What is natural monopoly quizlet? A natural monopoly is a single seller in a market which has falling average costs over the whole range of output resulting from economies of scale. … A natural monopolist can produce more cheaply than any two or more other firms.
What is a natural monopoly and why do they exist?
Definition and meaning A natural monopoly exists when it makes more economic sense for just one company to supply the whole market compared to having two or more competitors, mainly because of the economies of scale that are available in that market. Natural monopolies are common where expensive infrastructure has to be installed and maintained.
What are the characteristics of a natural monopoly?
Monopoly characteristics include profit maximizer, price maker, high barriers to entry, single seller, and price discrimination. What are the two key characteristics of natural monopoly? Natural monopolies are naturally occurring in the fact that there are economical forces that prevent more than one company from entering the market.
Which is the best example of natural monopoly?
The most common natural monopolies are:
- railways
- electricity
- water services
- telecom and utilities
What is true about a firm with a natural monopoly?
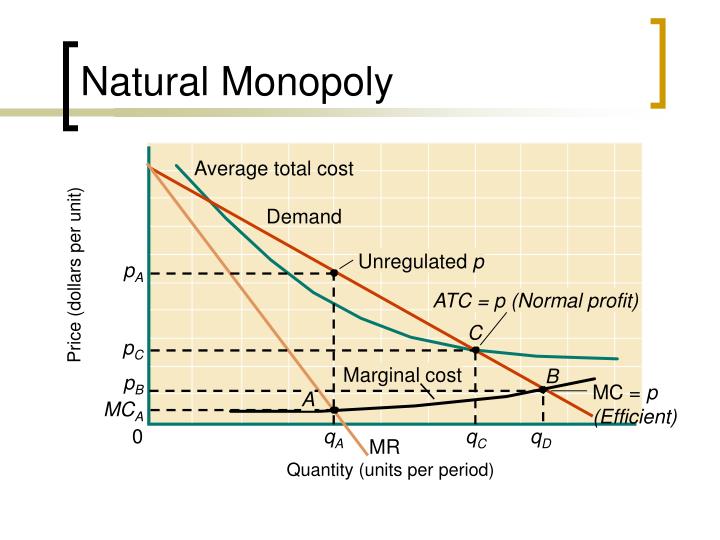
What is true of a natural monopoly? Definition: A natural monopoly occurs when the most efficient number of firms in the industry is one. A natural monopoly will typically have very high fixed costs meaning that it is impractical to have more than one firm producing the good. An example of a natural monopoly is tap water.
What defines a natural monopoly?
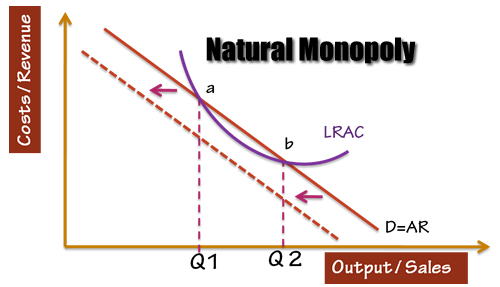
A natural monopoly exists in a particular market if a single firm can serve that market at lower cost than any combination of two or more firms.
Which is an example of a natural monopoly quizlet?
Bottled water is a good example of a natural monopoly. Increasing the number of firms in a natural monopoly cost environment would result in higher average total costs. Regulating a natural monopoly encourages them to be efficient and lower costs.
What is a natural monopoly give two examples?
A natural monopoly is a type of monopoly that occurs due to high fixed costs and a need to achieve extreme economies of scale. In other words, it is only economically viable for one business to serve the market. Examples include the likes of utilities and train lines.
What is a natural monopoly and what is an example of one?
Definition: A natural monopoly occurs when the most efficient number of firms in the industry is one. A natural monopoly will typically have very high fixed costs meaning that it is impractical to have more than one firm producing the good. An example of a natural monopoly is tap water.
Which is an example of a monopoly quizlet?
Examples of monopolies include: (1) the water producer in a small town, who owns a key resource, the one well in town; (2) a pharmaceutical company that is given a patent on a new drug by the government; and (3) a bridge, which is a natural monopoly because (if the bridge is uncongested) having just one bridge is ...
When an industry is a natural monopoly quizlet?
An industry is a natural monopoly when: A single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market at a lower cost than could two or more firms. It arises when there are economies of scale over the relevant range of output.
Is the monopoly a natural monopoly quizlet?
Is the monopoly a natural monopoly? The firm is a natural monopoly because it can supply the entire market at lower average total cost than can two or more firms.
What is the difference between monopoly and natural monopoly?
There are two types of monopoly, based on the types of barriers to entry they exploit. One is natural monopoly, where the barriers to entry are something other than legal prohibition. The other is legal monopoly, where laws prohibit (or severely limit) competition.
How does a natural monopoly function quizlet?
How does a natural monopoly function? A few firms are in perfect competition. Imperfect competition makes it difficult for firms to do business. A single firm supplies all the output.
Why do natural monopolies exist quizlet?
Explanation: A natural monopoly arises because of the interaction between size of the market and the efficient scale of operation of a single firm. Explanation: Monopolies have 100% of the market so they are able to set the price / output combination that maximizes profit.