it can be configured, with higher resolution measurements taking longer to complete. For example, a multimeter that has a 1 mV resolution on a 10 V scale can show changes in measurements in 1 mV increments.
Accuracy
Digital multimeters generally take measurements with accuracy superior to their analog counterparts. Standard analog multimeters measure with typically ±3% accuracy, though instruments of higher accuracy are made. Standard portable digital multimeters are specified to have an accuracy of typically ±0.5% on the DC voltage ranges. Mainstream bench-top multimeters are available with specified accuracy of better than ±0.01%. Laboratory grade instruments can h…
Sensitivity and input impedance
When used for measuring voltage, the input impedance of the multimeter must be very high compared to the impedance of the circuit being measured; otherwise circuit operation may be affected and the reading will be inaccurate.
Meters with electronic amplifiers (all digital multimeters and some analog meters) have a fixed input impedance that is high enough not to disturb most circuits. This is often either one or ten